Abstract
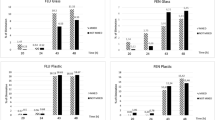
Fluoroquinolones (FQs) present in water environments pose threats to aquatic organisms. The concentration of FQs adsorbed onto sediments is generally higher than that in water. Here, we studied the toxicities of two FQ antibiotics, norfloxacin (NOR) and ofloxacin (OFL), on the snail Bellamya aeruginosa, an adaptable benthic animal. For this, we performed acute toxicity experiments on young snails and sub-chronic exposure experiments on adult snails by exposure to the FQs for 1–28 days. The 96 h median effective concentrations showed that NOR toxicity was higher than OFL toxicity, although both NOR and OFL were low-toxicity substances (EC50 > 100 mg L−1). Four concentrations were used in the sub-chronic exposure experiments. Results of the measurement of bioconcentration factors (BCF) showed that OFL accumulation was higher than NOR accumulation in snail tissues. During the depuration period (28–49 days), at low concentrations (2 and 20 μg L−1), both FQs required at least 7 days to reach the maximum residue limit (50 μg kg−1). Conversely, at high concentrations (200 and 2000 μg L−1), 14 days (NOR) and 21 days (OFL) were required. Our results could facilitate management of the environmental risks of antibiotics and conservation of aquatic animals.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- BCF:
-
Bioconcentration factor
- CIP:
-
Ciprofloxacin
- ENR:
-
Enrofloxacin
- FQs:
-
Fluoroquinolones
- HPLC-MS:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry
- LSD:
-
Least significant difference
- LOD:
-
Limit of detection
- LOQ:
-
Limit of quantitation
- MRL:
-
Maximum residue limit
- EC50:
-
Median effective concentrations
- NOR:
-
Norfloxacin
- log K ow :
-
Octanol–water distribution coefficient
- OFL:
-
Ofloxacin
- SNR:
-
Signal-to-noise ratio
- ww:
-
Wet weight
References
Bi, T., Zhao, H., & Zhang, S. (2015). Acute toxicity experience to goldfish of ofloxacin and norfloxacin lactate and enrofloxacin. Farm Products Processing., 8, 31–33 (In Chinese).
Bo, C., Changliang, K. E., Le, L. I., et al. (2017). Bioaccumulation and potential sources of DDTs in Trachinotus ovatus during typical cage cultured periods. Journal of Fisheries of China, 41, 1264–1275 (In Chinese).
Book Calfee Ministry of Environmental. Protection of the People’s Republic of China. (1993). Aquatic monitoring manual. Nanjing: Southeast University Press (In Chinese).
Cai, Z., Chen, Y., Zhou, J., & Zhu, X. (2012). Research and progress pf biomarkers in marine environmental field. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences., 9, 1035–1048 (In Chinese).
Carrasquillo, A. J., Bruland, G. L., Mackay, A. A., et al. (2008). Sorption of ciprofloxacin and oxytetracycline zwitterions to soils and soil minerals: Influence of compound structure. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 42, 7634–7642.
Conkle, J. L., Lattao, C., & White, J. R. (2010). Competitive sorption and desorption behavior for three fluoroquinolone antibiotics in a wastewater treatment wetland soil. Chemosphere., 80, 1353–1359.
Dhanani, J. A., Parker, S. L., Lipman, J., Wallis, S. C., Cohen, J., Fraser, J., et al. (2018). Recovery rates of combination antibiotic therapy using in vitro microdialysis simulating in vivo conditions. Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis., 8, 407–412.
Fang, W., Shao, J., Shi, Z., & Yang, X. (2003). Analytical method of norfloxacin in the giant tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) hemolymph and brief study on pharmacokinetics. Acta Hydrobiol. Sinica., 27, 13–17 (In Chinese).
Glorieux, C., Calderon, P., & B. (2017). Catalase, a remarkable enzyme: targeting the oldest antioxidant enzyme to find a new cancer treatment approach. Biological Chemistry, 398, 1095–1108.
González-Pleiter, M., Gonzalo, S., Rodea-Palomares, I., Leganés, F., Rosal, R., Boltes, K., Marco, E., & Fernaández-Piñas, F. (2013). Toxicity of five antibiotics and their mixtures towards photosynthetic aquatic organisms: implications for environmental risk assessment. Water Research, 47, 2050–2064.
Grave, K., Torren, E. J., & Mackay, D. (2010). Comparison of the sales of veterinary antibacterial agents between 10 European countries. The Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 65, 2037–2040.
He, X., Wang, Z., Nie, X., Yang, Y., Pan, D., & Leung, A. O. W. (2012). Residues of fluoroquinolones in marine aquaculture environment of the Pearl River delta. South China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 34, 323–335.
Hoang, T. T. T., Le, P. N., & Tu, T. C. L. (2011). Antibiotic contaminants in coastal wetlands from Vietnamese shrimp farming. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 18, 835–841.
Isidori, M., Lavorgna, M., & Nardelli, A. (2005). Toxic and genotoxic evaluation of six antibiotics on non-target organisms. The Science of the Total Environment, 346, 87–98.
ISO. (2006). Water quality-guidance on statistical interpretation of ecotoxicity data. ISO/TS 20281–2006.
Jang, H. M., Kim, Y. B., Choi, S., Lee, Y., Shin, S. G., Unno, T., et al. (2018). Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes from effluent of coastal aquaculture, South Korea. Environmental Pollution, 233, 1049–1057.
Le, T. X., & Munekage, Y. (2004). Residues of selected antibiotics in water and mud from shrimp ponds in mangrove areas in Viet Nam. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 49, 922–929.
Li, W., Shi, Y., Gao, L., Liu, J., & Cai, Y. (2012). Investigation of antibiotics in mollusks from coastal waters in the Bohai Sea of China. Environmental Pollution, 162, 56–62.
Liang, X., Jinyan, L. U., & Nie, X. (2010). Toxicity of the food additive BHA (butylated hydroxyanisole) and antibiotic NFLX (norfloxacin) to swordtail fish (Xiphophorus helleri). Acta Scienentiae Circumstantiae., 30, 172–179 (In Chinese).
Liang, X., Wang, L., Ou, R., Nie, X., Yang, Y., Wang, F., & Li, K. (2015). Effects of norfloxacin on hepatic genes expression of P450 isoforms (CYP1A and CYP3A), GST and P-glycoprotein (P-gp) in swordtail fish (Xiphophorus Helleri). Ecotoxicology., 24, 1566–1573.
Liu, J., Peng, J., Ma, T., Zhou, K., & Zhu, C. (2012). Toxicokinetics and reproductive effects of sediment-associated 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether(BDE-47) in Bellamya aeruginosa. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology., 7, 259–267 (In Chinese).
Liu, H., Tang, S., Zheng, X., Zhu, Y., Ma, Z., Liu, C., et al. (2015). Bioaccumulation, biotransformation, and toxicity of BDE-47, 6-OH-BDE-47, and 6-MeO-BDE-47 in early life-stages of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environmental Science & Technology, 49, 1823–1833.
Ma, T. W., Zhu, C., Wang, G. Y., Zhou, K., Peng, J. Y., & Liu, J. (2010). Bioaccumulation of sediment heavy metals in Bellamya aeruginosa and its relations with the metals geochemical fractions. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 21, 734–742.
Nallani, G. C., Paulos, P. M., Constantine, L. A., Venables, B. J., & Huggett, D. B. (2011). Bioconcentration of ibuprofen in fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) and channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Chemosphere., 84, 1371–1377.
Nie, X., Gu, J., Lu, J., Pan, W., & Yang, Y. (2009). Effects of norfloxacin and butylated hydroxyanisole on the freshwater microalga Scenedesmus obliquus. Ecotoxicology., 18, 677–684.
Oehlmann, J., Benedetto, P. D., Tillmann, M., Duft, M., Oetken, M., & Schulte-Oehlmann, U. (2007). Endocrine disruption in prosobranch molluscs: evidence and ecological relevance. Ecotoxicology., 16, 29–43.
Peng, X., Tan, J., Tang, C., Yu, Y., & Wang, Z. (2008). Multiresidue determination of fluoroquinolone, sulfonamide, trimethoprim, and chloramphenicol antibiotics in urban waters in China. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 27, 73–79.
Qu, X., Wang, Y., Li, S., Li, Z., Zhang, Z., & Chen, X. (2007). Studies on pharmacokinetics and the elimination regularity of norfloxacin residues in Scophthalmus maximus. Marine Fisheries Research., 28, 24–29 (In Chinese).
Ren, K., Liu, Y., Xu, J., Fang, X., Cai, Q., & Chen, Z. (2016). Residues characteristics of fluoroquinolones (FQs) in the river sediments and fish tissues in a drinking water protection area of Guangdong Province. Acta Scienentiae Circumstantiae., 36, 760–766 (In Chinese).
Robinson, A. A., Belden, J. B., & Lydy, M. J. (2005). Toxicity of fluoroquinolone antibiotics to aquatic organisms. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 24, 423–430.
Sandra, B., Martina, P., & Škorić, et al. (2013). Photolytic degradation of norfloxacin, enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in various aqueous media. Chemosphere. 91, 1635–1642.
Sara, R. M., Sara, C., Elisabet, M., Belinda, H., Meritxell, G., Alexandre, S. M., et al. (2015). Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in hospital and urban wastewaters and their impact on the receiving river. Water Research, 69, 234–242.
Sim, W., Lee, J., & Lee, E. (2011). Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceuticals in wastewater from households, livestock farms, hospitals and pharmaceutical manufactures. Chemosphere., 82, 179–186.
Tamtam, F., Mercier, F., Bot, B. L., Eurin, J., Dinh, Q. T., Clément, M., et al. (2008). Occurrence and fate of antibiotics in the Seine River in various hydrological conditions. The Science of the Total Environment, 393, 84–95.
The Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. (2002). Pollution-free food: maximum residue limit of the fishery drug 5070-2002. China Fish, 10, 70–71 (In Chinese).
Thi, T. T. H., Loan, T. C. T., & Nga, P. L. (2012). Fate of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in Vietnamese coastal wetland ecosystem. Wetlands Ecology and Management, 20, 399–408.
Tuan, X. L., & Yukihiro, K. (2004). Residues of selected antibiotics in water and mud from shrimp ponds in mangrove areas in Viet Nam. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 49, 922–929.
USEPA. (2002). US Environmental Protection Agency methods for measuring the acute toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater and marine organisms. EPA-821-R-02-012. Washington DC: Office of Water.
Van Doorslaer, X., Dewulf, J., Van Langenhove, H., & Demeestere, K. (2014). Fluoroquinolone antibiotics: an emerging class of environmental micropollutants. The Science of the Total Environment, 1, 250–269.
Wang, Q., Liu, Q., Li, J., & Wang, Q. (2008). Tissue distribution and elimination of norfloxacin in Japanese sea perch (Lateolabras japonicus) and black sea bream (Sparus macrocephalus) following multi-oral administration. Aquaculture, 278, 0–4.
Xu, W. H., Zhang, G., Zou, S. C., Li, X. D., & Liu, Y. C. (2007). Determination of selected antibiotics in the Victoria Harbour and the Pearl River, South China using high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Environmental Pollution, 145, 672–679.
Xu, J., Wang, N., Kong, D., & Shan, Z. (2015). Bioconcentration of sulfonamide antibiotics in Zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio) and model prediction assessment. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology., 10, 82–88 (In Chinese).
Yang, X., Lu, G., Liu, J., & Yan, Z. (2013). Multigenerational chronic effects of pharmaceuticals on Daphnia magna at environmentally relevant concentrations. China Environmental Science, 33, 538–545 (In Chinese).
Zhang, Y., Zhang, Z., Zheng, W., Liu, Y., Yang, Y., Zhang, J., et al. (2000). Study on pharmacokinetics of norfloxacin in carp following different forms administration. Journal of Fisheries of China, 24, 559–563 (In Chinese).
Zhang, Z., Li, J., Feng, W., He, Y., & Chen, P. (2011). Effects of norfloxacin on the non-specific immune response of Fenneropenaeus chinedsi. Progress in Fishery Sciences., 32, 53–59 (In Chinese).
Zhang, J., Wang, Z., Song, Z., Xie, Z., Li, L., & Song, L. (2012). Bioaccumulation of microcystins in two freshwater gastropods from a cyanobacteria-bloom plateau lake, Lake Dianchi. Environmental Pollution, 164, 227–234.
Zhang, Q., Xin, Q., Zhu, J., & Cheng, J. (2014). The antibiotic contaminations in the main water bodies in China and the associated environmental and human health impacts. Environment and Chemistry, 33, 1075–1083 (In Chinese).
Zhao, L., Dong, Y. H., & Wang, H. (2010). Residues of veterinary antibiotics in manures from feedlot livestock in eight provinces of China. The Science of the Total Environment, 408, 1069–1075.
Zhao, T., Chen, Y., Han, W., & He, Y. (2016). The contamination characteristics and ecological risk assessment of typical antibiotics in the upper reaches of the Dongjiang River. Ecology and Environmental Science., 25, 1707–1713 (In Chinese).
Zheng, S. (2013). Toxicology of toluene, etheylbenzene, and xylene to a native aquatic gastropod and the study of water quality criteria for toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylene in China (pp. 18–20). Tianjin: Nankai University (In Chinese).
Zhou, L., Ying, G., & Liu, S. (2013). Excretion masses and environmental occurrence of antibiotics in typical swine and dairy cattle farms in China. The Science of the Total Environment, 444, 183–195.
Zhou, D., Gao, X., Xu, Y., & Wang, Z. (2014). Advances in metrics and assessment of organic chemical bioaccumulation. Environment and Chemistry, 33, 175–185 (In Chinese).
Zhu, L., Zhang, Y., Qu, X., Ma, X., Xu, C., & Ding, S. (2014). Qccurrence of antibiotics in aquatic plants and organisms from Qing River, Beijing. Research of Environmental Scienes., 27, 139–146 (In Chinese).
Acknowledgments
We thank the Instrumental Analysis and Research Center in Sun Yat-sen University for support to S He.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFC 0502800) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics and Animal Welfare
All procedures were complied with National Institutes of Health guide for the care and use of Laboratory animals (NIH Publications No. 8023, revised 1978).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, S., Sun, Q., Liu, Y. et al. Acute Toxicity, Bioaccumulation, and Bioreduction of Two Antibiotics, Norfloxacin and Ofloxacin, in the Snail Bellamya aeruginosa. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 96 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-4458-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-4458-5