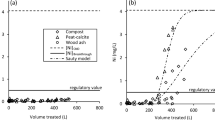
Abstract
Sorption is an effective process for the remediation of mine water with low metal concentrations. To identify promising low-cost organic sorbents for nickel (Ni), adsorption and retention properties of peat, compost, brown algae, sawdust, and wood ash were compared. Batch adsorption and desorption experiments were conducted at pH 7 in 0.05 M NaNO3 solutions to simulate the ionic strength and pH of a contaminated neutral drainage. Results of adsorption kinetic experiments were best represented by the Elovich model and the fastest rates were obtained with peat (796,075 mg g−1 min−1) and compost (791 mg g−1 min−1). Results of equilibration adsorption experiments were fitted to Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms and the highest adsorption capacities were observed for peat (around 22 mg g−1) and compost (around 9 mg g−1). Desorption experiments revealed that peat and compost adsorbed more Ni and also released a lower percentage of the adsorbed metal upon exposure to Ni-free solutions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison, J., Brown, D. S., Novo-Gradac, K. J. (2011). MINTEQA2/PRODEFA2, a geochemical assesment model for environmental systems: version 3.0 user’s manual.
APHA. (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (21st ed.). Washington, D.C.: American Public Health Association.
Arán, D., Antelo, J., Lodeiro, P., Macías, F., & Fiol, S. (2017). Use of waste-derived biochar to remove copper from aqueous solution in a continuous-flow system. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 56, 12755–12762. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.7b03056.
Bakatula, E. N., Richard, D., Neculita, C. M., & Zagury, G. J. (2018). Determination of point of zero charge of natural organic materials. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25, 7823–7833. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-1115-7.
Blanchard, G., Maunaye, M., & Martin, G. (1984). Removal of heavy metals from waters by means of natural zeolites. Water Research, 18, 1501–1507.
Brunauer, S., Emmett, P. H., & Teller, E. (1938). Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 60, 309–319.
Calugaru, I. L., Neculita, C. M., Genty, T., & Zagury, G. J. (2018). Metals and metalloids treatment in contaminated neutral effluents using modified materials. Journal of Environmental Management, 212, 142–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.02.002.
CEAEQ (2013). Détermination du carbone et du soufre: méthode par combustion et dosage par spectrophotométrie infrarouge, Méthode MA.310-CS 1.0. http://www.ceaeq.gouv.qc.ca/methodes/pdf/MA310CS10.pdf. Accessed 2019-06-18 2019.
Das, N., Vimala, R., & Karthika, P. (2008). Biosorption of heavy metals - an overview. Indian Journal of Biotechnology, 7, 159–169.
Davis, T. A., Volesky, B., & Mucci, A. (2003). A review of the biochemistry of heavy metal biosorption by brown algae. Water Research, 37, 4311–4330. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00293-8.
Fourest, E., & Volesky, B. (1996). Contribution of sulfonate groups and alginate to heavy metal biosorption by the dry biomass of Sargassum fluitans. Environmental Science and Technology, 30, 277–282. https://doi.org/10.1021/es950315s.
Freundlich, H. (1907). Über die adsorption in lösungen Zeitschrift für physikalische. Chemie, 57, 385–470.
Gustafsson, J. P. (2016). Visual MINTEQ ver. 3.0. https://vminteq.lwr.kth.se/. Accessed 2018-01-15 2018.
Guthrie, J. W., et al. (2005). Complexation of Ni, Cu, Zn, and Cd by DOC in some metal-impacted freshwater lakes: a comparison of approaches using electrochemical determination of free-metal-ion and labile complexes and a computer speciation model, WHAM V and VI. Analytica Chimica Acta, 528, 205–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2004.10.003.
Ho, Y. S. (1995). Adsorption of heavy metals from waste streams by peat. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Brimingham, Brimingham (UK).
Iakovleva, E., & Sillanpaa, M. (2013). The use of low-cost adsorbents for wastewater purification in mining industries. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 7878–7899. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1546-8.
Inglezakis, V. J., Fyrillas, M. M., & Park, J. (2019). Variable diffusivity homogeneous surface diffusion model and analysis of merits and fallacies of simplified adsorption kinetics equations. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 367, 224–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.12.023.
Lagergren, S. (1898). About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Sven Vetenskapsakad Handingarl, 24, 1–39.
Langmuir, I. (1918). The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 40, 1361–1403.
Mandal, R., Hassan, N. M., Murimboh, J., Chakrabarti, C. L., Back, M. H., Rahayu, U., & Lean, D. R. S. (2002). Chemical speciation and toxicity of nickel species in natural waters from the Sudbury area (Canada). Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 1477–1484. https://doi.org/10.1021/es015622e.
McLean, J. E., & Bledsoe, B. E. (1992). Behavior of metals in soils. Washington, DC: United States Environmental Protection Agency.
McLintock, I. S. (1967). The Elovich equation in chemisorption kinetics. Nature, 216, 1204–1205.
MDDELCC (2012) Directive 019 sur l’industrie minière. Ministère du Développement Durable, Environnement et Lutte contre les Changements Climatiques du Québec. http://www.mddelcc.gouv.qc.ca/milieu_ind/directive019/. Accessed 2019-06-18.
Mohan, D., Sarswat, A., Ok, Y. S., & Pittman Jr., C. U. (2014). Organic and inorganic contaminants removal from water with biochar, a renewable, low cost and sustainable adsorbent–a critical review. Bioresource Technology, 160, 191–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.120.
Rees, F., Simonnot, M. O., & Morel, J. L. (2014). Short-term effects of biochar on soil heavy metal mobility are controlled by intra-particle diffusion and soil pH increase. European Journal of Soil Science, 65, 149–161. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12107.
Roginsky, S. Z., & Zeldovich, J. (1934). The catalytic oxidation of carbon monoxide on manganese dioxide. Acta Physicochimica USSR, 1, 554.
Stokes, P. (1988). Nickel in aquatic systems. In H. Sigel & A. Sigel (Eds.), Metal ions in biological systems: nickel and its role in biology, vol 23 (pp. 31–46). New York: Marcel Dekker.
Stumm, W., & Morgan, J. (1996). Aquatic chemistry : chemical equilibria and rates in natural waters. Environmental Science and Technology (3rd ed.). New York: Wiley.
Tan, K. H. (2014). Humic matter in soil and the environment: principles and controversies (2nd ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group.
Tan, K. L., & Hameed, B. H. (2017). Insight into the adsorption kinetics models for the removal of contaminants from aqueous solutions. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 74, 25–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.01.024.
Tong, X.-j., Li, J.-y., Yuan, J.-h., & Xu, R.-k. (2011). Adsorption of Cu(II) by biochars generated from three crop straws. Chemical Engineering Journal, 172, 828–834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.06.069.
Tran, H. N., You, S.-J., Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A., & Chao, H.-P. (2017). Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: a critical review. Water Research, 120, 88–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.04.014.
Uchimiya, M., Wartelle, L. H., Klasson, K. T., Fortier, C. A., & Lima, I. M. (2011). Influence of pyrolysis temperature on biochar property and function as a heavy metal sorbent in soil. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 59, 2501–2510. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf104206c.
Wan Ngah, W. S., & Hanafiah, M. A. K. M. (2008). Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater by chemically modified plant wastes as adsorbents: a review. Bioresource Technology, 99, 3935–3948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.06.011.
Westholm, L. J., Repo, E., & Sillanpaa, M. (2014). Filter materials for metal removal from mine drainage-a review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 9109–9128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2903-y.
Xiao, Y., Azaiez, J., & Hill, J. M. (2018). Erroneous application of pseudo-second-order adsorption kinetics model: ignored assumptions and spurious correlations. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 57, 2705–2709. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.7b04724.
Xu, X., Cao, X., Zhao, L., Zhou, H., & Luo, Q. (2014). Interaction of organic and inorganic fractions of biochar with Pb(II) ion: further elucidation of mechanisms for Pb(II) removal by biochar. RSC Advances, 4, 44930–44937. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra07303g.
Xue, H. B., Jansen, S., Prasch, A., & Sigg, L. (2001). Nickel speciation and complexation kinetics in freshwater by ligand exchange and DPCSV. Environmental Science and Technology, 35, 539–546. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0014638.
Zhou, Y. F., & Haynes, R. J. (2010). Sorption of heavy metals by inorganic and organic components of solid wastes: significance to use of wastes as low-cost adsorbents and immobilizing agents. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 909–977. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380802586857.
Funding
This study was funded by the NSERC (Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada), grant no. 469489-14, and the industrial partners of the RIME UQAT Polytechnique Montreal, including Agnico Eagle, Mine Canadian Malartic, Iamgold, Raglan Mine Glencore, and Rio Tinto. D.R., also wishes to acknowledge support from the “Fonds de recherche Nature et technologies” (FQRNT) graduate scholarship program and from the “Fondation et alumni de Polytechnique Montréal” (Bourse Banque de Montréal).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 91 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richard, D., Mucci, A., Neculita, C.M. et al. Comparison of Organic Materials for the Passive Treatment of Synthetic Neutral Mine Drainage Contaminated by Nickel: Adsorption and Desorption Kinetics and Isotherms. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 556 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04917-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04917-z