Abstract
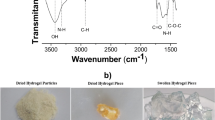
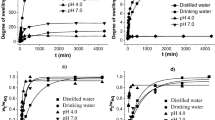
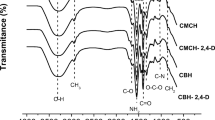
In this work was studied the single-component and multi-component abatement of metals in water using a hydrogel based on chitosan. The maximum single-component abatement capacities of cadmium (Cd) and lead (Pb) were 234.84 and 482.83 mg of metal per g of dried hydrogel at pH 6 and 40 °C, according to the Sips isotherm. The value for iron (Fe) was 386.59 mg g−1 at pH 4 and 40 °C, according to the Langmuir isotherm. The best kinetic fits were determined using the pseudo-second-order model, whereas the thermodynamic parameters inferred spontaneous, favorable abatement phenomena. Lower abatement capacities were determined for multi-component studies due to the hydrated ionic radius and electronegativity of the metals. The abatement processes were confirmed by scanning electron microscopy coupled to energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and Fourier-transform infrared spectra, indicating reversible chemical interactions between the hydrogel binding groups and Cd, Pb, and Fe. Such hydrogel proved to be a potential functional biopolymer for the treatment of water and wastewater contaminated by heavy metals.

Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham, J., Dowling, K., & Florentine, S. (2018). Assessment of potentially toxic metal contamination in the soils of a legacy mine site in Central Victoria, Australia. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.150.
Abukhadra, M. R., Dardir, F. M., Shaban, M., Ahmed, E. A., & Soliman, M. F. (2018). Superior removal of Co2+ , Cu2+ and Zn2+ contaminants from water utilizing spongy Ni/Fe carbonate–fluorapatite; preparation, application and mechanism. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.085.
Akkaya, R., & Ulusoy, U. (2008). Adsorptive features of chitosan entrapped in polyacrylamide hydrogel for Pb2+, UO22+, and Th4+. Journal of Hazardous Materials. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.05.084.
Ali, H., Khan, E., & Sajad, M. A. (2013). Phytoremediation of heavy metals-concepts and applications. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.075.
Bhattacharyya, K. G., & Gupta, S. S. (2006). Adsorption of Fe(III) from water by natural and acid activated clays: studies on equilibrium isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics of interactions. Adsorption. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-006-0145-0.
Boparai, H. K., Joseph, M., & O’Carroll, D. M. (2011). Kinetics and thermodynamics of cadmium ion removal by adsorption onto nano zerovalent iron particles. Journal of Hazardous Materials. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.11.029.
Calvete, T., Lima, E. C., Cardoso, N. F., Vaghetti, J. C. P., Dias, S. L. P., & Pavan, F. A. (2010). Application of carbon adsorbents prepared from Brazilian-pine fruit shell for the removal of reactive orange 16 from aqueous solution: kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Environmental Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.03.013.
Carolin, C. F., Kumar, P. S., Saravanan, A., Joshiba, G. J., & Naushad, M. (2017). Efficient techniques for the removal of toxic heavy metals from aquatic environment: a review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.05.029.
Chen, A., Shang, C., Shao, J., Lin, Y., Luo, S., Zhang, J., et al. (2017). Carbon disulfide-modified magnetic ion-imprinted chitosan-Fe(III): a novel adsorbent for simultaneous removal of tetracycline and cadmium. Carbohydrate Polymers. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.08.038.
Darezereshki, E., Darban, A. k., Abdollahy, M., & Jamshidi-Zanjani, A. (2018). Influence of heavy metals on the adsorption of arsenate by magnetite nanoparticles: kinetics and thermodynamic. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring and Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2018.04.002.
Dragan, E. S., Lazar, M. M., Dinu, M. V., & Doroftei, F. (2012). Macroporous composite IPN hydrogels based on poly(acrylamide) and chitosan with tuned swelling and sorption of cationic dyes. Chemical Engineering Journal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.07.126.
Dusek, P., & Schneider, S. A. (2012). Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. Current Opinion in Neurology. https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0b013e3283550cac.
Foo, K. Y., & Hameed, B. H. (2010). Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chemical Engineering Journal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.013.
Fosso-Kankeu, E., Mittal, H., Waanders, F., & Ray, S. S. (2017). Thermodynamic properties and adsorption behaviour of hydrogel nanocomposites for cadmium removal from mine effluents. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2016.12.033.
Gupta, V. K., Gupta, M., & Sharma, S. (2001). Process development for the removal of lead and chromium from aqueous solutions using red mud - an aluminium industry waste. Water Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00389-4.
Heidarinejad, Z., Rahmanian, O., Fazlzadeh, M., & Heidari, M. (2018). Enhancement of methylene blue adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from Date Press Cake by low frequency ultrasound. Journal of Molecular Liquids. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.05.100.
Ho, Y. S. (2003). Removal of copper ions from aqueous solution by tree fern. Water Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00002-2.
Hussain, C. M. (2015). Carbon nanomaterials as adsorbents for environmental analysis. In Nanomaterials for Environmental Protection. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118845530.ch14.
Järup, L. (2003). Hazards of heavy metal contamination. British Medical Bulletin. https://doi.org/10.1093/bmb/ldg032.
Kataria, N., & Garg, V. K. (2018). Green synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles loaded sawdust carbon for cadmium (II) removal from water: regeneration and mechanism. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.022.
Kırbıyık, Ç., Pütün, A. E., & Pütün, E. (2017). Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies of the adsorption of Fe(III) metal ions and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid onto biomass-based activated carbon by ZnCl2 activation. Surfaces and Interfaces. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2017.03.011.
Kopinke, F. D., Georgi, A., & Goss, K. U. (2018). Comment on “Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solution: A critical review, published by Tran et al. [Water Research 120, 2017, 88–116]”. Water Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.09.055.
Li, Z., Wang, L., Meng, J., Liu, X., Xu, J., Wang, F., & Brookes, P. (2018). Zeolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron: New findings on simultaneous adsorption of Cd(II), Pb(II), and As(III) in aqueous solution and soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.09.036.
Ma, J., Liu, Y., Ali, O., Wei, Y., Zhang, S., Zhang, Y., et al. (2018). Fast adsorption of heavy metal ions by waste cotton fabrics based double network hydrogel and influencing factors insight. Journal of Hazardous Materials. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.11.041.
Maneechakr, P., & Karnjanakom, S. (2017). Adsorption behaviour of Fe(II) and Cr(VI) on activated carbon: Surface chemistry, isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jct.2016.11.021.
Martini, B. K., Daniel, T. G., Corazza, M. Z., & De Carvalho, A. E. (2018). Methyl orange and tartrazine yellow adsorption on activated carbon prepared from boiler residue: kinetics, isotherms, thermodynamics studies and material characterization. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.10.013.
Milosavljević, N. B., Ristić, M. D., Perić-Grujić, A. A., Filipović, J. M., Štrbac, S. B., Rakočević, Z. L., & Krušić, M. T. K. (2011). Removal of Cu2+ ions using hydrogels of chitosan, itaconic and methacrylic acid: FTIR, SEM/EDX, AFM, kinetic and equilibrium study. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2011.08.011.
Mohammadzadeh Pakdel, P., & Peighambardoust, S. J. (2018). A review on acrylic based hydrogels and their applications in wastewater treatment. Journal of Environmental Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.03.076.
Nagajyoti, P. C., Lee, K. D., & Sreekanth, T. V. M. (2010). Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review. Environmental Chemistry Letters. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-010-0297-8.
Naushad, M. (2018). A new generation material graphene: applications in water technology. A new generation material Graphene: Applications in Water Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-75484-0.
Ngah, W. S. W., Ab Ghani, S., & Kamari, A. (2005). Adsorption behaviour of Fe(II) and Fe(III) ions in aqueous solution on chitosan and cross-linked chitosan beads. Bioresource Technology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2004.05.022.
Nightingale, E. R. (1959). Phenomenological theory of ion solvation. Effective radii of hydrated ions. Journal of Physical Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1021/j150579a011.
Norouzi, S., Heidari, M., Alipour, V., Rahmanian, O., Fazlzadeh, M., Mohammadi-moghadam, F., et al. (2018). Preparation, characterization and Cr(VI) adsorption evaluation of NaOH-activated carbon produced from Date Press Cake: an agro-industrial waste. Bioresource Technology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.02.106.
Parr, R. G., & Pearson, R. G. (1983). Absolute hardness: companion parameter to absolute electronegativity. Journal of the American Chemical Society. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00364a005.
Paulino, A. T., Belfiore, L. A., Kubota, L. T., Muniz, E. C., Almeida, V. C., & Tambourgi, E. B. (2011a). Effect of magnetite on the adsorption behavior of Pb(II), Cd(II), and Cu(II) in chitosan-based hydrogels. Desalination. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.02.056.
Paulino, A. T., Belfiore, L. A., Kubota, L. T., Muniz, E. C., & Tambourgi, E. B. (2011b). Efficiency of hydrogels based on natural polysaccharides in the removal of Cd2+ ions from aqueous solutions. Chemical Engineering Journal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.12.037.
Redlich, O., & Peterson, D. L. (1959). A useful adsorption isotherm. Journal of Physical Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1021/j150576a611.
Sastre, M., Ritchie, C. W., & Hajji, N. (2015). Metal ions in Alzheimer’s disease brain. JSM Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Dementia.
Shakir, S. K., Azizullah, A., Murad, W., Daud, M. K., Nabeela, F., Rahman, H., et al. (2017). Toxic metal pollution in Pakistan and its possible risks to public health. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology. https://doi.org/10.1007/398_2016_9.
Shang, Z., Zhang, L. W., Zhao, X., Liu, S., & Li, D. (2019). Removal of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Hg(II) from aqueous solution by mercapto-modified coal gangue. Journal of Environmental Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.072.
Sharififard, H., Shahraki, Z. H., Rezvanpanah, E., & Rad, S. H. (2018). A novel natural chitosan/activated carbon/iron bio-nanocomposite: Sonochemical synthesis, characterization, and application for cadmium removal in batch and continuous adsorption process. Bioresource Technology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.09.094.
Sips, R. (1948). On the structure of a catalyst surface. The Journal of Chemical Physics. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1746922.
Tchounwou, P. B., Yedjou, C. G., Patlolla, A. K., & Sutton, D. J. (2012). Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. EXS. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7643-8340-4_6.
Thapa, R., Gupta, S., Kaur, H., & Rajak, S. (2019). Search for potential iron contamination zones in Burdwan district: an approach through fuzzy logic. Sustainable Water Resources Management. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-018-0277-x.
Tran, H. N., You, S. J., Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A., & Chao, H. P. (2017). Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: a critical review. Water Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.04.014.
Vieira, R. M., Vilela, P. B., Becegato, V. A., & Paulino, A. T. (2018). Chitosan-based hydrogel and chitosan/acid-activated montmorillonite composite hydrogel for the adsorption and removal of Pb+2 and Ni+2 ions accommodated in aqueous solutions. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.04.018.
Vilela, P. B., Dalalibera, A., Duminelli, E. C., Becegato, V. A., & Paulino, A. T. (2019). Adsorption and removal of chromium (VI) contained in aqueous solutions using a chitosan-based hydrogel. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3208-3.
Vu, H. C., Dwivedi, A. D., Le, T. T., Seo, S. H., Kim, E. J., & Chang, Y. S. (2017). Magnetite graphene oxide encapsulated in alginate beads for enhanced adsorption of Cr(VI) and As(V) from aqueous solutions: role of crosslinking metal cations in pH control. Chemical Engineering Journal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.058.
Wang, Y., Wang, J., Yuan, Z., Han, H., Li, T., Li, L., & Guo, X. (2017). Chitosan cross-linked poly(acrylic acid) hydrogels: drug release control and mechanism. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.01.008.
Wise, J. T. F., Wang, L., Zhang, Z., & Shi, X. (2017). The 9th conference on metal toxicity and carcinogenesis: the conference overview. In Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2017.04.007.
Wu, D., Wang, Y., Li, Y., Wei, Q., Hu, L., Yan, T., et al. (2019). Phosphorylated chitosan/CoFe 2 O 4 composite for the efficient removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solution: Adsorption performance and mechanism studies. Journal of Molecular Liquids. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.12.098.
Yan, X. P., Hendry, J. M., & Kerrich, R. (2000). Speciation of dissolved iron(III) and iron(II) in water by on-line coupling of flow injection separation and preconcentration with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac9909655.
Zhang, L., Zeng, Y., & Cheng, Z. (2016). Removal of heavy metal ions using chitosan and modified chitosan: a review. Journal of Molecular Liquids. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.12.013.
Zheng, Y., Huang, D., & Wang, A. (2011). Chitosan-g-poly(acrylic acid) hydrogel with crosslinked polymeric networks for Ni2+ recovery. Analytica Chimica Acta. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2010.12.026.
Zhou, G., Luo, J., Liu, C., Chu, L., & Crittenden, J. (2018). Efficient heavy metal removal from industrial melting effluent using fixed-bed process based on porous hydrogel adsorbents. Water Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.12.067.
Zhu, Q., & Li, Z. (2015). Hydrogel-supported nanosized hydrous manganese dioxide: synthesis, characterization, and adsorption behavior study for Pb2+, Cu2+, Cd2+ and Ni2+ removal from water. Chemical Engineering Journal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.06.068.
Funding
ATP was financially supported by the State of Santa Catarina Research and Innovation Foundation, FAPESC/Brazil (grant number: 2019/TR672) and was a recipient of the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development, CNPq/Brazil, research productivity scholarship (grant number 312467/2019-2). This study was financed in part by the Coordination for the Advancement of Higher Education Personnel, CAPES/Brazil (Finance Code 001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1366 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vilela, P.B., Dalalibera, A., Becegato, V.A. et al. Single-Component and Multi-Component Metal Abatement in Water Using a Hydrogel Based on Chitosan: Characterization, Isotherm, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Results. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 507 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04873-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04873-8