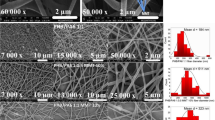
Abstract
Hydroxyapatite-silica fibers were prepared by sol-gel process and electrospinning, and their capacity for adsorption of cadmium and lead ions in aqueous solution was studied. The samples were characterized by SEM, FTIR, TGA, DSC, BET, and XRD. The composite consists on a network of continuous rough fibers with mean diameter of 150 ± 40 nm after thermal treatment. The fibers present a mesoporous structure with pore size of 15.75 nm. Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction demonstrated the presence of crystalline hydroxyapatite and amorphous silica. Adsorption process is represented by Freundlich isotherm, while the adsorption kinetics follow the pseudo-second-order model. The capacity shown by the fibrous material for the removal of lead ions (466.98 mg/g) was five times higher than the capacity observed for the adsorption of cadmium (93.30 mg/g). Therefore, the hydroxyapatite-silica electrospun fibers represent a suitable material for the efficient removal of lead and cadmium ions from aqueous solution.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-aziz, A. M., El-Maghraby, A., & Taha, N. A. (2017). Comparison between polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofiber and polyvinyl alcohol nanofiber (PVA)/hydroxyapatite (HA) for removal of Zn2+ ions from wastewater. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 10, 1052–1060.
Aliabadi, M., Irani, M., Ismaeili, J., & Najafzadeh, S. (2014). Design and evaluation of chitosan/hydroxyapatite composite nanofiber membrane for the removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 45, 518–526.
Brinker, C. J., & Scherer, G. W. (1990). Sol-gel science. The physics and chemistry of sol-gel processing. San Diego: Academic Press, Inc.
Chand, P., & Pakade, Y. B. (2015). Synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles impregnated on apple pomace to enhanced adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II), and Ni(II) ions from aqueous solution. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 10919–10929.
Cheng, T. W., Lee, M. L., Ko, M. S., Ueng, T. H., & Yang, S. F. (2012). The heavy metal adsorption characteristics on metakaolin-based geopolymer. Applied Clay Science, 56, 90–96.
Choi, S., & Jeong, Y. (2008). The removal of heavy metals in aqueous solution by hydroxyapatite/cellulose composite. Fibers and Polymers, 9(3), 267–270.
Dai, Y., Liu, W., Formo, E., Sun, Y., & Xia, Y. (2011). Ceramic nanofibers fabricated by electrospinning and their applications in catalysis, environmental science, and energy technology. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 22, 326–338.
Esfahani, H., Jose, R., & Ramakrishna, S. (2017). Electrospun ceramic nanofiber mats today: synthesis, properties, and applications. Materials, 10, 1238.
Franco, P. Q., João, C. F. C., Silva, J. C., & Borge, J. P. (2012). Electrospun hydroxyapatite fibers from simple sol-gel system. Materials Letters, 67, 233–236.
Fu, F., & Wang, Q. (2011). Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. Journal of Environmental Management, 92, 407–418.
Garibay-Alvarado, J. A., Espinosa-Cristóbal, L. F., & Reyes-López, S. Y. (2017). Fibrous silica-hydroxyapatite composite by electrospinning. International Journal of Research-Granthaalayah, 5, 39–47.
Garibay-Alvarado, J. A., Farias, R., & Reyes-López, S. Y. (2019). Sol-gel and electrospinning synthesis of lithium niobate-silica nanofibers. Coatings, 9, 212.
Gupta, N., Kushwaha, A. K., & Chattopadhyaya, M. C. (2012). Adsorptive removal of Pb+2, Cd+2 and Ni+2 by hydroxyapatite/chitosan composite from aqueous solution. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 43, 125–131.
Hench, L. L., & West, J. K. (1990). The sol-gel process. Chemical Reviews, 90, 33–72.
Iconaru, S. L., Motelica-Heino, M., Guegan, R., Beuran, M., Costescu, A., & Predoi, D. (2018). Adsorption of Pb(II) ions onto hydroxyapatite nanopowders in aqueous solutions. Materials, 11, 2204.
Koutsopoulos, S. (2002). Synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite crystals: a review study on the analytical methods. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 62, 600–612.
Lee, J. H., & Kim, Y. J. (2014). Hydroxyapatite nanofibers fabricated through electrospinning and sol-gel process. Ceramics International, 40, 3361–3369.
Li, D., & Xia, Y. (2004). Electrospinning of nanofibers: reinventing the wheel? Advanced Materials, 16, 1151–1170.
Martínez-Hernández, A. M., & Reyes-López, S. Y. (2017). Development of a composite of poly-ε-caprolactone-cerium oxide. International Journal of Research-Granthaalayah, 5, 493–505.
Mobasherpour, I., Salahi, E., & Pazouki, M. (2012). Comparative of the removal of Pb+2, Cd+2 and Ni+2 by nanocrystallite hydroxyapatite from aqueous solutions: adsorption isotherm study. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 5, 439–446.
Park, S., Gomez-Flores, A., Chung, Y. S., & Kim, H. (2015). Removal of cadmium and lead from aqueous solution by hydroxyapatite/chitosan hybrid fibrous sorbent: kinetics and equilibrium studies. Journal of Chemistry, 2015, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/396290
Pazos-Ortiz, E., Roque-Ruiz, J. H., Hinojos-Márquez, E. A., López-Esparza, J., Donohue-Cornejo, A., Cuevas-González, J. C., et al. (2017). Dose-dependent antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles on polycaprolactone fibers against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2017, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4752314.
Persson, I. (2010). Hydrated metal ions in aqueous solution: how regular are their structures? Pure and Applied Chemistry, 82, 1901–1917.
Qiu, H., Lv, L., Pan, B. C., Zhang, Q. J., Zhang, W. M., & Zhang, Q. X. (2009). Critical review in adsorption kinetic models. Journal of Zheijiang University-SCIENCE A, 10, 716–724.
Ramdani, A., Kadeche, A., Adjdir, M., Taleb, Z., Ikhou, D., Taleb, S., & Deratani, A. (2020). Lead and cadmium removal by adsorption process using hydroxyapatite porous materials. Water Practice Technology, 15(1), 130–141.
Roque-Ruiz, J. H., Cabrera-Ontiveros, E. A., Torres-Pérez, J., & Reyes-López, S. Y. (2016a). Preparation of PCL/clay and PVA/clay electrospun fibers for cadmium (Cd+2), chromium (Cr+3), copper (Cu+2) and Lead (Pb+2) removal from water. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 227, 286.
Roque-Ruiz, J. H., Cabrera-Ontiveros, E. A., González-García, G., & Reyes-López, S. Y. (2016b). Thermal degradation of aluminum formate sol-gel; synthesis of α-alumina and characterization by 1H, 13C and 27Al MAS NMR and XRD spectroscopy. Results in Physics, 6, 1096–1102.
Roque-Ruiz, J. H., Martínez-Máynez, H., Zalapa-Garibay, M. A., Arizmendi-Morquecho, A., Farias, R., & Reyes-López, S. Y. (2017). Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy in nanofibers mats of SiO2-TiO2-Ag. Results in Physics, 7, 2520–2527.
Roque-Ruiz, J. H., Meraz-Ángel, J., Farias, R., Meléndez-Lira, M., & Reyes-López, S. Y. (2019a). Sol-gel synthesis of strontium titanante nanofibers by electrospinning. Journal of Ceramic Science and Technology, 10, 29–38.
Roque-Ruiz, J. H., Medellín-Castillo, N. A., & Reyes-López, S. Y. (2019b). Fabrication of α-alumina fibers by sol-gel and electrospinning of aluminum nitrate precursor solutions. Results in Physics, 12, 193–204.
Safatian, F., Doago, Z., Torabbeigi, M., Shams, H. R., & Ahadi, N. (2019). Lead ion removal from water by hydroxyapatite nanostructures synthesized from egg sells with microwave irradiation. Applied Water Science, 9, 108.
Sing, K. S. W., Everett, D. H., Haul, R. A. W., Moscou, L., Pierotti, R. A., Rouquerol, J., & Siemieniewska, T. (1985). Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 57, 603–619.
Smith, D. W. (1977). Ionic hydration enthalpies. Journal of Chemical Education, 54, 540–542.
Wu, Y., Hench, L. L., Du, J., & Choy, K. L. (2004). Preparation of hydroxyapatite fibers by electrospinning technique. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 87, 1988–1991.
Yi, Z., Wang, K., Tian, J., Shu, Y., Yang, J., Xiao, W., Li, B., & Liao, X. (2016). Hierarchical porous hydroxyapatite fibers with a hollow structure as drug delivery carriers. Ceramics International, 42, 19079–19085.
Zhang, Z., Li, M., Chen, W., Zhu, S., Liu, N., & Zhu, L. (2010). Immobilization of lead and cadmium from aqueous solution and contaminated sediment using nano-hydroxyapatite. Environmental Pollution, 158, 514–519.
Zhang, H., Fu, Q. F., Sun, T. W., Chen, F., Qi, C., Wu, J., Cai, Z. Y., Qian, Q. R., & Zhu, Y. J. (2015). Amorphous calcium phosphate, hydroxyapatite and poly (D, L-lactic acid) composite nanofibers: electrospinning preparation, mineralization and in vivo bone defect repair. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 136, 27–36.
Zhou, Y., Li, S., Wang, D., & Han, X. (2019). Electrospinning synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanofibers assembled from nanorods and their adsorption for heavy metal ions. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 28, 981–988.
Funding
PRODEP, Universidad Autónoma de Ciudad Juárez and CONACYT provided funding this investigation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Investigation: J. H. R. R. and J. A. G. A.; formal analysis: J. H. R. R., J. A. G. A. and N. A. M. C.; writing—original draft: J. H. R. R.; methodology: N. A. M. C. and S. Y. R. L.; resources: N. A. M. C. and S. Y. R. L.; conceptualization: S. Y. R. L.; writing—review and editing: S. Y. R. L.; funding acquisition: S. Y. R. L.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roque-Ruiz, J.H., Garibay-Alvarado, J.A., Medellín-Castillo, N.A. et al. Preparation of Electrospun Hydroxyapatite-Glass Fibers for Removal of Cadmium (Cd+2) and Lead (Pb+2) from Aqueous Media. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 497 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04856-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04856-9