Abstract
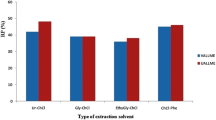
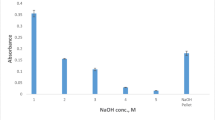
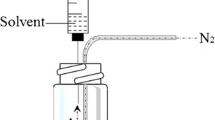
A method for the preconcentration of mercury using vortex-assisted temperature-controlled dispersive liquid-phase microextraction (VA-TC-DLPME) is proposed. A miniaturized gas-liquid separator (m-GLS) was developed and applied to the determination of mercury after VA-TC-DLPME. The detection was performed using cold vapor atomic absorption spectrometry (CV AAS). Ammonium pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (APDC) reagent was used as a complexing agent for Hg(II). The VA-TC-DLPME method consists in dispersing the ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ([Bmim][PF6]) in the aqueous phase by vigorous vortexing, followed by heating and cooling in an ice bath. The mixture was submitted to centrifugation, and the sedimented rich phase was then dissolved in an acid solution to reduce viscosity. Mercury was quantified in the final solution using m-GLS and CV AAS. Under optimized conditions, the method presents a limit of detection of 4.5 × 10−2 μg L−1, and an enrichment factor of 54. The accuracy was evaluated by the determination of mercury in reference material-certified ERM-CE 278, mussel tissue. The method was applied to the determination of mercury in fish oil samples. The developed m-GLS can be tested for use after other LPME procedures.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulra’uf, L. B., Sirhan, A. Y., & Tan, G. H. (2012). Recent developments and applications of liquid phase microextraction in fruits and vegetables analysis. Journal of Separation Science, 35, 3540–3553.
Aguilera-Herrador, E., Lucena, R., Cardenas, S., & Valcarcel, M. (2010). The roles of ionic liquids in sorptive microextraction techniques. Trac-Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 29, 602–616.
Andruch, V., Balogh, I. S., Kocurova, L., & Sandrejova, J. (2013). Five years of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. Applied Spectroscopy Reviews, 48, 161–259.
Aydin, F., Yilmaz, E., & Soylak, M. (2016). Ultrasonic-assisted supramolecular solvent-based liquid phase microextraction of mercury as 1-(2-pyridylazo)-2-naphthol complexes from water samples. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 96, 1356–1366.
Baghdadi, M., & Shemirani, F. (2008). Cold-induced aggregation microextraction: a novel sample preparation technique based on ionic liquids. Analytica Chimica Acta, 613, 56–63.
Baghdadi, M., & Shemirani, F. (2009). In situ solvent formation microextraction based on ionic liquids: a novel sample preparation technique for determination of inorganic species in saline solutions. Analytica Chimica Acta, 634, 186–191.
Bello-Lopez, M. A., Ramos-Payan, M., Ocana-Gonzalez, J. A., Fernandez-Torres, R., & Callejon-Mochon, M. (2012). Analytical applications of hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction (HF-LPME): a review. Analytical Letters, 45, 804–830.
de la Calle, I., Pena-Pereira, F., Lavilla, I., & Bendicho, C. (2016). Liquid-phase microextraction combined with graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry: a review. Analytica Chimica Acta, 936, 12–39.
Espino, M., Fernandez, M. D., Gomez, F. J. V., & Silva, M. F. (2016). Natural designer solvents for greening analytical chemistry. Trac-Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 76, 126–136.
Fang, Z., Dong, L., & Xu, S. (1992). Critical evaluation of the efficiency and synergistic effects of flow injection techniques for sensitivity enhancement in flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 7, 293–299.
Fernandez, E., Vidal, L., Martin-Yerga, D., Blanco, M. D., Canals, A., & Costa-Garcia, A. (2015). Screen-printed electrode based electrochemical detector coupled with ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and microvolume back-extraction for determination of mercury in water samples. Talanta, 135, 34–40.
Fernandez, E., Vidal, L., Costa-Garcia, A., & Canals, A. (2016). Mercury determination in urine samples by gold nanostructured screen-printed carbon electrodes after vortex-assisted ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. Analytica Chimica Acta, 915, 49–55.
Fleischer, H., Vorberg, E., & Thurow, K. (2014). Determination of total mercury content in wood materials-part 3: miniaturization using ICP-MS. American Laboratory, 46, 16–19.
Gao, Z. B., & Ma, X. G. (2011). Speciation analysis of mercury in water samples using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography. Analytica Chimica Acta, 702, 50–55.
Gharehbaghi, M., Shemirani, F., & Baghdadi, M. (2009). Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on ionic liquid and spectrophotometric determination of mercury in water samples. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 89, 21–33.
Gribble, M. O., Karimi, R., Feingold, B. J., Nyland, J. F., O’Hara, T. M., Gladyshev, M. I., & Chen, C. Y. (2016). Mercury, selenium and fish oils in marine food webs and implications for human health. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 96, 43–59.
Han, D., Tang, B., Lee, Y. R. & Row, K. H.: 2012, Application of ionic liquid in liquid phase microextraction technology. Journal of Separation Science, Journal of Separation Science 35, 2949–2961.
Ho, T. D., Canestraro, A. J., & Anderson, J. L. (2011). Ionic liquids in solid-phase microextraction: a review. Analytica Chimica Acta, 695, 18–43.
Hu, B., He, M., Chen, B. B., & Xia, L. B. (2013). Liquid phase microextraction for the analysis of trace elements and their speciation. Spectrochimica Acta, Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 86, 14–30.
Kato, M., Saka-Kato, K., & Toyo’oka, T. (2006). Miniaturization of analytical systems using immobilized biomolecules for high-throughput screening. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 384, 50–52.
Khan, M., & Soylak, M. (2016). Switchable solvent based liquid phase microextraction of mercury from environmental samples: a green aspect. RSC Advances, 6, 24968–24975.
Kutter, J. P. (2002). Special issue - miniaturization in analytical chemistry - preface. Talanta, 56, 221–221.
Lemos, V. A., & dos Santos, L. O. (2014). A new method for preconcentration and determination of mercury in fish, shellfish and saliva by cold vapour atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chemistry, 149, 203–207.
Lemos, V. A., & Vieira, U. S. (2013). Single-drop microextraction for the determination of manganese in seafood and water samples. Microchimica Acta, 180, 501–507.
Lemos, V. A., Oliveira, R. V., Lopes dos Santos, W. N., Menezes, R. M., Santos, L. B., & Costa Ferreira, S. L. (2019). Liquid phase microextraction associated with flow injection systems for the spectrometric determination of trace elements. Trac-Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 110, 357–366.
Liu, J.-f., Jiang, G.-b., Liu, J.-f., & Jönsson, J. Å. (2005). Application of ionic liquids in analytical chemistry. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 24, 20–27.
Martinis, E. M., Berton, P., Olsina, R. A., Altamirano, J. C., & Wuilloud, R. G. (2009). Trace mercury determination in drinking and natural water samples by room temperature ionic liquid based-preconcentration and flow injection-cold vapor atomic absorption spectrometry. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 167, 475–481.
Matysik, F. M. (2003). Miniaturization of electroanalytical systems. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 375, 33–35.
Mei, N., Lai, B. H., Liu, J. X., Mao, X. F., & Chen, G. Y. (2018). Speciation of trace mercury impurities in fish oil supplements. Food Control, 84, 221–225.
Nilsson, S., & Laurell, T. (2004). Miniaturization in analytical and bioanalytical chemistry. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 378, 1676–1677.
O’Connor, D., Hou, D. Y., Ok, Y. S., Mulder, J., Duan, L., Wu, Q. R., Wang, S. X., Tack, F. M. G., & Rinklebe, J. (2019). Mercury speciation, transformation, and transportation in soils, atmospheric flux, and implications for risk management: a critical review. Environment International, 126, 747–761.
Pedersen-Bjergaard, S., & Rasmussen, K. E. (2005). Bioanalysis of drugs by liquid-phase microextraction coupled to separation techniques. Journal of Chromatography, B: Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences, 817, 3–12.
Prosen, H. (2014). Applications of liquid-phase microextraction in the sample preparation of environmental solid samples. Molecules, 19, 6776–6808.
Raj, D., & Maiti, S. K. (2019). Sources, toxicity, and remediation of mercury: an essence review. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191.
Ramos, L., Ramos, J. J., & Brinkman, U. A. T. (2005). Miniaturization in sample treatment for environmental analysis. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 381, 119–140.
Redivo, D. D. B., Jesus, C. H. A., Sotomaior, B. B., Gasparin, A. T., & Cunha, J. M. (2019). Acute antinociceptive effect of fish oil or its major compounds, eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids on diabetic neuropathic pain depends on opioid system activation. Behavioural Brain Research, 372.
Saini, R. K., & Keum, Y. S. (2018). Omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids: dietary sources, metabolism, and significance - a review. Life Sciences, 203, 255–267.
Šandrejová, J., Campillo, N., Viñas, P., & Andruch, V. (2016). Classification and terminology in dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Microchemical Journal, 127, 184–186.
Santos, A. P., dos Santos, M. J. S., Korn, A., & M. d. G. & Lemos, V. A. (2019). Determination of cadmium in bread and biscuit samples using ultrasound-assisted temperature-controlled ionic liquid microextraction. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 99, 4609–4614.
Sereshti, H., Jamshidi, F., Nouri, N. & Nodeh, H. R. (2020). Hyphenated dispersive solid- and liquid-phase microextraction technique based on a hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent: application for trace analysis of pesticides in fruit juices, Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture.
Shirkhanloo, H., Khaligh, A., Mousavi, H. Z., Eskandari, M. M., & Miran-Beigi, A. A. (2015). Ultra-trace arsenic and mercury speciation and determination in blood samples by ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with flow injection-hydride generation/cold vapor atomic absorption spectroscopy. Chemical Papers, 69, 779–790.
Stanisz, E., Werner, J., & Matusiewicz, H. (2013). Mercury species determination by task specific ionic liquid-based ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with cold vapour generation atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchemical Journal, 110, 28–35.
Stanisz, E., Werner, J., & Matusiewicz, H. (2014). Task specific ionic liquid-coated PTFE tube for solid-phase microextraction prior to chemical and photo-induced mercury cold vapour generation. Microchemical Journal, 114, 229–237.
Trujillo-Rodriguez, M. J., Rocio-Bautista, P., Pino, V., & Afonso, A. M. (2013). Ionic liquids in dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. Trac-Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 51, 87–106.
Tuzen, M., & Soylak, M. (2005). Mercury contamination in mushroom samples from Tokat, Turkey. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 74, 968.
Vickackaite, V., & Padarauskas, A. (2012). Ionic liquids in microextraction techniques. Central European Journal of Chemistry, 10, 652–674.
Wyttenbach, A., & Bajo, S. (1975). Extractions with metal-dithiocarbamates as reagents. Analytical Chemistry, 47, 1813–1817.
Xu, L., Basheer, C., & Lee, H. K. (2007). Developments in single-drop microextraction. Journal of Chromatography A, 1152, 184–192.
Yao, C. H., Jiang, S. J., Sahayam, A. C., & Huang, Y. L. (2017). Speciation of mercury in fish oils using liquid chromatography inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Microchemical Journal, 133, 556–560.
Funding
This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001. The authors also acknowledge the financial support of the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (311419/2018-6) and the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado da Bahia
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent is not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Menezes, R.M., Santos, W.N.L., Silva, U.N. et al. A Miniaturized Gas-Liquid Separator for Use in Liquid-Phase Microextraction Procedures: Determination of Mercury in Food. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 473 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04837-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04837-y