Abstract
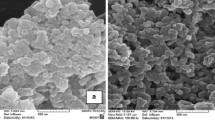
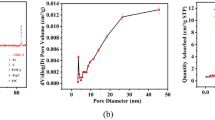
The impregnation process has successfully prepared a novel composite of iron oxide/carbon from black liquor (CA-BL/Fe) as an adsorbent for the removal of tripolyphosphate ions. Black liquor is a secondary product of the bioethanol pre-treatment process. X-ray diffraction results showed that the main iron oxide species present in the CA-BL/Fe was goethite (α-FeOOH). Interestingly, the specific surface area of CA-BL/Fe was 504 m2/g higher than that of commercial activated carbon of 356 m2/g. The adsorption performance showed that tripolyphosphate ion removal efficiency increased by increasing the adsorbent dosage, pH, and contact time. At the same time, it decreased with an increase in the initial concentration of tripolyphosphate. By controlling the environment pH value, the optimum removal efficiency of tripolyphosphate ions with CA-BL/Fe was 96.87%, with the adsorption capacity of 1.5922 mg/g for 1 h measurement. In this study, the dominant mechanisms of tripolyphosphate adsorption are electrostatic attraction and ion exchange. The result of this study is expected to be the basis for further promising adsorbent material for tripolyphosphate ion.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CA-BL:
-
Carbonaceous adsorbents-black liquor
- PAC:
-
Polyaluminum chloride
- CA-BL/Fe:
-
Carbonaceous adsorbents-black liquor/iron oxide
- BET:
-
Brunauer-Emmett-Teller
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
- SEM-EDX:
-
Scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy
- FTIR:
-
Fourier-transform infrared
References
“The Effect of Contact Time and PH on Methylene Blue Removal by Volcanic Ash.” 2014. In . https://doi.org/10.17758/iaast.a0514002.
Abussaud, B., Asmaly, H. A., Ihsanullah, Saleh, T. A., Gupta, V. K., Laoui, T., & Atieh, M. A. (2016). Sorption of phenol from waters on activated carbon impregnated with iron oxide, aluminum oxide and titanium oxide. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 213, 351–359.
Al-Zboon, K. K. (2018). Phosphate removal by activated carbon–silica nanoparticles composite, kaolin, and olive cake. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 20(6), 2707–2724.
Amriani, F., Barlianti, V., Muryanto, & Sari, A. A. (2015). Activated carbon from lignin-based black liquor coagulated by polyaluminium chloride. Procedia Chemistry, 16, 134–140.
Bhargava, D. S., & Sheldarkar, S. B. (1993). Use of TNSAC in phosphate adsorption studies and relationships. Literature, experimental methodology, kustification and effects of process variables. Water Research, 27(2), 303–312.
Blaney, L., Cinar, S., & Senggupta, A. (2007). Hybrid anion exchanger for trace phosphate removal from water and wastewater. Water Research, 41(7), 1603.
Borgnino, L., Giacomelli, C. E., Avena, M. J., & De Pauli, C. P. (2010). Phosphate adsorbed on Fe(III) modified montmorillonite: surface complexation studied by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 353(2–3), 238–244.
Cai, R., Wang, X., Ji, X., Peng, B., Tan, C., & Huang, X. (2017). Phosphate reclaim from simulated and real eutrophic water by magnetic biochar derived from water hyacinth. Journal of Environmental Management, 187, 212–219.
Castro, C. S., Guerreiro, M. C., Gonçalves, M., Oliveira, L. C. A., & Anastácio, A. S. (2009). Activated carbon/Iron oxide composites for the removal of atrazine from aqueous medium. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164(2–3), 609.
Cheremisinoff, P. N.. (2019). Membrane filtration. In Handbook of water and wastewater treatment technology, 481–518. Routledge.
Chmielewská, E., Hodossyová R., and Bujdoš M.. (2014). Kinetic and thermodynamic studies for phosphate removal using natural adsorption materials. In Environmental zeolites and aqueous media: examples of practical solutions, edited by Eva Chmielewska, 71–99. BENTHAM SCIENCE PUBLISHERS.
Fierro, V., Muñiz, G., Gonzalez-Sánchez, G., Ballinas, M. L., & Celzard, A. (2009). Arsenic removal by iron-doped activated carbons prepared by ferric chloride forced hydrolysis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168(1), 430–437.
Fu, K., Yue, Q., Gao, B., Sun, Y., & Zhu, L. (2013). Preparation, characterization and application of lignin-based activated carbon from black liquor lignin by steam activation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 228, 1074–1082.
Girgis, B. S., Temerk, Y. M., Gadelrab, M. M., & Abdullah, I. D. (2007). X-ray diffraction patterns of activated carbons prepared under various conditions. Carbon science, 8(2), 95–100.
Gu, Z., Fang, J., & Deng, B. (2005). Preparation and evaluation of adsorbents for arsenic removal. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(10), 3833–3843.
Huang, X., Liao, X., & Shi, B. (2009). Adsorption removal of phosphate in industrial wastewater by using metal-loaded skin Split waste. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 166(2–3), 1261.
Karaca, S., Gürses, A., Ejder, M., & Açıkyıldız, M. (2004). Kinetic modeling of liquid-phase adsorption of phosphate on dolomite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 277(2), 257–263.
Karaca, S., Gurses, A., Ejder, M., & Acikyldiz, M. (2006). Adsorptive removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions using raw and calcinated dolomite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 128(2–3), 273–279.
Krishnan, K. A., & Haridas, A. (2008). Removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions and sewage using natural and surface modified coir pith. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 152(2), 527–535.
Kumar, S., Prashanth, T. P., Korving, L., Keesman, K. J., Dugulan, I., van Loosdrecht, M. C. M., & Witkamp, G.-J. (2017). Effect of pore size distribution on iron oxide coated granular activated carbons for phosphate adsorption – importance of mesopores. Chemical Engineering Journal, 326, 231–239.
Lacasa, E., Cañizares, P., Sáez, C., Fernández, F. J., & Rodrigo, M. A. (2011). Electrochemical phosphates removal using iron and aluminium electrodes. Chemical Engineering Journal, 172(1), 137–143.
Lalley, J., Han, C., Li, X., Dionysiou, D. D., & Nadagouda, M. N. (2016). Phosphate adsorption using modified iron oxide-based sorbents in lake water: kinetics, equilibrium, and column tests. Chemical Engineering Journal, 284, 1386–1396.
Landmesser, H. (1997). Interior surface hydroxyl groups in ordered mesoporous silicates. Solid State Ionics, 101–103, 271–277.
Li, R., Wang, J. J., Zhou, B., Awasthi, M. K., Ali, A., Zhang, Z., Gaston, L. A., Lahori, A. H., & Mahar, A. (2016). Enhancing phosphate adsorption by Mg/Al layered double hydroxide functionalized biochar with different Mg/Al ratios. Science of the Total Environment, 559, 121–129.
Liu, J., Zhou, Q., Chen, J., Zhang, L., & Chang, N. (2013). Phosphate adsorption on hydroxyl–iron–lanthanum doped activated carbon fiber. Chemical Engineering Journal, 215–216, 859–867.
Mashkoor, F., Nasar, A., Inamuddin, & Asiri, A. M. (2018). Exploring the reusability of synthetically contaminated wastewater containing crystal violet dye using Tectona Grandis sawdust as a very low-cost adsorbent. Scientific Reports, 8, 8314.
Moharami, S., and Jalali, M. (2014). Effect of TiO2, Al2O3, and Fe3O4 nanoparticles on phosphorus removal from aqueous solution. Environ. Prog. Sustainable Energy, 33(4), 1209–1219.
Ndi Nsami, J., & Mbadcam, J. K. (2013). The adsorption efficiency of chemically prepared activated carbon from cola nut shells by on methylene blue. Journal of Chemistry, I2013, 1–7.
Ogata, T., Morisada, S., Oinuma, Y., Seida, Y., & Nakano, Y. (2011). Preparation of adsorbent for phosphate recovery from aqueous solutions based on condensed tannin gel. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 192(2), 698–703.
Pohan, M.,S.A., Sutarno & Suyanta (2016). Studi adsorpsi-desorpsi anion fosfat pada zeolit termodifikasi CTAB. Jurnal Penelitian Sains, 18(3), 123–35.
Pradana, M. A., Ardhyananta H., and Farid, M.. (2017). Pemisahan Selulosa Dari Lignin Serat Tandan Kosong Kelapa Sawit Dengan Proses Alkalisasi Untuk Penguat Bahan Komposit Penyerap Suara. Jurnal Teknik ITS, 6(2).
Rafati, L., Nabizadeh, R., Mahvi, A. H., & Dehghani, M. H. (2012). Removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions by iron nano-particle resin Lewatit (FO36). Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 29(4), 473–477.
Rittmann, B. E., Mayer, B., Westerhoff, P., & Edwards, M. (2011). Capturing the lost phosphorus. Chemosphere, 84(6), 846–853.
Sari, A. A., Amriani, F., Muryanto, M., Triwulandari, E., Sudiyani, Y., Barlianti, V., Lotulung, P. D. N., & Hadibarata, T. (2017). Mechanism, adsorption kinetics and applications of carbonaceous adsorbents derived from black liquor sludge. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 77, 236–243.
Shi, Z.-l., Fu-mei, L., & Shu-hua, Y. (2011). Adsorptive removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions using activated carbon loaded with Fe(III) oxide. New Carbon Materials, 26(4), 299–306.
Siswandari, A. M., Hindun, I., & Sukarsono, S. (2017). Phytoremediation of phosphate content in liquid laundry waste by using Echinodorus Paleafolius and Equisetum hyemale used as biology learning resource. Jurnal Pendidikan Biologi Indonesia, 2(3), 222.
Siwek, H., Bartkowiak, A., & Włodarczyk, M. (2019). Adsorption of phosphates from aqueous solutions on alginate/goethite hydrogel composite. Water (Switzerland), 11(4), 1–13.
Sparks, D. L. (2003). Environmental soil chemistry: second edition. Environmental soil chemistry: Second Edition.
Su, Y., Yang, W., Sun, W., Li, Q., & Shang, J. K. (2015). Synthesis of mesoporous cerium–zirconium binary oxide Nanoadsorbents by a solvothermal process and their effective adsorption of phosphate from water. Chemical Engineering Journal, 268, 270–279.
Tofan, L., Paduraru, C., and Toma, O. (2015). Zinc remediation of aqueous solutions by natural hemp fibers: batch desorption/regeneration study, Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(27), 12644–12652.
Vikrant, K., Kim, K.-H., Ok, Y. S., Tsang, D. C. W., Tsang, Y. F., Giri, B. S., & Singh, R. S. (2018). Engineered/designer biochar for the removal of phosphate in water and wastewater. Science of the Total Environment, 616–617, 1242–1260.
Wan, S., Wang, S., Li, Y., & Gao, B. (2017). Functionalizing biochar with Mg–Al and Mg–Fe layered double hydroxides for removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 47, 246–253.
Wang, Z., Nie, E., Li, J., Yang, M., Zhao, Y., Luo, X., & Zheng, Z. (2012). Equilibrium and kinetics of adsorption of phosphate onto iron-doped activated carbon. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 19(7), 2908–2917.
Wang, Z., Shi, M., Li, J., & Zheng, Z. (2014). Influence of moderate pre-oxidation treatment on the physical, chemical and phosphate adsorption properties of iron-containing activated carbon. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 26(3), 519–528.
Xia, P., Wang, X., Wang, X., Zhang, J., Wang, H., Song, J., Ma, R., Wang, J., & Zhao, J. (2017). Synthesis and characterization of MgO modified diatomite for phosphorus recovery in eutrophic water. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 62(1), 226–235.
Xie, F., Wu, F., Liu, G., Yunsong, M., Feng, C., Wang, H., & Giesy, J. P. (2014). Removal of phosphate from eutrophic lakes through adsorption by in situ formation of magnesium hydroxide from diatomite. Environmental Science and Technology, 48(1), 528–290.
Xiong, W., Tong, J., Yang, Z., Zeng, G., Zhou, Y., Wang, D., Song, P., Xu, R., Zhang, C., & Cheng, M. (2017). Adsorption of phosphate from aqueous solution using Iron-zirconium modified activated carbon nanofiber: performance and mechanism. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 493, 17–23.
Ya’aini, N., Pillay A., Krishnan L. G., and Ripin A.. (2019). Synthesis of activated carbon doped with transition metals for hydrogen storage. In E3S Web of Conferences, 90, 1016.
Yang, Q., Wang, X., Luo W., Sun, J., Xu, Q., Chen, F., Zhao J., et al. (2018). Effectiveness and mechanisms of phosphate adsorption on Iron-modified biochars derived from waste activated sludge. Bioresource Technology.
Yuan, X., Xia W., An, J., Yin, J., Zhou, X., and Yang, W.. (2015). Kinetic and thermodynamic studies on the phosphate adsorption removal by dolomite mineral. Journal of Chemistry.
Zhang, M., Zhang, H., Xu, D., L., H., Zhang, J., Zhang, L., Wu, W., & Tian, B. (2011). Removal of phosphate from aqueous solution using zeolite synthesized from fly ash by alkaline fusion followed by hydrothermal treatment. Separation Science and Technology, 46(14), 2260–2274.
Zhang, Z., Yan, L., Yu, H., Yan, T., & Li, X. (2019). Adsorption of phosphate from aqueous solution by vegetable biochar/layered double oxides: fast removal and mechanistic studies. Bioresource Technology, 284, 65–71.
Zhu, H., Jia, Y., Wu, X., & He, W. (2009). Removal of arsenic from water by supported nano zero-valent iron on activated carbon. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172(2–3), 1591–1596.
Zong, E., Huang, G., Liu, X., Lei, W., Jiang, S., Ma, Z., Wang, J., & Song, P. (2018). A lignin-based nano-adsorbent for superfast and highly selective removal of phosphate. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 6(21), 9971–9983.
Funding
This research was financially supported by INSINAS - Ministry of Research, Technology, and Higher Education Fiscal Year 2018, ELSA LIPI - Indonesian Institute of Sciences for the instruments support, and Deputy for Engineering Sciences - Indonesian Institute of Sciences for supporting professional checking English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 610 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sari, A.A., Akhmad, R.I.S., Asmara, A.A. et al. Characterization and Mechanisms of a New Carbonaceous Adsorbent Based on Black Liquor Loaded with Iron Oxide for Removal of Tripolyphosphate Ions. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 449 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04816-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04816-3