Abstract
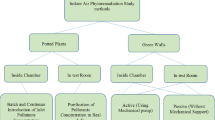
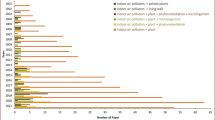
Air pollutants originated from natural and anthropogenic sources and able to bio-magnify and bio-accumulate in the trophic levels, thus increase toxicity in the food chain. Various air pollutants (particulate matters (PMs), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), inorganic air pollutants (IAP), persistent organic pollutants (POPs), heavy metals, and black carbon) resulted in adverse effects on environmental and human health after prolonged exposure. These airborne particles can travel in gaseous form for long distance and deteriorate the air quality of downstream areas. Air pollution abatement can be implemented by reducing emissions at source and purifying pollutants with remediation techniques. However, air pollution remained as the dominant issue to cause burden in human and ecosystem well-being. Due to drawbacks like expensive, high maintenance, and likelihood for pollutants’ reemission, existing conventional remediation technologies is insufficient for air pollutants mitigation. Phytoremediation enters the picture of air pollution control as a cost-effective, energy-saving, and environmental-friendly technology in remediating air pollutants. In phytoremediation, plant organs and associating microbes in the phyllosphere and rhizosphere interacted with each other to remediate air pollutants. Phytoremediation of air pollutants involves the rhizosphere of plants as pollutants may deposit in the soil during leaf fall and precipitation. Additionally, the phytoremediation mechanisms involve phytoextraction, phytovolatilization, phytodegradation, phytostabilization, rhizodegradation, and rhizofiltration. A brief overview of phytoremediation mechanisms for each air pollutants is presented. In short, the benefits of phytoremediation and its associated gaps in air pollution control are described.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adnan, L. A., Mohd Yusoff, A. R., Hadibarata, T. & Khudhair, A. B. (2014). Biodegradation of Bis-Azo dye reactive black 5 by white-rot fungus Trametes gibbosa sp. WRF 3 and its metabolite characterization. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 225, 2119.
Adnan, Z., Mir, S., & Habib, M. (2017). Exhaust gases depletion using non-thermal plasma (NTP). Atmospheric Pollution Research, 8, 338–343.
Agarwal, P., Sarkar, M., Chakraborty, B. & Banerjee, T. (2018), Phytoremediation of air pollutants: prospects and challenges. InTech Open.
Alharbi, O. M. L., Basheer, A. A., Khattab, R. A., & Ali, I. (2018). Health and environmental effects of persistent organic pollutants. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 263, 442–453.
Awa, S. H., & Hadibarata, T. (2020). Removal of heavy metals in contaminated soil by phytoremediation mechanism: a review. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 231, 47.
Borm, P. & Donaldson, K.: 2006, An introduction to particle toxicology: From coal mining to nanotechnology, pp. 1-12.
Bozkurt, Z., Doğan, G., Arslanbaş, D., Pekey, B., Pekey, H., Dumanoğlu, Y., Bayram, A., & Tuncel, G. (2015). Determination of the personal, indoor and outdoor exposure levels of inorganic gaseous pollutants in different microenvironments in an industrial city. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 590.
Brilli, F., Fares, S., Ghirardo, A., de Visser, P., Calatayud, V., Muñoz, A., Annesi-Maesano, I., Sebastiani, F., Alivernini, A., Varriale, V., & Menghini, F. (2018). Plants for sustainable improvement of indoor air quality. Trends in Plant Science, 23, 507–512.
Burken, J. G. (2003). Uptake and metabolism of organic compounds: green-liver model. Phytoremediation, 59–84.
Chandra, I., Kim, S., Seto, T., Otani, Y., Takami, A., Yoshino, A., Irei, S., Park, K., Takamura, T., Kaneyasu, N., & Hatakeyama, S. (2016). New particle formation under the influence of the long-range transport of air pollutants in East Asia. Atmospheric Environment, 141, 30–40.
Chen, G., Jin, Z., Li, S., Jin, X., Tong, S., Liu, S., Yang, Y., Huang, H. & Guo, Y. (2018). Early life exposure to particulate matter air pollution (PM1, PM2.5 and PM10) and autism in Shanghai, China: a case-control study. Environment International, 121.
Cristaldi, A., Conti, G. O., Jho, E. H., Zuccarello, P., Grasso, A., Copat, C., & Ferrante, M. (2017). Phytoremediation of contaminated soils by heavy metals and PAHs. A brief review. Environmental Technology and Innovation, 8, 309–326.
Cunningham, S. D., Berti, W. R., & Huang, J. W. (1995). Phytoremediation of contaminated soils. Trends in Biotechnology, 13, 393–397.
Dominguez, J. J. A., Inoue, C., & Chien, M.-F. (2020). Hydroponic approach to assess rhizodegradation by sudangrass (Sorghum x drummondii) reveals pH- and plant age-dependent variability in bacterial degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 387, 121695.
Duan, K., Sun, G., Zhang, Y., Yahya, K., Wang, K., Madden, J. M., Caldwell, P. V., Cohen, E. C., & McNulty, S. G. (2017). Impact of air pollution induced climate change on water availability and ecosystem productivity in the conterminous United States. Climatic Change, 140, 259–272.
Erakhrumen, A., & Agbontalor. (2007). Phytoremediation: an environmentally sound technology for pollution prevention, control and remediation in developing countries. Educational Research Review, 2, 151–156.
Fang, M., Yi, N., Di, W., Wang, T., & Wang, Q. (2020). Emission and control of flue gas pollutants in CO2 chemical absorption system – a review. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 93, 102904.
Feng, N.-X., Yu, J., Zhao, H.-M., Cheng, Y.-T., Mo, C.-H., Cai, Q.-Y., Li, Y.-W., Li, H., & Wong, M.-H. (2017). Efficient phytoremediation of organic contaminants in soils using plant–endophyte partnerships. Science of the Total Environment, 583, 352–368.
Feng, Y., Ning, M., Lei, Y., Sun, Y., Liu, W., & Wang, J. (2019). Defending blue sky in China: effectiveness of the “air pollution prevention and control action plan” on air quality improvements from 2013 to 2017. Journal of Environmental Management, 252, 109603.
Francke, K. P., Miessner, H., & Rudolph, R. (2000). Plasmacatalytic processes for environmental problems. Catalysis Today, 59, 411–416.
Gao, X., Liu, S., Zhang, Y., Luo, Z., Ni, M., & Cen, K. (2011). Adsorption and reduction of NO2 over activated carbon at low temperature. Fuel Processing Technology, 92, 139–146.
Gawronski, S. W., & Gawronska, H. (2017). Air phytoremediation. In A. A. Ansari, S. S. Gill, R. Gill, G. R. Lanza, & L. Newman (Eds.), Phytoremediation: management of environmental contaminants (Vol. 5, pp. 487–504). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Gawronski, S. W., Gawronska, H., Lomnicki, S., Sæbo, A., & Vangronsveld, J. (2017). Chapter eight - plants in air phytoremediation. In A. Cuypers & J. Vangronsveld (Eds.), Advances in Botanical Research (pp. 319–346). Academic Press.
Guarino, F., Miranda, A., Castiglione, S., & Cicatelli, A. (2020). Arsenic phytovolatilization and epigenetic modifications in Arundo donax L. assisted by a PGPR consortium. Chemosphere, 251, 126310.
Guieysse, B., Hort, C., Platel, V., Munoz, R., Ondarts, M., & Revah, S. (2008). Biological treatment of indoor air for VOC removal: potential and challenges. Biotechnology Advances, 26, 398–410.
Guo, Y., Li, Y., Zhu, T., & Ye, M. (2015). Investigation of SO2 and NO adsorption species on activated carbon and the mechanism of NO promotion effect on SO2. Fuel, 143, 536–542.
Guo, Z., Xie, Y., Hong, I., & Kim, J. (2001). Catalytic oxidation of NO to NO2 on activated carbon. Energy Conversion and Management, 42, 2005–2018.
Hadibarata, T., & Kristanti, R. A. (2012). Effect of environmental factors in the decolorization of Remazol Brilliant Blue R by Polyporus sp. S133. Journal of the Chilean Chemical Society, 57, 1095–1098.
Ho, A. F. W., Wah, W., Earnest, A., Ng, Y. Y., Xie, Z., Shahidah, N., Yap, S., Pek, P. P., Liu, N., Lam, S. S. W., & Ong, M. E. H. (2018). Health impacts of the Southeast Asian haze problem – a time-stratified case crossover study of the relationship between ambient air pollution and sudden cardiac deaths in Singapore. International Journal of Cardiology, 271, 352–358.
Huang, Y., Ho, S. S. H., Lu, Y., Niu, R., Xu, L., Cao, J., & Lee, S. (2016). Removal of indoor volatile organic compounds via photocatalytic oxidation: a short review and prospect. Molecules, 21, 56.
Jafarinejad, S. (2017). 5 - control and treatment of air emissions. In S. Jafarinejad (Ed.), Petroleum Waste Treatment and Pollution Control (pp. 149–183). Butterworth-Heinemann.
Kagalkar, A. N., Jadhav, M. U., Bapat, V. A., & Govindwar, S. P. (2011). Phytodegradation of the triphenylmethane dye Malachite Green mediated by cell suspension cultures of Blumea malcolmii Hook. Bioresource Technology, 102, 10312–10318.
Kampa, M., & Castanas, E. (2008). Human health effects of air pollution. Environmental Pollution, 151, 362–367.
Kanthasamy, S., Hadibarata, T., Hidayat, T., Alamri, S. A., & Al-Ghamdi, A. A. (2020). Adsorption of azo and anthraquinone dye by using watermelon peel powder and corn peel powder: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Biointerface Research in Applied Chemistry, 10, 4706–4713.
Kavamura, V. N., & Esposito, E. (2010). Biotechnological strategies applied to the decontamination of soils polluted with heavy metals. Biotechnology Advances, 28, 61–69.
Kelly, F. J., & Fussell, J. C. (2015). Air pollution and public health: emerging hazards and improved understanding of risk. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 37, 631–649.
Kristanti, R. A., Kanbe, M., Hadibarata, T., Toyama, T., Tanaka, Y., & Mori, K. (2012). Isolation and characterization of 3-nitrophenol-degrading bacteria associated with rhizosphere of Spirodela polyrrhiza. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 19, 1852–1858.
Kumar, R., & Gupta, P. (2016). Air pollution control policies and regulations (pp. 133–149).
Lasat, M. (2001). Phytoextraction of toxic metals: a review of biological mechanisms. Journal of Environmental Quality, 31, 109–120.
Lau, K. B. K., Hadibarata, T., Eliwina, E., Dewi, R., Al Sahil, A. A., & Al-Ghamdi, A. A. (2020). Reactive dyes adsorption via Citrus hystrix peel powder and Zea mays cob powder: characterization, isotherm and kinetic studies. Biointerface Research in Applied Chemistry, 10, 4803–4810.
Lee, M., & Yang, M. (2010). Rhizofiltration using sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) and bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L. var. vulgaris) to remediate uranium contaminated groundwater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 173, 589–596.
Li, J., Liu, C., Cheng, Y., Guo, S., Sun, Q., Kan, L., Chen, R., Kan, H., Bai, H., & Cao, J. (2018). Association between ambient particulate matter air pollution and ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a case-crossover study in a Chinese city. Chemosphere, 219, 724–729.
Li, Y., Zhang, J., Zhu, G., Liu, Y., Wu, B., Ng, W. J., Appan, A., & Tan, S. K. (2016). Phytoextraction, phytotransformation and rhizodegradation of ibuprofen associated with Typha angustifolia in a horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland. Water Research, 102, 294–304.
Liu, W.-S., Chen, Y.-Y., Huot, H., Liu, C., Guo, M.-N., Qiu, R.-L., Morel, J. L., & Tang, Y.-T. (2020). Phytoextraction of rare earth elements from ion-adsorption mine tailings by Phytolacca americana: effects of organic material and biochar amendment. Journal of Cleaner Production, 275, 122959.
Luengas, A., Barona, A., Hort, C., Gallastegui, G., Platel, V., & Elias, A. (2015). A review of indoor air treatment technologies. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 14, 499–522.
Ly, B.-T., Kajii, Y., Nguyen, T.-Y.-L., Shoji, K., Van, D.-A., Do, T.-N.-N., Nghiem, T.-D., & Sakamoto, Y. (2020). Characteristics of roadside volatile organic compounds in an urban area dominated by gasoline vehicles, a case study in Hanoi. Chemosphere, 254, 126749.
Ma, Y., Oliveira, R. S., Freitas, H., & Zhang, C. (2016). Biochemical and molecular mechanisms of plant-microbe-metal interactions: relevance for phytoremediation. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7, 918.
Mohsin, M., Kuittinen, S., Salam, M. M. A., Peräniemi, S., Laine, S., Pulkkinen, P., Kaipiainen, E., Vepsäläinen, J., & Pappinen, A. (2019). Chelate-assisted phytoextraction: growth and ecophysiological responses by Salix schwerinii E.L Wolf grown in artificially polluted soils. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 205, 106335.
Mølhave, L. (1991). Volatile organic compounds, indoor air quality and health. Indoor Air, 1, 357–376.
Morikawa, H., & Erkin, Ö. C. (2003). Basic processes in phytoremediation and some applications to air pollution control. Chemosphere, 52, 1553–1558.
Najeeb, U., Ahmad, W., Zia, M. H., Zaffar, M., & Zhou, W. (2017). Enhancing the lead phytostabilization in wetland plant Juncus effusus L. through somaclonal manipulation and EDTA enrichment. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 10, S3310–S3317.
Ndong Ba, A., Verdin, A., Cazier, F., Garcon, G., Thomas, J., Cabral, M., Dewaele, D., Genevray, P., Garat, A., Allorge, D., Diouf, A., Loguidice, J. M., Courcot, D., Fall, M., & Gualtieri, M. (2019). Individual exposure level following indoor and outdoor air pollution exposure in Dakar (Senegal). Environmental Pollution, 248, 397–407.
Oh, H.-R., Ho, C.-H., Kim, J., Chen, D., Lee, S., Choi, Y.-S., Chang, L.-S., & Song, C.-K. (2015). Long-range transport of air pollutants originating in China: a possible major cause of multi-day high-PM10 episodes during cold season in Seoul, Korea. Atmospheric Environment, 109, 23–30.
Othman, J., Sahani, M., Mahmud, M., & Sheikh Ahmad, M. K. (2014). Transboundary smoke haze pollution in Malaysia: inpatient health impacts and economic valuation. Environmental Pollution, 189, 194–201.
Pandey, V. C., & Bajpai, O. (2019). Chapter 1 - phytoremediation: from theory toward practice. In C. Pandey & K. Bauddh (Eds.), V (pp. 1–49). Phytomanagement of polluted sites: Elsevier.
Pettit, T., Irga, P. J., & Torpy, F. R. (2018). Towards practical indoor air phytoremediation: a review. Chemosphere, 208, 960–974.
Popek, E. (2018). Chapter 2 - environmental chemical pollutants. In E. Popek (Ed.), Sampling and analysis of environmental chemical pollutants (2nd ed., pp. 13–69). Berlin: Elsevier.
Ramos, J. L., Molina, L., & Segura, A. (2009). Removal of organic toxic chemicals in the rhizosphere and phyllosphere of plants. Microbial Biotechnology, 2, 144–146.
Ranzani, O. T., Milà, C., Sanchez, M., Bhogadi, S., Kulkarni, B., Balakrishnan, K., Sambandam, S., Sunyer, J., Marshall, J. D., Kinra, S., & Tonne, C. (2020). Personal exposure to particulate air pollution and vascular damage in peri-urban South India. Environment International, 139, 105734.
Reddy, P., Kim, K.-H., & Kim, Y.-H. (2011). A review of photocatalytic treatment for various air pollutants. Asian Journal of Atmospheric Environment, 5, 181–188.
Ren, Y., Ge, Y., Gu, B., Min, Y., Tani, A., & Chang, J. (2014). Role of management strategies and environmental factors in determining the emissions of biogenic volatile organic compounds from urban greenspaces. Environmental Science & Technology, 48, 6237–6246.
Roland, U., Holzer, F., & Kopinke, F. D. (2002). Improved oxidation of air pollutants in a non-thermal plasma. Catalysis Today, 73, 315–323.
Salim, S. d., Hadibarata, T., Elwina, E., Dewi, R., Alaraidh, I. A., Al-Ghamdi, A. A., & Alsahli, A. A. (2019). Development of activated carbon from Eichhornia Crassipes via chemical activation and its application to remove a synthetic dye. Biointerface Research in Applied Chemistry, 9, 4394–4400.
Sandermann, H. J. (1994). Higher plant metabolism of xenobiotics: the ‘green liver’ concept. Pharmacogenetics and Genomics, 4, 225–241.
Scott, P. S., Andrew, J. P., Bundy, B. A., Grimm, B. K., Hamman, M. A., Ketcherside, D. T., Li, J., Manangquil, M. Y., Nuñez, L. A., Pittman, D. L., Rivero-Zevallos, A., Uhlorn, R. & Johnston, N. A. C. (2020). Observations of volatile organic and sulfur compounds in ambient air and health risk assessment near a paper mill in rural Idaho, U. S. A. Atmospheric Pollution Research, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2020.07.014.
Sedjo, R., & Sohngen, B. (2012). Carbon sequestration in forests and soils. Annual Review of Resource Economics, 4, 127–144.
Shiraishi, F., & Ishimatsu, T. (2009). Toluene removal from indoor air using a miniaturized photocatalytic air purifier including a preceding adsorption/desorption unit. Chemical Engineering Science, 64, 2466–2472.
Singh, S. N., & Verma, A. (2007). Phytoremediation of air pollutants: a review. In S. N. Singh & R. D. Tripathi (Eds.), Environmental Bioremediation Technologies (pp. 293–314). Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Singh, V., Pandey, B., & Suthar, S. (2019). Phytotoxicity and degradation of antibiotic ofloxacin in duckweed (Spirodela polyrhiza) system. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 179, 88–95.
Sinha, R. K., Herat, S., & Tandon, P. K. (2007). Phytoremediation: role of plants in contaminated site management. In S. N. Singh & R. D. Tripathi (Eds.), Environmental Bioremediation Technologies (pp. 315–330). Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Sitaras, I. E., & Siskos, P. A. (2008). The role of primary and secondary air pollutants in atmospheric pollution: Athens urban area as a case study. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 6, 59–69.
Sun, T., Wu, H., Wang, X., Ji, C., Shan, X., & Li, F. (2019). Evaluation on the biomagnification or biodilution of trace metals in global marine food webs by meta-analysis. Environmental Pollution, 264, 113856.
Tapia, Y., Bustos, P., Salazar, O., Casanova, M., Castillo, B., Acuña, E., & Masaguer, A. (2017). Phytostabilization of Cu in mine tailings using native plant Carpobrotus aequilaterus and the addition of potassium humates. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 183, 102–113.
Wang, X., Hart, J., Liu, Q., Wu, S., Nan, H., & Laden, F. (2020). Association of particulate matter air pollution with leukocyte mitochondrial DNA copy number. Environment International, 141, 105761.
Weber, F., Kowarik, I., & Säumel, I. (2014). Herbaceous plants as filters: Immobilization of particulates along urban street corridors. Environmental Pollution, 186, 234–240.
Wei, X., Lyu, S., Yu, Y., Wang, Z., Liu, H., Pan, D., & Chen, J. (2017). Phylloremediation of air pollutants: exploiting the potential of plant leaves and leaf-associated microbes. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8, 1318.
Weyens, N., Thijs, S., Popek, R., Witters, N., Przybysz, A., Espenshade, J., Gawronska, H., Vangronsveld, J., & Gawronski, S. W. (2015). The role of plant–microbe interactions and their exploitation for phytoremediation of air pollutants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16, 25576–25604.
Weyens, N., van der Lelie, D., Taghavi, S., & Vangronsveld, J. (2009). Phytoremediation: plant–endophyte partnerships take the challenge. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 20, 248–254.
Wood, D., Shaw, S., Cawte, T., Shanen, E., & Van Heyst, B. (2019). An overview of photocatalyst immobilization methods for air pollution remediation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 391, 123490.
Zeng, Y., Xie, R., Cao, J., Chen, Z., Fan, Q., Liu, B., Lian, X., & Huang, H. (2020). Simultaneous removal of multiple indoor-air pollutants using a combined process of electrostatic precipitation and catalytic decomposition. Chemical Engineering Journal, 388, 124219.
Zhang, P., & Zhou, X. (2020). Health and economic impacts of particulate matter pollution on hospital admissions for mental disorders in Chengdu, Southwestern China. Science of the Total Environment, 733, 139114.
Zhang, Y., Mo, J., Li, Y., Sundell, J., Wargocki, P., Zhang, J., Little, J., Corsi, R., Deng, Q., Leung, M. K. H., Fang, L., & Chen, W. (2011). Can commonly-used fan-driven air cleaning technologies improve indoor air quality? A literature review. Atmospheric Environment, 45, 4329–4343.
Zheng, H., Kong, S., Xing, X., Mao, Y., Hu, T., Ding, Y., Li, G., Liu, D., Li, S., & Qi, S. (2018). Monitoring of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from an oil and gas station in northwest China for 1 year. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 18, 4567–4595.
Funding
This project was partially supported by Nagao Environmental Foundation, Japan (2018) Cycle 2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, B.X.Y., Hadibarata, T. & Yuniarto, A. Phytoremediation Mechanisms in Air Pollution Control: a Review. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 437 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04813-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04813-6