Abstract
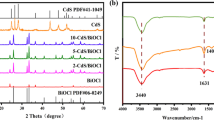
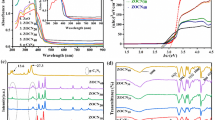
Photocatalytic reduction is a promising approach to detoxifying carcinogenic Cr(VI) in water. Herein, CdS-sensitized Cs3PW12O40 composites were fabricated by electrostatic self-assembly followed by hydrothermal post-treatment strategy. The composite with 28.6 wt% CdS loading (CdS/CsPW) was characterized by XRD, FT-IR, SEM/TEM, EDX, UV-vis DRS, XPS, potentiometric titration, and N2 adsorption. The catalytic activity was evaluated by reducing Cr(VI) in the presence of EDTA under UV and visible light irradiation. The results revealed that CdS/CsPW had good photocatalytic reduction performance for Cr(VI) degradation under both UV and visible light illumination. After four-time repetitive use, ~ 93% of catalytic activity still remained. The photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI) under visible light irradiation followed pseudo-first-order kinetics; the decreasing solution pH and initial Cr(VI) concentration, and increasing catalyst dosage and EDTA concentration were beneficial to Cr(VI) photoreduction. XPS analyses further indicated that the Cr(VI) adsorbed on surface of the catalyst was also reduced to Cr(III), and CdS and Cs3PW12O40 existed strong interaction. Meanwhile, the photoelectrons in CdS could migrate to Cs3PW12O40. Further, PL results verified CdS/CsPW heterostructure effectively suppressed the photogenerated electron-hole recombination. Based on experimental results, the mechanisms for Cr(VI) photoreduction by the prepared catalyst were proposed. This work may provide an attractive avenue to construct the efficient photocatalyst using polyoxometalates for environmental remediation.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah, H., Kuo, D., & Chen, Y. (2016). High-efficient n-type TiO2/p-type Cu2O nanodiode photocatalyst to detoxify hexavalent chromium under visible light irradiation. Journal of Materials Science, 51, 8209–8223.
Ahmad, A., Ghazi, Z. A., Saeed, M., Ilyas, M., Ahmad, R., Muqsit, K. A., & Iqbal, A. (2017). A comparative study of the removal of Cr(VI) from synthetic solution using natural biosorbents. New Journal of Chemistry, 41, 10799–10807.
Chakrabarti, S., Chaudhuri, B., Bhattacharjee, S., Ray, A. K., & Dutta, B. K. (2009). Photo-reduction of hexavalent chromium in aqueous solution in the presence of zinc oxide as semiconductor catalyst. Chemical Engineering Journal, 153, 86–93.
Chava, R. K., Do, J. Y., & Kang, M. (2018). Smart hybridization of Au coupled CdS nanorods with few layered MoS2 nanosheets for high performance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 6, 6445–6457.
Chen, S., & Kimura, K. (1999). A new strategy for the synthesis of semiconductor-metal hybrid nanocomposites: electrostatic self-assembly of nanoparticles. Chemistry Letters, 233–234.
Chen, D. W., & Ray, A. K. (2001). Removal of toxic metal ions from wastewater by semiconductor photocatalysis. Chemical Engineering Science, 56, 1561–1570.
Chen, C., Wang, Q., Lei, P., Song, W., Ma, W., & Zhao, J. (2006). Photodegradation of dye pollutants catalyzed by porous K3PW12O40 under visible irradiation. Environmental Science & Technology, 40, 3965–3970.
Chenthamarakshan, C. R., & Rajeshwar, K. (2000). Photocatalytic reduction of divalent zinc and cadmium ions in aqueous TiO2 suspensions: an interfacial induced adsorption–reduction pathway mediated by formate ions. Electrochemistry Communications, 2, 527–530.
Dolbecq, A., Mialane, P., Keita, B., & Nadjo, L. (2012). Polyoxometalate-based materials for efficient solar and visible light harvesting: application to the photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 22, 24509–24521.
Eary, L. E., & Rai, D. (1988). Chromate removal from aqueous wastes by reduction with ferrous ion. Environmental Science & Technology, 22, 972–977.
Feng, W., Zhang, L., Fang, J., Lu, S., Wu, S., Chen, Y., et al. (2017). Improved photodegradation efficiency of 2,4-DCP through a combined Q3Fe(III)-decorated porous g-C3N4/H2O2 system. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 228(9), 373.
Friesen, D. A., Headley, J. V., & Langford, C. H. (1999). The photooxidative degradation of N-methylpyrrolidinone in the presence of Cs3PW12O40 and TiO2 colloid photocatalysts. Environmental Science & Technology, 33, 3193–3198.
Gardea-Torresdey, J. L., Tiemann, K. J., Armendariz, V., Bess-Oberto, L., Chianelli, R. R., Rios, J., Parsons, J. G., & Gamez, G. (2000). Characterization of Cr(VI) binding and reduction to Cr(III) by the agricultural byproducts of avena monida (Oat) biomass. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 80, 175–188.
Gkika, E., Troupis, A., Hiskia, A., & Papaconstantinou, E. (2006). Photocatalytic reduction of chromium and oxidation of organics by polyoxometalates. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 62, 28–34.
Gupta, S., & Babu, B. V. (2009). Removal of toxic metal Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using sawdust as adsorbent: equilibrium, kinetics and regeneration studies. Chemical Engineering Journal, 150, 352–365.
Haber, J., Matachowski, L., Mucha, D., Stoch, J., & Sarv, P. (2005). New evidence on the structure of potassium salts of 12-tungstophosphoric acid, KxH3-xPW12O40. Inorganic Chemistry, 44, 6695–6703.
Han, S. H., Liu, H. M., Sun, C. C., Jin, P. J., & Chen, Y. (2018). Photocatalytic performance of AgCl@Ag core–shell nanocubes for the hexavalent chromium reduction. Journal of Materials Science, 53, 12030–12039.
Henningsson, A., Rensmo, H., Sandell, A., Södergren, S., & Siegbahn, H. (2004). Insertion of H+, Li+, Na+ and K+ into thin films prepared from silicotungstic acid–a photoelectron spectroscopy study. Thin Solid Films, 461, 237–242.
Hu, X., Ji, H., Chang, F., & Luo, Y. (2014). Simultaneous photocatalytic Cr(VI) reduction and 2,4,6-TCP oxidation over g-C3N4 under visible light irradiation. Catalysis Today, 224, 34–40.
Hug, S. J., Laubscher, H., & James, B. R. (1997). Iron(III) catalyzed photochemical reduction of chromium (VI) by oxalate and citrate in aqueous solutions. Environmental Science & Technology, 31, 160–170.
Jo, W., & Selvam, N. C. S. (2017). Z-scheme CdS/g-C3N4 composites with RGO as an electron mediator for efficient photocatalytic H2 production and pollutant degradation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 317, 913–924.
Kantar, C., Ari, C., & Keskin, S. (2015). Comparison of different chelating agents to enhance reductive Cr(VI) removal by pyrite treatment procedure. Water Research, 76, 66–75.
Ke, T. L., Guo, H. G., Zhang, Y. L., & Liu, Y. (2017). Photoreduction of Cr(VI) in water using BiVO4-Fe3O4 nano-photocatalyst under visible light irradiation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 28239–28247.
Kim, S., Yeo, J., & Choi, W. (2008). Simultaneous conversion of dye and hexavalent chromium in visible light-illuminated aqueous solution of polyoxometalate as an electron transfer catalyst. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 84, 148–155.
Ku, Y., & Jung, I. (2001). Photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI) in aqueous solutions by UV irradiation with the presence of titanium dioxide. Water Research, 35, 135–142.
Lee, S. M., Cho, I. H., Chang, Y. Y., & Yang, J. K. (2007). Effects of the density of carboxyl groups in organic compounds on the photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI) in a TiO2 suspension. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part A, 42, 543–548.
Li, G., Zhang, K., Shen, H. D., Wang, C., Zhao, Q., Wang, D., Fu, F., & Liang, Y. (2019). Magnetically recyclable Fe3O4@SiO2/Bi2WO6−xF2x photocatalyst with well-designed core-shell nanostructure for the reduction of Cr(VI). Chemical Engineering Journal, 370, 1522–1533.
Li, G., Zhang, K., Shen, H., Wang, C., Zhao, Q., Wang, D., Fu, F., & Liang, Y. (2020). 2D/2D type-II Cu2ZnSnS4/Bi2WO6 heterojunctions to promote visible-light-driven photo-fenton catalytic activity. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 41, 503–513.
Lin, S. H., & Kiang, C. D. (2003). Chromic acid recovery from waste acid solution by an ion exchange process: equilibrium and column ion exchange modeling. Chemical Engineering Journal, 92, 193–199.
Liu, X., Pan, L., Lv, T., Zhu, G., Sun, Z., & Sun, C. (2011). Microwave-assisted synthesis of CdS–reduced graphene oxide composites for photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI). Chemical Communications, 47, 11984–11986.
Liu, F., Chen, X. J., Xia, Q., Tian, L., & Chen, X. B. (2015). Ultrathin tungsten oxide nanowires: oleylamine assisted nonhydrolytic growth, oxygen vacancies and good photocatalytic properties. RSC Advances, 5, 77423–77428.
Lv, J., Li, D., Dai, K., Liang, C., Jiang, D., & Lu, L. (2017). Multi-walled carbon nanotube supported CdS-EDTA nanocomposite for efficient visible light photocatalysis. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 186, 372–381.
Madden, T. H., Datye, A. K., Fulton, M., Prairie, M. R., Majumdar, A., & Stange, B. M. (1997). Oxidation of metal-EDTA complexes by TiO2 photocatalysis. Environmental Science & Technology, 31, 3475–3481.
Marinho, B. A., Cristóvão, R. O., Djellabi, R., Loureiro, J. M., Boaventura, R. A. R., & Vilar, V. J. P. (2017). Photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI) over TiO2-coated cellulose acetate monolithic structures using solar light. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 203, 18–30.
Matachowski, L., Drelinkiewicz, A., Lalik, E., Mucha, D., Gil, B., Brozek-Mucha, Z., & Olejniczak, Z. (2011). The influence of reagent used for the precipitation of Cs2HPW12O40 salt on its textural and catalytic properties. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 144, 46–56.
Meichtry, J. M., Christophe, C. J., Custo, G., & Litter, M. I. (2014). TiO2-photocatalytic transformation of Cr(VI) in the presence of EDTA: comparison of different commercial photocatalysts and studies by time resolved microwave conductivity. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 144, 189–195.
Nasrallah, N., Kebir, M., & Koudri, Z. (2011). Photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI) on the novel hetero-system CuFe2O4/CdS. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 185, 1398–1404.
Newman, A. D., Brown, D. R., Siril, P., Lee, A. F., & Wilson, K. (2006). Structural studies of high dispersion H3PW12O40/SiO2 solid acid catalysts. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 8, 2893–2902.
Okuhara, T., Watanabe, H., Nishimura, T., Inumaru, K., & Misono, M. (2000). Microstructure of cesium hydrogen salts of 12-tungstophosphoric acid relevant to novel acid catalysis. Chemistry Materials, 12, 2230–2238.
Pérez-Maqueda, L. A., & Matijević, E. (1998). Preparation of uniform colloidal particles of salts of tungstophosphoric acid. Chemistry Materials, 10, 1430–1435.
Sasca, V., Doca, N., Popa, A., & Jaeger, N. (2012). Kinetics of the reduction with CO and reoxidation on the 12-molybdophosphoric, 1-vanado-11-molybdophosphoric acids and their salts with NH4+, K+ and Cs+ studied by “in situ” UV-vis-DRS spectroscopy. Reaction Kinetics, Mechanisms and Catalysis, 105, 207–221.
Schwarz, J. A., Driscoll, C. T., & Bhanot, A. K. (1984). The zero point of charge of silica-alumina oxide suspensions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 97, 55–61.
Shi, H., Zhao, T., Zhang, Y., Tan, H., Shen, W., Wang, W., Li, Y., & Wang, E. (2019). Pt/POMs/TiO2 composite nanofibers with an enhanced visible-light photocatalytic performance for environmental remediation. Dalton Transactions, 48, 13353–13359.
Siemon, U., Bahnemann, D., Testa, J. J., Rodríguez, D., Litter, M. I., & Bruno, N. (2002). Heterogeneous photocatalytic reactions comparing TiO2 and Pt/TiO2. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 148, 247–255.
Sivakumar, R., Thomas, J., & Yoon, M. (2012). Polyoxometalate-based molecular/nano composites: advances in environmental remediation by photocatalysis and biomimetic approaches to solar energy conversion. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology C: Photochemistry Reviews, 13, 277–298.
Testa, J. J., Grela, M. A., & Litter, M. I. (2001). Experimental evidence in favor of an initial one-electron-transfer process in the heterogeneous photocatalytic reduction of chromium(VI) over TiO2. Langmuir, 17, 3515–3517.
Testa, J. J., Grela, M. A., & Litter, M. I. (2004). Heterogeneous photocatalytic reduction of chromium(VI) over TiO2 particles in the presence of oxalate : involvement of Cr(V) species. Environmental Science & Technology, 38, 1589–1594.
Troupis, A., Hiskia, A., & Papaconstantinou, E. (2004). Selective photocatalytic reduction-recovery of palladium using polyoxometallates. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 52, 41–48.
Venkateswaran, P., & Palanivelu, K. (2004). Solvent extraction of hexavalent chromium with tetrabutyl ammonium bromide from aqueous solution. Separation and Purification Technology, 40, 279–284.
Wang, X. L., Pehkonen, S., & Ray, A. (2004). Removal of aqueous Cr(VI) by a combination of photocatalytic reduction and coprecipitation. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 43, 1665–1672.
Wang, X., Liu, G., Chen, Z. G., Li, F., Wang, L., Lu, G. Q., & Cheng, H. M. (2009). Enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution by prolonging the lifetime of carriers in ZnO/CdS heterostructures. Chemical Communications, 23, 3452–3454.
Wang, H., Yuan, X., Wu, Y., Zeng, G., Chen, X., Leng, L., Wu, Z., Jiang, L., & Li, H. (2015). Facile synthesis of amino-functionalized titanium metal-organic frameworks and their superior visible-light photocatalytic activity for Cr(VI) reduction. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 286, 187–194.
Wang, C. C., Du, X. D., Li, J., Guo, X. X., Wang, P., & Zhang, J. (2016a). Photocatalytic Cr(VI) reduction in metal-organic frameworks: a mini-review. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 193, 198–216.
Wang, Q., Shi, X. D., Xu, J. J., Crittenden, J. C., Liu, E. Q., Zhang, Y., & Cong, Y. Q. (2016b). Highly enhanced photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI) on AgI/TiO2 under visible light irradiation: influence of calcination temperature. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 307, 213–220.
Wang, Q., Shi, X. D., Xu, J. J., Crittenden, J. C., Liu, E. Q., Ma, X. J., Zhang, Y., & Cong, Y. Q. (2016c). Facile synthesis of AgI/BiOI-Bi2O3 multi-heterojunctions with high visible light activity for Cr(VI) reduction. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 317, 8–16.
Wittbrodt, P. R., & Palmer, C. D. (1995). Reduction of Cr(VI) in the presence of excess soil fulvic acid. Environmental Science & Technology, 29, 255–263.
Xu, F., Ma, T., Shi, L., & Zhang, J. (2014). Bioreduction of Cr(VI) by bacillus sp. QH-1 isolated from soil under chromium-containing slag heap in high altitude area. Annals of Microbiology, 64, 1073–1080.
Xue, C., Zhang, T., Ding, S., Wei, J., & Yang, G. (2017). Anchoring tailored low-index faceted BiOBr nanoplates onto TiO2 nanorods to enhance the stability and visible-light-driven catalytic activity. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9, 16091–16102.
Yao, Z., Du, S., Zhang, Y., Zhu, B., Zhu, L., & John, A. E. (2015). Positively charged membrane for removing low concentration Cr(VI) in ultrafiltration process. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 8, 99–107.
Yu, J., Wang, T., & Rtimi, S. (2019). Magnetically separable TiO2/FeOx/POM accelerating the photocatalytic removal of the emerging endocrine disruptor: 2,4-dichlorophenol. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 254, 66–75.
Zhang, Y., & Park, S. J. (2019). Facile construction of MoO3@ZIF-8 core-shell nanorods for efficient photoreduction of aqueous Cr(VI). Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 240, 92–101.
Zhang, Y., & Yang, J. (2019). UV-light catalyzed reduction of Cr(VI) by graphene oxide and its significance for Cr(VI) transformation in an oxisol. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 230(5), 103.
Zhang, L., Wong, K., Chen, Z., Yu, J. C., Zhao, J., Hu, C., Chan, C., & Wong, P. (2009). AgBr-Ag-Bi2WO6 nanojunction system: a novel and efficient photocatalyst with double visible-light active components. Applied Catalysis A-General, 363, 221–229.
Zhang, Y. C., Li, J., Zhang, M., & Dionysiou, D. D. (2011). Size-tunable hydrothermal synthesis of SnS2 nanocrystals with high performance in visible light-driven photocatalytic reduction of aqueous Cr(VI). Environmental Science & Technology, 45, 9324–9331.
Zhang, Y. C., Li, J., & Xu, H. Y. (2012). One-step in situ solvothermal synthesis of SnS2/TiO2 nanocomposites with high performance in visible light-driven photocatalytic reduction of aqueous Cr(VI). Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 123–124, 18–26.
Zhao, L., Zhao, Y., Yang, B., & Teng, H. (2019). Application of carboxymethyl cellulose–stabilized sulfidated nano zerovalent iron for removal of Cr(VI) in simulated groundwater. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 230(6), 113.
Zhou, Y., Chen, G., Long, Z., & Wang, J. (2014). Recent advances in polyoxometalate-based heterogeneous catalytic materials for liquid-phase organic transformations. RSC Advances, 4, 42092–42113.
Zhou, M., Wang, S., Yang, P., Huang, C., & Wang, X. (2018). Boron carbon nitride semiconductors decorated with CdS nanoparticles for photocatalytic reduction of CO2. ACS Catalysis, 8, 4928–4936.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (No. 2017JM2035), Open Funding Project of State Key Laboratory of Eco-hydraulics in Northwest Arid Region, Xi’an University of Technology (No. 2016KFKT-3), and National Science Foundation of China (Grants 51979223).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 6913 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Y., Lu, Z., Wei, H. et al. Electrostatic Self-assembly Aided Synthesis of CdS/Cs3PW12O40 Hybrids for Photocatalytic Reduction of Cr(VI). Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 345 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04727-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04727-3