Abstract
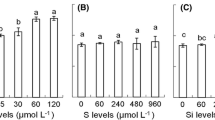
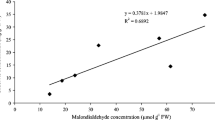
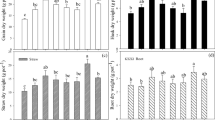
In the absence of adequate molecular oxygen in a continuously flooded soil, other oxidizing anions can potentially oxidize arsenite (As(III)) into arsenate (As(V)) and reduce the bioavailability of arsenic (As) to rice while maintaining high rice yield. We conducted a greenhouse study to evaluate the effect of two prevalent oxyanions (10 mg/L nitrate and/or 50 μg/L perchlorate) on the As uptake, speciation, and accumulation in a hybrid rice (XL753) at the heading and maturity stages. The presence of nitrate and/or perchlorate at the used concentrations increased the rice grain yield by 35–93% to16.6–23.8 g/pot while lowering the total As in rice grains by 34–45% to 0.81–0.97 mg/kg dry weight. Perchlorate alone led to the greatest decrease in total As. Organic As was the predominant species in rice grains, with dimethylarsinic acid (DMA) accounting for 66–76% of total As in all treatments. In contrast, inorganic As was the dominant As form in rice straws and roots, with As(V) accounting for 62.4–91.4% of total As in all treatments. The translocation and accumulation of different As species in rice tissues varied at different growth stages in the presence of two tested oxyanions, as indicated by the ratios of inorganic vs organic As and inorganic As(III) vs As(V). Overall, the presence of oxyanions in irrigation water at the tested concentrations significantly decreased the total As accumulation in rice grains, while enhancing the rice yield.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blake, G. R., & Hartge, K. H. (1986). Bulk density. In A. Klute (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis. Part 1. 2nd ed. Agron. Monogr. 9 (pp. 363–375). Madison: ASA and SSSA.
Carey, A. M., Scheckel, K. G., Lombi, E., Newville, M., Choi, Y., Norton, G. J., Charnock, J. M., Feldmann, J., Price, A. H., & Meharg, A. A. (2010). Grain unloading of arsenic species in rice. Plant Physiology, 152, 309–319.
Carey, A. M., Norton, G. J., Deacon, C., Scheckel, K. G., Lombi, E., et al. (2011). Phloem transport of arsenic species from flag leaf to grain during grain filling. New Phytologist, 192, 87–98.
Carlson, H. K., Kuehl, J. V., Hazra, A. B., Justice, N. B., Stoeva, M. K., Sczesnak, A., Mullan, M. R., Iavarone, A. T., Engelbrektson, A., Price, M. N., Deutschbauer, A. M., Arkin, A. P., & Coates, J. D. (2015). Mechanisms of direct inhibition of the respiratory sulfate-reduction pathway by (per) chlorate and nitrate. ISME Journal, 9(6), 1295–1305.
Carrijo, D. R., Lundy, M. E., & Linquist, B. A. (2017). Rice yields and water use under alternate wetting and drying irrigation: a metal-analysis. Field Crop Research, 203, 173–180.
Chen, G. K., Li, X. B., He, H. Z., Li, H. S., & Zhang, Z. M. (2015a). Varietal differences in the growth of rice seedling exposed to perchlorate and their antioxidative defense mechanisms. Environmental Toxicology Chemistry, 34(8), 1926–1933.
Chen, G. K., He, H. Z., Gao, H. S., Li, H. S., & Zhang, Z. M. (2015b). Differential responses of two rice varieties to perchlorate stress. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 24(1), 67–74.
Chen, Y. S., Han, Y. H., Cao, Y., Zhu, Y. G., Rathinasabapathi, B., & Ma, L. Q. (2017). Arsenic transport inrice and biological solutions to reduce arsenic risk from rice. Frontier in Plant Science., 8, 268.
Chiang, H. C., & Tsou, T. C. (2009). Arsenite enhances the benzo [a] pyrene diol epoxide (BPDE)-induced mutagenesis with no marked effect on repair of BPDE-DNA adducts in human lung cells. Toxicology In Vitro, 23(5), 897–905.
Davidson, E.A., David, M.B., Galloway, J.N., Goodale, C.L., Haeuber, R., Harrison, J.A., Howarth, R.W., Jaynes, D.B., Lowrance, R.R., Nolan, B.T., Peel, J.L., Pinder, R.W., Porter, E., Snyder, C.S., Townsend, A.R., Ward, M.H. (2012). Excess nitrogen in the U.S. environment: trends, risks, and solutions. Issues in Ecology, Report Number 15, Winter 2012.
Dixit, S., & Hering, J. G. (2003). Comparison of arsenic(V) and arsenic (III) sorption onto iron oxide minerals: implications for arsenic mobility. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(18), 4182–4189.
Dou, F., & Tarpley, L. (2014). 2012 Variety evaluation for main crop yield potential. In M. O. Way, G. N. McCauley, S. Zhou, L. T. Wilson, & B. Morace (Eds.), Texas rice production guidelines (Vol. B-6131, pp. 24–26). Texas A&M AgriLife Extension and Texas A&M AgriLife Research.
Dou, F., Wright, A. L., & Hons, F. M. (2008). Dissolved and soil organic C after long-term conventional and no-till sorghum cropping. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 39, 667–679.
Duan, Y. H., Zhang, Y. L., Ye, L. T., Fan, X. R., Xu, G. H., & Shen, Q. R. (2007). Response of rice cultivars with different nitrogen use efficiency to partial nitrate nutrition. Annals of Botany, 99, 1153–1160.
Dubrovsky, N.M., Burow, K.R., Clark, G.M., Gronberg, J.M., Hamilton, P.A., Hitt, K.J., Mueller, D.K., Munn, M.D., Nolan, B.T., Puckett, L.J., Rupert, M.G., Short, T.M., Spahr, N.E., Sprague, L.A., Wilber, W.G. (2010). Nutrients in the nation’s streams and groundwater, 1992–2004. USGS Circular 1350, United States Geological Survey.
Gilbert-Diamond, D., Cottingham, K.L., Gruber, J.F., Punshon, T., Sayarath, V., Gandolfi, A.J., Baker, E.R., Jackson, B.P., Folt, C.L., Karagas, M.R. (2011). Rice consumption contributes to arsenic exposure in US women. Proceedings of National Academy of Science of USA (PNAS), 108, 20656-20660.
Gurdak, J. J., & Qi, S. L. (2012). Vulnerability of recently recharged groundwater in principle aquifers of the United States to nitrate contamination. Environmental Science & Technology, 46(11), 6004–6012.
Harter, T., Dzurella, K., Kourakos, G., Hollander, A., Bell, A., Santos, N., Hart, Q., King, A., Quinn, J., Lampinen, G., Liptzin, D., Rosenstock, T., Zhang, M., Pettygrove, G.S., Tomich, T. (2017). Nitrogen fertilizer loading to groundwater in the Central Valley. Final report to the fertilizer research education program, Projects 11-0301 and 15-0454, California Department of Food and Agriculture and University of California Davis, 325p.
Hu, M., Li, F., Liu, C., & Wu, W. (2015). The diversity and abundance of As (III) oxidizers on root iron plaque is critical for arsenic bioavailability to rice. Scientific Reports, 5, 13611.
ITRC (Interstate Technology & Regulatory Council). (2005). Perchlorate: overview of issues, status, and remedial options. PERCHLORATE-1. Washington, D.C.: Interstate Technology & Regulatory Council, Perchlorate Team. Available on the internet at http://www.itrcweb.org. Accessed 1 Dec 2019.
Jackson, A., Anandam, S. K., Anderson, T., Lehman, T., Rainwater, K., Rajagopalan, S., Ridley, M., & Tock, R. (2005). Perchlorate occurrence in the Texas southern high plains aquifer system. Ground Water Monitoring and Remediation, 25(1), 137–149.
Jackson, W. A., Bohlke, J. K., Andraski, B. J., Fahlquist, L., Bexfield, L., Echardt, F. D., Gates, J. B., Davila, A. F., Mckay, C. P., Rao, B., Sevanthi, R., Rajagopalan, S., Estrada, N., Sturchio, N., Hatzinger, P. B., Anderson, T. A., Orris, G., Betancout, J., Stonestrom, D., Latorre, C., Li, Y., & Harvey, G. J. (2015). Global patterns and environmental controls of perchlorate and nitrate co-occurrence in arid and semi-arid environments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 164, 502–522.
Jia, Y., Huang, H., Chen, Z., & Zhu, Y. G. (2014). Arsenic uptake by rice is influenced by microbe-mediated arsenic redox changes in the rhizosphere. Environmental Science & Technology, 48(2), 1001–1007.
Khan, M. A., Stroud, I. E., Zhu, Y. G., Mcgrath, S. P., & Zhao, F. J. (2010). Arsenic bioavailability to rice is elevated in Bangladeshi paddy soils. Environmental Science & Technology, 44, 8515–8521.
Lin, Z. J., Wang, X., Wu, X., Liu, D. H., Yin, Y. L., Zhang, Y., Xiao, S., & Xing, B. S. (2018). Nitrate reduced arsenic redox transformation and transfer in flooded paddy soil-rice system. Environmental Pollution, 243, 1015–1025.
Linquist, B. A., Anders, M. M., Adviento-Borbe, M. A., Chaney, R. L., Nalley, L. L., Da Rosa, E. F., & van Kessel, C. (2015). Reducing greenhouse gas emissions, water use, and grain arsenic levels in rice systems. Global Change Biology, 21, 407–417.
Liu, W. J., Zhu, Y. G., Hu, Y., Williams, P. N., Gault, A. G., Meharg, A. A., Charnock, J. M., & Smith, F. A. (2006). Arsenic sequestration in iron plaque, its accumulation and speciation in mature rice plants (Oryza sativa L.). Environmental Science & Technology, 40, 5730–5736.
Ma, J. F., Yamaji, N., Mitani, N., Xu, X. Y., Sy, Y. H., McGrath, S. P., & Zhao, F. J. (2008). Transporters of arsenite in rice and their role in arsenic accumulation in rice grain. Proceedings of National Academy of Science of USA (PNAS), 105, 9931–9935.
Nalley, L., Linquist, B., Kovacs, K., & Anders, M. (2015). The economic viability of alternative wetting and drying irrigation in Arkansas rice production. Agronomy Journal, 107, 579–587.
Nolan, B. T., & Hitt, K. J. (2006). Vulnerability of shallow groundwater and drinking-water wells to nitrate in the United States. Environmental Science & Technology, 40(24), 7834–7840.
Norton, G. J., Douglas, A., Lahner, B., Yakubova, E., Guerinot, M. L., et al. (2014). Genome wide association mapping of grain arsenic, copper, molybdenum and zinc in rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown at four international field sites. PLoS One, 9(2), e89685.
Oremland, R. S., & Stolz, J. F. (2003). The ecology of arsenic. Science, 300(5621), 939–944.
Oremland, R. S., & Stolz, J. F. (2005). Arsenic, microbes and contaminated aquifers. Trends in Microbiology, 13(2), 45–49.
Pinson, S. R., Tarpley, L., Yan, W., Yeater, K., Lahner, B., Yakubova, E., Huang, X. Y., Zhang, M., Guerinot, M. L., & Salt, D. E. (2015). Worldwide genetic diversity for mineral element concentrations in rice grain. Crop Science, 55, 294–311.
Pushon, T., Jackson, B. P., Meharg, A. A., Warczark, T., Scheckel, K., & Guerinot, M. L. (2017). Understanding arsenic dynamics in agronomic systems to predict and prevent uptake by crop plants. Science of the Total Environment, 581-582, 209–220.
Rahman, M. A., Hasegawa, H., Rahman, M. M., Rahman, M. A., & Miah, M. A. M. (2007). Accumulation of arsenic in tissues of rice plant (Oryza sativa L.) and its distribution in fractions of rice grain. Chemosphere, 69, 942–948.
Rhoades, J. D. (1982). Soluble salts. In A. L. Page et al. (Eds.), Methods of soil analysis: part 2. Agronomy Monogr. 9 (2nd ed., pp. 167–178). Madison: ASA and SSSA.
Ringuet, S., Sassano, L., & Johnson, Z. I. (2011). A suite of microplate reader-based colorimetric methods to quantify ammonium, nitrate, orthophosphate and silicate concentrations for aquatic nutrient monitoring. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 13, 370–376.
Sanchez, C. A., Krieger, R. I., Khandaker, R. N., Moore, R. C., Holts, K. C., & Neidel, L. L. (2005). Accumulation and perchlorate exposure potential of lettuce produced in the lower Colorado River region. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 53(13), 5479–5486.
Schofield, R. K., & Taylor, A. W. (1955). The measurement of soil pH. Soil Science Society of America Proceedings., 19, 164–167.
Shi, S., Wang, T., Chen, Z., Tang, Z., Wu, Z., Salt, D. E., et al. (2016). OsHAC1;1 and OsHAC1;2 function as arsenate reductases and regulate arsenic accumulation. Plant Physiologist, 172, 1708–1719.
Shri, M., Singh, P. K., Kidwai, M., Gautum, N., Dubey, S., Verma, G., & Chakrabarty, D. (2019). Recent advances in arsenic metabolism in plants: current status, challenges and highlighted biotechnological intervention to reduce grain arsenic in rice. Metallomics, 11, 519–532.
Singh, N., Kumar, D., & Sahu, A. P. (2007). Arsenic in the environment: effects on human health and possible prevention. Journal of Environmental Biology, 28, 359–365.
Song, W. Y., Yamaki, T., Yamaji, N., Ko, D., Jung, K. H., Fujii-Kashino, M., An, G., Martinoia, E., Lee, Y., & Ma, J. F. (2014). A rice ABC transporter, OsABCC1, reduces arsenic accumulation in the grain. Proceedings of National Academy of Science of USA (PNAS), 111, 15699–15704.
Sowers, T. D., Harrington, J. M., Polizzotto, M. L., & Duckworth, O. W. (2017). Sorption of arsenic to biogenic iron (oxyhydr)oxides produced in circumneutral environments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 198, 194–207.
Su, Y., McGrath, S. P., & Zhao, F. J. (2010). Rice is more efficient in arsenite uptake and translocation than wheat and barley. Plant and Soil, 328, 27–34.
Sun, W. J., Sierra-Alvarez, R., Fernandez, N., Sanz, J. L., Amils, R., Legatzki, A., Maier, R. M., & Field, J. A. (2009a). Molecular characterization and in situ quantification of anoxic arsenite-oxidizing denitrifying enrichment cultures. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 68(1), 72–85.
Sun, W. J., Sierra-Alvarez, R., Milner, L., Oremland, R., & Field, J. A. (2009b). Arsenite and ferrous iron oxidation linked to chemolithotrophic denitrification for the immobilization of arsenic in anoxic environments. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(17), 6585–6591.
Sun, W. J., Sierra-Alvarez, R., Milner, L., & Field, J. A. (2010). Anaerobic oxidation of arsenite linked to chlorate reduction. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76(20), 6804–6811.
Suriyagoda, L. D. B., Dittert, K., & Lambers, H. (2018). Mechanism of arsenic uptake, translocation and plant resistance to accumulate arsenic in rice grains. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 253, 23–37.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (U.S. FDA). (2013). Arsenic in rice: full analytical result from rice/rice product sampling. September. U.S. FDA, Silver Spring, MD, USA.
Van Metre, P. C., Frey, J. W., Musgrove, M., Nakagaki, N., Qi, S., Mahler, B. J., Wieczorek, M. E., & Button, D. T. (2016). High nitrate concentrations in some Midwest United States streams in 2013 after the 2012 drought. Journal of Environmental Quality, 45(5), 1696–1704.
Wang, X. Q., Liu, T. X., Li, F. B., Li, B., & Liu, C. P. (2018a). Effects of simultaneous application of ferrous iron and nitrate on arsenic accumulation in rice grown in contaminated paddy soil. ACS Earth Space Chemistry, 2(2), 103–111.
Wang, X. X., Sun, W. J., Zhang, S., Sharifan, H., & Ma, X. M. (2018b). Elucidating the effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles and zinc oxide nanoparticles on arsenic uptake and speciation in rice (Oryza sativa) in a hydroponic system. Environmental Science & Technology, 52(17), 10040–10047.
Xie, Y. F., Tao, G. S., Chen, Q., & Tian, X. Y. (2014). Effects of perchlorate stress on growth and physiological characteristics of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Water, Air & Soil Pollution, 225, 2077.
Xu, X. Y., MaGrath, S. P., Meharg, A. A., & Zhao, F. J. (2008). Growing rice aerobically markedly decreases arsenic accumulation. Environmental Science & Technology, 42, 5574–5579.
Ye, W. L., Wood, B. A., Stroud, J. L., Andralojc, P. J., Raab, A., McGrath, S. P., Feldmann, J., & Zhao, F. J. (2010). Arsenic speciation in phloem and xylem exudates of castor bean. Plant Physiologist, 154, 1505–1513.
Zhang, J., Zhao, S., Xu, Y., Zhou, W., Huang, K., Tang, Z., et al. (2017). Nitrate stimulates anaerobic microbial arsenite oxidation in paddy soils. Environmental Science & Technology, 51, 4377–4386.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, X., Sun, K.Y., Dou, F. et al. Impact of Elevated Nitrate and Perchlorate in Irrigation Water on the Uptake, Speciation, and Accumulation of Arsenic in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 309 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04701-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04701-z