Abstract
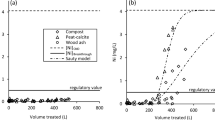
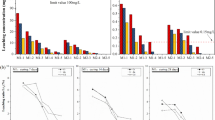
Raw and activated dolomite or wood ash were comparatively evaluated in column reactors for the simultaneous removal of Ni and Zn in synthetic contaminated neutral drainage (CND) over 119 days. Dolomite was thermally activated by charring, while wood ash was subject to alkaline fusion followed by hydrothermal treatment. Column testing was performed using CND with 51.5 mg/L Ni and 46.5 mg/L Zn, at pH 6. Testing was considered complete when metal concentrations in the final effluent reached 0.5 mg/L to meet Canadian regulations on discharge. Results showed that thermally activated wood ash was the most efficient among all tested materials as it removed 64 mg/g Ni and 61.6 mg/g Zn. Based on these results, thermally activated wood ash could be considered a promising option for Ni and Zn treatment in CND, although final pH correction of treated effluent might be necessary. At the end of the testing period, metals could be recovered by dissolution with concentrated acid and by hydrometallurgical processes from spent activated dolomite and wood ash, respectively. As spent material could be used for recovery of treated metals, sludge management issues could be alleviated.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akar, T., Kaymar, Z., Ulusoy, S., Yuvaci, D., Ozsari, G., & Akar, S. T. (2009). Enhanced biosorption of nickel (II) ions by silica-gel-immobilized waste biomass: Biosorption characteristics in batch and dynamic flow mode. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163, 1134–1141.
Bright, D. A., & Sandys, N. (2015) Beyond ML/ARD: The many faces of neutral mine drainage in the context of mine closure, Mine Closure, Vancouver, Canada, 1–3 June 2015.
Calugaru, I. L., Neculita, C. M., Genty, T., Bussière, B., & Potvin, R. (2016). Performance of thermally activated dolomite for the treatment of Ni and Zn in contaminated neutral drainage. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 310, 48–55.
Calugaru, I. L., Neculita, C. M., Genty, T., Bussière, B., & Potvin, R. (2017). Removal of Ni and Zn in contaminated neutral drainage by raw and modified wood ash. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A: Toxic/Hazardous Substances and Environmental Engineering, 52, 117–126.
Calugaru, I. L., Neculita, C. M., Genty, T., & Zagury, G. J. (2018). Metals and metalloids treatment in contaminated neutral effluents using modified materials. Journal of Environmental Management, 212, 142–159.
Frau, F., Medas, D., Da Pelo, S., Wanty, R. B., & Cidu, R. (2015). Environmental effects on the aquatic system and metal discharge to the Mediterranean Sea from a near-neutral zinc-ferrous sulfate mine drainage. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 226, 55.
Genç-Fuhrman, H., Wu, P., Zhou, Y., & Ledin, A. (2008). Removal of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni and Zn from polluted water using an iron based sorbent. Desalination, 226, 357–370.
Genty, T., Bussière, B., Potvin, R., Benzaazoua, M., & Zagury, G. J. (2012). Dissolution of calcitic marble and dolomitic rock in high iron concentrated acid mine drainage: Application to anoxic limestone drains. Environmental Earth Sciences, 66, 2387–2401.
Heikkinen, P. M., Räisänen, M. L., & Johnson, R. H. (2009). Geochemical characterization of seepage and drainage water quality from two sulfide mine tailings impoundments: Acid mine drainage versus neutral mine drainage. Mine Water and the Environment, 28, 30–49.
Hengen, T. J., Squillace, M. K., O’Sullivan, A. D., & Stone, J. J. (2014). Life cycle assessment analysis of active and passive acid mine drainage treatment technologies. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 86, 160–167.
Ivanets, A. I., Kitikova, N. V., Shashkova, I. L., Oleksiienko, O. V., Levchuk, I., & Sillanpää, M. (2014a). Removal of Zn2+, Fe2+, Cu2+, Pb2+, Cd2+, Ni2+ and Co2+ ions from aqueous solutions using modified phosphate dolomite. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2, 981–987.
Ivanets, A. I., Shashkova, I. L., Kitikova, N. V., & Drozdova, N. V. (2014b). Extraction of Co(II) ions from aqueous solutions with thermally activated dolomite. Russian Journal of Applied Chemistry, 87, 270–275.
Ivanets, A., Kitikova, N., Shashkova, I., Matrunchik, Y., & Kul’bitskaya, L. (2016a). Non-acidic synthesis of phosphatized dolomite and its sorption behaviour towards Pb2+, Zn2+, Cu2+, Cd2+, Ni2+, Sr2+ and Co2+ ions in multicomponent aqueous solutions. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 6, 152–164.
Ivanets, A. I., Kitikova, N. V., Shashkova, I. L., Oleksiienko, O. V., Levchuk, I., & Sillanpää, M. (2016b). Using of phosphatized dolomite for treatment of real mine water from metal ions. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 9, 246–253.
Ivanets, A. I., Shashkova, I. L., Kitikova, N. V., & Morozov, Y. (2016c). The kinetic studies of the cobalt ion removal from aqueous solutions by dolomite-bases sorbent. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 13, 2561–2568.
Ivanets, A. I., Srivastava, V., Kitikova, N. V., Shashkova, I. L., & Sillanpää, M. (2017). Non-apatite Ca-Mg phosphate sorbent for removal of toxic metal ions from aqueous solutions. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 5, 2010–2017.
Jones, A., Rogerson, M., Greenway, G., Potter, H. A. B., & Mayes, W. M. (2013). Mine water geochemistry and metal flux in a major historic Pb-Zn-F orefield, the Yorkshire Pennines, UK. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 7570–7581.
Kalavathy, H., Karthik, B., & Miranda, L. R. (2010). Removal and recovery of Ni and Zn from aqueous solution using activated carbon from Hevea brasiliensis: Batch and column studies. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 78, 291–302.
Kučerová, G., Majzlan, J., Lalinská-Voleková, B., Radková, A., Bačík, P., Michňová, J., Šottník, P., Jurkovič, L., Klimko, T., Steininger, R., & Göttlicher, J. (2014). Mineralogy of neutral mine drainage in the tailings of siderite-Cu ores in Eastern Slovakia. The Canadian Mineralogist, 52, 779–798.
Kumar, R., Bhatia, D., Singh, R., Rani, S., & Bishnoi, N. R. (2011). Sorption of heavy metals from electroplating effluent using immobilized biomass Trichoderma viride in a continuous packed-bed column. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 65, 1133–1139.
Lee, J. Y., Choi, J. C., Yi, M. J., Kim, J. W., Cheon, J. Y., Choi, Y. K., Choi, M. J., & Lee, K. K. (2005). Potential groundwater contamination with toxic metals in and around an abandoned Zn mine, Korea. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 165, 167–185.
Lindsay, M. B. J., Condon, P. D., Jambor, J. L., Lear, K. G., Blowes, D. W., & Ptacek, C. J. (2009). Mineralogical, geochemical, and microbial investigation of a sulfide-rich tailings deposit characterized by neutral drainage. Applied Geochemistry, 24, 2212–2221.
Lindsay, M. B. J., Moncur, M. C., Bain, J. G., Jambor, J. L., Ptacek, C. J., & Blowes, D. W. (2015). Geochemical and mineralogical aspects of sulfide mine tailings. Applied Geochemistry, 57, 157–177.
Malkoc, E., & Nuhoglu, Y. (2006). Removal of Ni(II) ions from aqueous solutions using waste of tea factory: Adsorption on a fixed-bed column. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 135, 328–336.
Mayes, W. M., Potter, H. A. B., & Jarvis, A. P. (2009). Novel approach to zinc removal from circum-neutral mine waters using pelletised recovered hydrous ferric oxide. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 162, 512–520.
Ministry of Justice Government of Canada (2018) Metal and Diamond Mining Effluent Regulations (MMER). http://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/regulations/SOR-2002-222/ (accessed 28 Feb 2019).
Nordstrom, K., Blowes, D. W., & Ptacek, C. J. (2015). Hydrogeochemistry and microbiology of mine drainage: An update. Applied Geochemistry, 57, 3–16.
Nuttall, C. A., & Younger, P. L. (2000). Zinc removal from hard, circum-neutral mine waters using a novel closed-bed limestone reactor. Water Research, 34, 1262–1268.
Pansini, M., Colella, C., Caputo, D., de’Gennaro, M., & Langella, A. (1996). Evaluation of phillipsite as cation exchanger in lead removal from water. Microporous Materials, 5, 357–364.
Rakotonimaro, T., Neculita, C. M., Bussiere, B., Benzaazoua, M., & Zagury, G. J. (2017). Recovery and reuse of sludge from active and passive treatment of mine drainage-impacted waters: A review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 73–91.
Rat’ko, A. I., Ivanets, A. I., Kulak, A. I., Morozov, E. A., & Sakhar, I. O. (2011). Thermal decomposition of natural dolomite. Inorganic Materials, 47, 1372–1377.
Sapsford, D. J. (2013). New perspectives on the passive treatment of ferruginous circumneutral mine waters in the UK. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 7827–7836.
Shah, B. A., Mistry, C. B., & Shah, A. V. (2013). Sequestration of Cu(II) and Ni(II) from wastewater by synthesized zeolitic materials: Equilibrium, kinetic and column dynamics. Chemical Engineering Journal, 220, 172–184.
Shokes, T. E., & Möller, G. (1999). Removal of dissolved heavy metals from acid rock drainage using iron metal. Environmental Science and Technology, 33, 282–287.
Skousen, J., Zipper, C. E., Rose, A., Ziemkiewicz, P. F., Nairn, R., McDonald, L. M., & Kleinmann, R. L. (2017). Review of passive systems for acid mine drainage treatment. Mine Water and the Environment, 36, 133–153.
Song, H., Yim, G., Ji, S., Neculita, C. M., & Hwang, T. (2012). Pilot-scale passive bioreactors for the treatment of acid mine drainage: Efficiency of mushroom compost vs. mixed substrates for metal removal. Journal of Environmental Management, 111, 150–158.
Stantec Consulting Ltd. (2004). Review of water quality issues in neutral pH drainage: examples and emerging priorities for the mining industry in Canada, Report prepared for the MEND initiative.
Takeno, N. (2005). Atlas of Eh-pH diagrams, Intercomparison of thermodynamic databases. National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology Research Center for Deep Geological Environments Geological Survey of Japan.
Vijayaraghavan, K., Jegan, J., Palanivelu, K., & Velan, M. (2004). Removal of nickel (II) ions from aqueous solution using crab shell particles in a packed bed up-flow column. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 113, 223–230.
Visual MINTEQ version 3.1. (2013). http://vminteq.lwr.kth.se/ (accessed 28 February 2019).
Walker, G. M., Hanna, J.-A., & Allen, S. J. (2005). Treatment of hazardous shipyard wastewater using dolomitic sorbents. Water Research, 39, 2422–2428.
Wang, C., Li, J., Sun, X., Wang, L., & Sun, X. (2009). Evaluation of zeolites synthetized from fly ash as potential adsorbents for wastewater containing heavy metals. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 21, 127–136.
Warrender, R., Pearce, N. J. G., Perkins, W. T., Florence, K. M., Brown, A. R., Sapsford, D. J., Bowell, R. J., & Dey, M. (2011). Field trials of low-cost reactive media for the passive treatment of circum-neutral metal mine drainage in Mid-Wales, UK. Mine Water and the Environment, 30, 82–89.
Westholm, L. J., Repo, E., & Sillanpää, M. (2014). Filter materials for metal removal from mine drainage – A review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 9109–9128.
Xue, Y., Gao, B., Yao, Y., Inyang, M., Zhang, M., & Zimmerman, A. R. (2012). Hydrogen peroxide modification enhances the ability of biochar (hydrochar) produced from hydrothermal carbonization of peanut hull to remove aqueous heavy metals: Batch and column test. Chemical Engineering Journal, 200-202, 673–680.
Yim, G., Ji, S., Cheong, Y., Neculita, C. M., & Song, H. (2015). The influence of the amount of organic substrate on the performance of pilot-scale passive bioreactors for acid mine drainage treatment. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73, 4717–4727.
Funding
This research was funded by Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), Canada Research Chairs Program, the College of Abitibi-Témiscamingue, the industrial partners of CTRI, including Regénération, Iamgold Corporation, Hecla Québec, Canadian Malartic Mine, Technosub, and Organisme Bassin Versant du Témiscamingue, as well as the industrial partners of RIME UQAT-Polytechnique Montréal, including Agnico Eagle, Canadian Malartic Mine, Éléonore-Newmont Goldcorp, Iamgold Corporation, Raglan Mine-Glencore, and Rio Tinto. The funding sources had no involvement in the design of the study, in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data, in the writing of the report, and in the decision to submit the present article for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 73 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calugaru, I.L., Neculita, C.M., Genty, T. et al. Removal and Recovery of Ni and Zn from Contaminated Neutral Drainage by Thermally Activated Dolomite and Hydrothermally Activated Wood Ash. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 226 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04600-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04600-3