Abstract
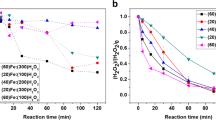
Among all female sex hormones, 17β-estradiol (E2) has been most often detected in discharge water from animal farms. The objectives of this study were to evaluate the performance of UV/heat-activated persulfate to degrade E2 and the technical feasibility to use this system for treating real wastewater. As an individual persulfate (PS) homogeneous activator, UV-activated PS removed E2 better than using low heat (40 °C) and solar irradiation to activate PS. When both UV and heat (25–65 °C) were used to activate PS, the Arrhenius equation represented well the observed rate constant, with activation energy of 118.07 kJ mol−1. Inorganic ion concentrations increased the degradation rate. These ions included Cl− (3500 mg L−1), which increased rates by 18.1%, HCO3− (250 mg L−1) by 4.6%, and NO3− (5 mg L−1) by 7.9%. However, lesser impacts on degradation kinetics were observed at higher concentrations for all constituents due to SO4·− scavenging by the formed radicals such as Cl2·−, Cl·, HCO3·, CO3·−, and NO3·. The E2 degradation observed rate constant (kobs) was highest at pH 3. Although both synthetic wastewater and real wastewater showed inhibitory effects due to UV blocking from turbidity and the existence of the –COOH and –OH functional groups that acted as radical scavengers, E2 degradation was still observed. The overall results provided proof-of-concept that UV/heat-activated PS can be applied to treat E2 in wastewater containing a high organic content and can minimize the chemical and operating costs, as solar irradiation provides the heating source.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, M., Teel, A. L., & Watts, R. J. (2013). Mechanism of persulfate activation by phenols. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(11), 5864–5871.
Andaluri, G., & Suri, R. S. (2017). Oxidative sonication of estrogen hormones in water and municipal wastewater. Research Journal of Environmental Sciences, 11, 71–81.
Angkaew, A., Sakulthaew, C., Satapanajaru, T., Poapolathep, A., & Chokejaroenrat, C. (2019). UV-activated persulfate oxidation of 17β-estradiol: Implications for discharge water remediation. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 7, 102858.
Anipsitakis, G. P., & Dionysiou, D. D. (2004). Radical generation by the interaction of transition metals with common oxidants. Environmental Science and Technology, 38(13), 3705–3712.
Anipsitakis, G. P., Dionysiou, D. D., & Gonzalez, M. A. (2006). Cobalt-mediated activation of peroxymonosulfate and sulfate radical attack on phenolic compounds. Implications of chloride ions. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 1000–1007.
Barbosa, M. O., Moreira, N. F. F., Ribeiro, A. R., Pereira, M. F. R., & Silva, A. M. T. (2016). Occurrence and removal of organic micropollutants: An overview of the watch list of EU decision 2015/495. Water Research, 94, 257–279.
Belfroid, A. C., Van der Horst, A., Vethaak, A. D., Schäfer, A. J., Rijs, G. B., Wegener, J., & Cofino, W. P. (1999). Analysis and occurrence of estrogenic hormones and their glucuronides in surface water and waste water in the Netherlands. Science of the Total Environment, 225, 101–108.
Chokejaroenrat, C., Sakulthaew, C., Angkaew, A., Satapanajaru, T., Poapolathep, A., & Chirasatienpon, T. (2019). Remediating sulfadimethoxine-contaminated aquaculture wastewater using ZVI-activated persulfate in a flow-through system. Aquacultural Engineering, 84, 99–105.
Chokejaroenrat, C., Sakulthaew, C., Satapanajaru, T., Tikhamram, T., Pho-Ong, A., & Mulseesuk, T. (2015). Treating methyl orange in a two-dimensional flow tank by in situ chemical oxidation using slow-release persulfate activated with zero-valent iron. Environmental Engineering Science, 32, 1007–1015.
Exner, M., Herrmann, H., & Zellner, R. (1992). Laser-based studies of reactions of the nitrate radical in aqueous solution. Berichte der Bunsengesellschaft für Physikalische Chemie, 96, 470–477.
Fan, Y., Ji, Y., Kong, D., Lu, J., & Zhou, Q. (2015). Kinetic and mechanistic investigations of the degradation of sulfamethazine in heat-activated persulfate oxidation process. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 300, 39–47.
Feng, Y., Lee, P.-H., Wu, D., & Shih, K. (2017). Surface-bound sulfate radical-dominated degradation of 1,4-dioxane by alumina-supported palladium (Pd/Al2O3) catalyzed peroxymonosulfate. Water Research, 120, 12–21.
Fonseca, A.P., Lima, D.L., Esteves, V. (2010). Degradation by solar radiation of estrogenic hormones monitored by UV–visible spectroscopy and capillary electrophoresis. Water Air and Soil Pollution. 215. 441-447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0489-7.
Ghauch, A., Tuqan, A. M., & Kibbi, N. (2012). Ibuprofen removal by heated persulfate in aqueous solution: A kinetics study. Chemical Engineering Journal, 197, 483–492.
Ghauch, A., Tuqan, A. M., & Kibbi, N. (2015). Naproxen abatement by thermally activated persulfate in aqueous systems. Chemical Engineering Journal, 279, 861–873.
Goslich, R., Dillert, R., & Bahnemann, D. (1997). Solar water treatment: Principles and reactors. Water Science and Technology, 35, 137–148.
Hansen, P. D., Dizer, H., Hock, B., Marx, A., Sherry, J., McMaster, M., & Blaise, C. H. (1998). Vitellogenin—a biomarker for endocrine disruptors. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 17, 448–451.
Hayon, E., Treinin, A., & Wilf, J. (1972). Electronic spectra, photochemistry, and autoxidation mechanism of the sulfite-bisulfite-pyrosulfite systems. SO2−, SO3−, SO4−, and SO5− radicals. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 94(1), 47–57. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00756a009.
Hill, D. D., Owens, W. E., & Tchoounwou, P. B. (2005). Impact of animal waste application on runoff water quality in field experimental plots. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2(2), 314–321.
Huang, G.-Y., Liang, Y.-Q., Liu, Y.-S., Shi, W.-J., Liu, S.-S., Hu, L.-X., Xie, L., & Ying, G.-G. (2019). Swine farm wastewater discharge causes masculinization of western mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis). Environment International, 123, 132–140.
Ike, I. A., Linden, K. G., Orbell, J. D., & Duke, M. (2018). Critical review of the science and sustainability of persulphate advanced oxidation processes. Chemical Engineering Journal, 338, 651–669.
Jeon, P., Park, S.-M., & Baek, K. (2017). Controlled release of iron for activation of persulfate to oxidize orange G using iron anode. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 34, 1305–1309.
Ji, Y., Dong, C., Kong, D., Lu, J., & Zhou, Q. (2015). Heat-activated persulfate oxidation of atrazine: Implications for remediation of groundwater contaminated by herbicides. Chemical Engineering Journal, 263, 45–54.
Kolodziej, E. P., & Sedlak, D. L. (2007). Rangeland grazing as a source of steroid hormones to surface waters. Environmental Science and Technology, 41(10), 3514–3520.
Kuch, H. M., & Ballschmitter, K. (2001). Determination of endocrine-disrupting phenolic compounds and estrogens in surface and drinking water by HRGC-(NCI)-MS in the picogram per liter range. Environmental Science & Technology, 35, 3201–3206.
Kushniarou, A., Garrido, I., Fenoll, J., Vela, N., Flores, P., Navarro, G., Hellín, P., & Navarro, S. (2018). Solar photocatalytic reclamation of agro-waste water polluted with twelve pesticides for agricultural reuse. Chemosphere, 214, 839–845.
Li Puma, G., Puddu, V., Tsang, H. K., Gora, A., & Toepfer, B. (2010). Photocatalytic oxidation of multicomponent mixtures of estrogens (estrone (E1), 17β-estradiol (E2), 17α-ethynylestradiol (EE2) and estriol (E3)) under UVA and UVC radiation: Photon absorption, quantum yields and rate constants independent of photon absorption. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 99(3–4), 388–397.
Li, X., Zheng, W., & Kelly, W. R. (2013). Occurrence and removal of pharmaceutical and hormone contaminants in rural wastewater treatment lagoons. Science of the Total Environment, 445-446, 22–28.
Li, Y., Liu, L.-D., Liu, L., Liu, Y., Zhang, H.-W., & Han, X. (2016). Efficient oxidation of phenol by persulfate using manganite as a catalyst. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 411, 264–271.
Liang, C., & Guo, Y. Y. (2010). Mass transfer and chemical oxidation of naphthalene particles with zerovalent iron activated persulfate. Environmental Science and Technology, 44, 8203–8208.
Liang, C., Bruell, C. J., Marley, M. C., & Sperry, K. L. (2003). Thermally activated persulfate oxidation of trichloroethylene (TCE) and 1,1,1-trichloroethane (TCA) in aqueous systems and soil slurries. Soil and Sediment Contamination, 12(2), 207–228.
Liang, C., Wang, Z.-S., & Mohanty, N. (2006). Influences of carbonate and chloride ions on persulfate oxidation of trichloroethylene at 20 °C. Science of the Total Environment, 370, 271–277.
Lin, C. C., & Wu, M. S. (2014). UV/S2O82- process for degrading polyvinyl alcohol in aqueous solutions. Chemical Engineering and Processing, 85, 209–215.
Lin, C.-C., Lee, L.-T., & Hsu, L.-J. (2014). Degradation of polyvinyl alcohol in aqueous solutions using UV-365 nm/S2O8 2− process. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 11, 831–838.
Liu, B., & Liu, X. (2003). Direct photolysis of estrogens in aqueous solutions. The Science of the Total Environment, 320(2–3), 269–274.
Lutze, H. V., Bircher, S., Rapp, I., Kerlin, N., Bakkour, R., Geisler, M., von Sonntag, C., & Schmidt, T. C. (2015). Degradation of chlorotriazine pesticides by sulfate radicals and the influence of organic matter. Environmental Science and Technology, 49, 1673–1680.
Guedes Maniero, M., Maia Bila, D., & Dezotti, M. (2008). Degradation and estrogenic activity removal of 17β-estradiol and 17α-ethinylestradiol by ozonation and O3/H2O2. Science of the Total Environment, 407, 105–115.
Olmez-Hanci, T., Arslan-Alaton, I., & Genc, B. (2013). Bisphenol A treatment by the hot persulfate process: Oxidation products and acute toxicity. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 263, 283–290.
Matzek, L. W., & Carter, K. E. (2016). Activated persulfate for organic chemical degradation: A review. Chemosphere, 151, 178–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.02.055.
Nie, M., Yang, Y., Zhang, Z., Yan, C., Wang, X., Li, H., & Dong, W. (2014). Degradation of chloramphenicol by thermally activated persulfate in aqueous solution. Chemical Engineering Journal, 246, 373–382.
Nie, M. H., Yan, C. X., Xiong, X. Y., Wen, X. M., Yang, X., Lv, Z. L., & Dong, W. B. (2018). Degradation of chloramphenicol using a combination system of simulated solar light, Fe2+ and persulfate. Chemical Engineering Journal, 348, 455–463.
Norzaee, S., Taghavi, M., Djahed, B., & Kord Mostafapour, F. (2018). Degradation of penicillin G by heat activated persulfate in aqueous solution. Journal of Environmental Management, 215, 316–323.
Oh, S.-Y., Kang, S.-G., & Chiu, P. C. (2010). Degradation of 2,4-dinitrotoluene by persulfate activated with zero-valent iron. Science of the Total Environment, 408(16), 3464–3468.
Ohko, Y., Iuchi, K., Niwa, C., Tatsuma, T., Nakashima, T., Iguchi, T., & Kubota, Y. (2002). Fujishima, (2002). A. 17b-estradiol degradation by TiO2 photocatalysis as a means of reducing estrogenic activity. Environmental Science & Technology, 36, 4175–4181.
Pal, A., Gin, K. Y.-H., Lin, A. Y.-C., & Reinhard, M. (2010). Impacts of emerging organic contaminants on freshwater resources: Review of recent occurrences, sources, fate and effects. Sci. Total Environ., 408, 6062–6069.
Racz, L., & Goel, R. (2010). Fate and removal of estrogens in municipal wastewater. Journal of environmental monitoring : JEM, 12(1), 58–70.
Raman, D. R., Williams, E. L., Layton, A. C., Burns, R. T., Easter, J. P., Daugherty, A. S., & Sayler, G. S. (2004). Estrogen content of dairy and swine wastes. Environmental Science & Technology, 38, 3567–3573.
Rodríguez-Chueca, J., García-Cañibano, C., Lepistö, R. J., Encinas, Á., Pellinen, J., & Marugán, J. (2019). Intensification of UV-C tertiary treatment: Disinfection and removal of micropollutants by sulfate radical based advanced oxidation processes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 372, 94–102.
Rose, J., Holbech, H., Lindholst, C., Norum, U., Povlsen, A., Korsgaard, B., & Bjerregaard, P. (2002). Vitellogenin induction by 17 beta-estradiol and 17 alpha-ethinylestradiol in male zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comp Biochem Phys C, 12, 531–539.
Sahoo, M. K., Sinha, B., Marbaniang, M., & Naik, D. B. (2011). Degradation and mineralization of Calcon using UV365/H2O2 technique: Influence of pH. Desalination, 280, 266–272.
Shappell, N. W., Billey, L. O., & Shipitalo, M. J. (2016). Estrogenic activity and nutrient losses in surface runoff after winter manure application to small watersheds. Science of the Total Environment, 543, 570–580.
Smith, G.A., A.D. Zaffiro, M.L. Zimmerman, D.J. Munch, (2010). Determination of hormones in drinking water by solid phase extraction (SPE) and liquid chromatography electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (LC/ESIMS/MS), EPA Method 539, 1–37. https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPURL.cgi?Dockey=P100J76V.txt Accessed 7 October 2019.
Tabata, A., Kashiwa, S., Ohnishi, Y., Ishikawa, H., Miyamoto, N., Itoh, M., & Magara, Y. (2001). (2001). Estrogenic influence of estradiol-17b, p-nonylphenol and bisphenol A on Japanese Medaka (Oryzias iatipes) at detected environmental concentrations. Water Science and Technology, 43(2), 109–116.
Tan, C., Gao, N., Deng, Y., Rong, W., Zhou, S., & Lu, N. (2013). Degradation of antipyrine by heat activated persulfate. Separation and Purification Technology, 109, 122–128.
Ternes, T. A., Meisenheimer, M., McDowell, D., Sacher, F., Brauch, H.-J., Haist-Gulde, B., Preuss, G., Wilme, U., & Zulei-Seibert, N. (2002). Removal of pharmaceuticals during drinking water treatment. Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 3855–3863.
Tsitonaki, A., Smets, B. F., & Bjerg, P. L. (2008). Effects of heat-activated persulfate oxidation on soil microorganisms. Water Research, 42, 1013–1022.
Tsitonaki, A., Petri, B., Crimi, M., MosbÆK, H., Siegrist, R. L., & Bjerg, P. L. (2010). In situ chemical oxidation of contaminated soil and groundwater using persulfate: A review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 55–91. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380802039303.
Vela, N., Fenoll, J., Garrido, I., Pérez-Lucas, G., Flores, P., Hellín, P., & Navarro, S. (2019). Reclamation of agro-wastewater polluted with pesticide residues using sunlight activated persulfate for agricultural reuse. Science of the Total Environment, 660, 923–930.
Xiao, Y., Zhang, L., Zhang, W., Lim, K.-Y., Webster, R. D., & Lim, T.-T. (2016). Comparative evaluation of iodoacids removal by UV/persulfate and UV/H 2 O 2 processes. Water Research, 102, 629–639.
Yang, Y., Pignatello, J. J., Ma, J., & Mitch, W. A. (2014). Comparison of halide impacts on the efficiency of contaminant degradation by sulfate and hydroxyl radical-based advanced oxidation processes (AOPs). Environmental Science and Technology, 48, 2344–2351.
Zhang, P., Tan, X., Liu, S., Liu, Y., Zeng, G., Ye, S., Liu, N. (2019). Catalytic degradation of estrogen by persulfate activated with iron-doped graphitic biochar: Process variables effects and matrix effects. Chemical Engineering Journal, 122141.
Zhao, L., Hou, H., Fujii, A., Hosomi, M., & Li, F. (2014). Degradation of 1,4-dioxane in water with heat- and Fe2+-activated persulfate oxidation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 7457–7465.
Zuo, Z., Cai, Z., Katsumura, Y., Chitose, N., & Muroya, Y. (1999). Reinvestigation of the acid-base equilibrium of the (bi)carbonate radical and ph dependence of its reactivity with inorganic reactants. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 55(1), 15–23.
Acknowledgments
This research supporting fund was provided by the Environmental Technology for Emerging Issue Management Research Unit from the Faculty of Environment, Kasetsart University, Bangkok, Thailand. Our appreciation is also extended to Mr. Haruechai Santiphapchai for granting access to collect discharge water from his farm located in Nakhon Pathom province, Thailand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 229 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakulthaew, C., Chokejaroenrat, C., Satapanajaru, T. et al. Removal of 17β-Estradiol Using Persulfate Synergistically Activated Using Heat and Ultraviolet Light. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 247 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04571-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04571-5