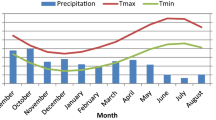
Abstract
The Equity Silver mine site, British Columbia, Canada, is known for its management and treatment of acid rock drainage. The accurate prediction of full-scale seepage flow rate in field conditions is critical for mine site management, flood control, and contaminant treatment strategies. In this study, a machine learning methodology based on artificial neural network (ANN) is proposed to correlate measured seepage flow rate with the weather monitoring data collected from the field of Equity Silver mine. Comparing with traditional numerical and water balance approaches, the ANN approach generally requires much fewer investigations on hydrogeological mechanisms or definitions of parameters and equations. The measured seepage flow rates from the Bessemer Dump and the weather monitoring data during 1998–2017 are used for training the proposed ANN. The calculated results from the trained ANN show good agreement with the measurements. In addition, the proposed ANN approach is further refined by including time tags of the monitoring data in the input layer, which enable the ANN to investigate the effects of long-term weather trends, climate change, and dynamics inside waste rock piles on seepage flow. The prediction results for the following year (2017–2018) from the refined ANN and the original ANN are compared, which shows the improvement of the refined ANN approach.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aryafar, A., Gholami, R., Rooki, R., et al. (2012). Heavy metal pollution assessment using support vector machine in the Shur River, Sarcheshmeh copper mine, Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 67, 1191–1199.
Aziz, M. L., & Ferguson, K. D. (1997). Equity silver mine - integrated case study. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Acid Rock Drainage, Vancouver, Canada, May 31-June 6.
Betrie, G. D., Tesfamariam, S., Morin, K. A., et al. (2013). Predicting copper concentrations in acid mine drainage: A comparative analysis of five machine learning techniques. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185, 4171–4182.
Bishop, C. M. (1995). Neural networks for pattern recognition. Oxford: Clarendon.
Hassoun, M. H. (1995). Fundamentals of artificial neural networks, Cambridge, England.
Isabel, D., Gelinas, P. J., Bourque, E., Nastev, M. & Precourt S., (1994). Water budget for the waste rock dump at La Mine Doyon, Quebec. MEND report 1.14.2d.
Khandelwal, M., & Singh, T. N. (2005). Prediction of mine water quality by physical parameters. Journal of Scientific and Industrial Research, 64, 564–570.
Lahmira, B., Lefebvre, R., Aubertin, M., & Bussiere, B. (2017). Effect of material variability and compacted layers on transfer processes in heterogeneous waste rock piles. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 204, 66–78.
Lin, T. Y. D. (2010). Modeling the 3D net infiltration distribution at the equity silver mine waste dump, M.A. Science Thesis, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, B.C., Canada.
Ma, L., Huang, C., Liu, Z. S., Morin, K., Aziz, M., & Meints, C. (2019). Prediction of acid rock drainage in waste rock piles part 1: water film model for geochemical reactions and application to a full-scale case study. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 220, 98–107.
Molson, J. W., Fala, O., Aubertin, M., & Bussiere, B. (2005). Numerical simulations of pyrite oxidation and acid mine drainage in unsaturated waste rock piles. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology., 78, 343–371.
Morin, K.A. (2017). Spectral analysis for identifying interactions of physical, geochemical, and biological processes creating contaminated drainages at minesites. In GeoOttawa 2017, the 70th Canadian Geotechnical Conference and the 12th Joint CGS/IAH-CNC Groundwater Conference, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, October 1–4.
Morin, K.A., & Hutt N.M., (2001). Environmental geochemistry of minesite drainage: practical theory and case studies, digital edition. MDAG Publishing (www.mdag.com), Surrey, British Columbia. ISBN: 0-9682039-1-4.
Morin, K. A., Hutt, N. M., & Aziz M. (2010). Twenty-three years of monitoring minesite-drainage chemistry, during operation and after closure: the Equity Silver minesite, British Columbia, Canada. MDAG Internet Case Study #35, www.mdag.com/case_studies/cs35.html.
Morin, K. A., Hutt, N. M., & Aziz, M., (2012). Case studies of thousands of water analyses through decades of monitoring: selected observations from three minesites in British Columbia, Canada. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Acid Rock Drainage, Ottawa, Canada, May 22-24.
O’Kane, M., Wilson, G.W., Barbour, S.L., & Swanson, D.A., (1995). Aspects on the performance of the till cover system at equity silver mines LTD. In Conference on Mining and the Environment, Sudbury, Ontario, May 28-June 1.
Saretzky, G. T. (1998). Hydrological characterization of a sulphide waste rock dump, M.S. Thesis, the University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada.
Swanson, D. A. (1995). Predictive modeling of moisture movement in engineered soil covers for acid generating mine waste. M.Sc Thesis, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada.
Swanson, D. A., Barbour, S. L., Wilson, G. W., & O’Kane, M. (2003). Soil-atmosphere modeling of an engineered soil cover for acid-generating mine waste in a humid, alpine climate. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 40, 276–292.
Weeks, B. (2006). Three dimensional flux boundary conditions for soil covers. Ph.D. Thesis, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, B.C., Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, L., Huang, C., Liu, ZS. et al. Artificial Neural Network for Prediction of Full-Scale Seepage Flow Rate at the Equity Silver Mine. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 179 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04541-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04541-x