Abstract
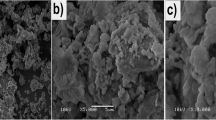
Phosphogypsum (PG), the waste byproduct resulting from wet process phosphoric acid production, is employed as a selective and effective adsorbent for total rare earth elements (REEs) from aqueous solution and leach liquor. The elaboration of PG adsorbent complemented after some physical treatments. Adsorption and elution studies carried out in experimental batches, including the effect of pH, adsorbent dose, initial REE concentration, and equilibrium time. Adsorption of REEs onto PG fitted well with Langmuir isotherm with a theoretical capacity surpassed 357 mg/g. REEs were effectively eluted from loaded PG with 2 mol L−1 HCl acid with an efficiency of 94%. PG showed an outstanding selectivity towards REEs in the presence of many cations and anions, for instance (Fe3+, UO22+, Ca2+, SO42−, NO3−). Different qualitative techniques such as EDS, SEM, and FTIR used to emphasize the adsorption of REEs onto PG. The film diffusion model was the preponderant adsorption mechanism for REEs; also, the adsorption process has a good accordance with pseudo-second-order kinetic model.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, R., & Kumar, R. (2011). Adsorption of Amaranth dye onto alumina reinforced polystyrene. Clean – Soil, Air, Water, 39(1), 74–82.
Ang, K. L., Li, D., & Nikoloski, A. N. (2017). The effectiveness of ion exchange resins in separating uranium and thorium from rare earth elements in acidic aqueous sulfate media. Part 1. Anionic and cationic resins, Hydrometallurgy, 174, 147–155.
Azizian, S., Eris, S., & Wilson, L. D. (2018). Re-evaluation of the century-old Langmuir isotherm for modeling adsorption phenomena in solution. Chemical Physics, 513, 99–104.
Barnes, P., & Bensted, J. (2001). Structure and Performance of Cements (p. 259). Spon Press.
Bouchaud, B., Balmain, J., Bonnet, G., & Pedraza, F. (2012). pH-distribution of cerium species in aqueous systems. Journal of Rare Earths, 30(6), 559–562.
Cánovas, C. R., Chapron, S., Arrachart, G., & Pellet-Rostaing, S. (2019). Leaching of rare earth elements (REEs) and impurities from phosphogypsum: A preliminary insight for further recovery of critical raw materials. Journal of Cleaner Production, 219, 225–235.
Chen, Q., Ma, X., Zhang, X., Liu, Y., & Yu, M. (2018). Extraction of rare earth ions from phosphate leach solution using emulsion liquid membrane in concentrated nitric acid medium. Journal of Rare Earths, 36(11), 1190–1197.
Coey, J. M. D. (2019). 2019, perspective and prospects for rare earth permanent magnets. Engineering, In press, Available online. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2018.11.034.
Crini, G., Peindy, H. N., Gimbert, F., & Robert, C. (2007). Removal of basic green 4 (malachite green) from aqueous solutions by adsorption using cyclodextrin-based adsorbent: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Separation and Purification Technology, 53, 97–110.
El Afifi, E. M., Hilal, M. A., Attallah, M. F., & EL-Reefy, S. A. (2009). Characterization of phosphogypsum wastes associated with phosphoric acid and fertilizers production. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 100, 407–412.
El-Didamony, H., Gado, H. S., Awwad, N. S., Fawzy, M. M., & Attallah, M. F. (2013). Treatment of phosphogypsum waste produced from phosphate ore processing. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 244-245, 596–602.
Forsyth, M., & Hinton, B. (2014). Rare earth-based corrosion inhibitors. In T. Behrsing, G. B. Deacon, & P. C. Junk (Eds.), The chemistry of rare earth metals, compounds, and corrosion inhibitors (pp. 2–37). Woodhead Publishing Series- Elsevier Ltd..
Goodenough, K. M., Wall, F., & Merriman, D. (2018). The rare earth elements: Demand, Global Resources, and Challenges for Resourcing Future Generations. Natural Resourses Research, 27, 201.
Gupta, S. S., & Bhattacharyya, K. G. (2011). Kinetics of adsorption of metal ions on inorganic materials: A review. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 162, 39–58.
Gupta, N. K., Gupta, A., Ramteke, P., Sahoo, H., & Sengupta, A. (2019). Biosorption-a green method for the preconcentration of rare earth elements (REEs) from waste solutions: A review. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 274, 148–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.10.134
Hagag, M.SA., 2019, Comparative study of fabricated composites based on phosphogypsum and Al-hydroxide for uranium separation from aqueous and waste solutions, https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2019.1670826.
Hentati, O., Abrantes, N., Caetano, A. L., Bouguerra, S., Gonçalves, F., Römbke, J., & Pereiraef, R. (2015). Phosphogypsum as a soil fertilizer: Ecotoxicity of amended soil and elutriates to bacteria, invertebrates, algae and plants. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 294, 80–89.
Hiskey, J. B., & Copp, R. G. (2018). Solvent extraction of yttrium and rare earth elements from copper pregnant leach solutions using Primene JM-T. Minerals Engineering, 125, 265–270.
Hunter, A., 1989, Use of Phosphogypsum fortified with other selected essential elements as a soil amendment on low Cation exchange soils. Final report, FIPR publication no. 01-034-081.
Idris, S., Alotaibi, K. M., Peshkur, T. A., Anderson, P., Morris, M., & Gibson, L. T. (2013). Adsorption kinetics: Effect of adsorbent pore size distribution on the rate of Cr(VI) uptake. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 165, 99–105.
Islam, G. M. S., Chowdhury, F. H., Raihan, M. T., Amit, S. K. S., & Islam, M. R. (2017). Effect of Phosphogypsum on the properties of Portland cement. Procedia Engineering, 171, 744–751.
Jebali, R., Triki, M., Alomair, N.A., Kochkar, H., 2019, From adsorption of rare earth elements on TiO2 nanotubes to preconcentration column application microchemical journal, 149, 104.
Kandila, A. T., Cheira, M. F., Gado, H. S., Soliman, M. H., & Akl, M. H. (2017). Ammonium sulfate preparation from phosphogypsum waste. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences, 10(1), 24–33.
Karge, H., Geidel, E., & Weitkamp, J. (2004). Mol. Sieves science and technology-characterization I. Vibrational Spectroscopy, 72.
Li, L., Lu, W., Ding, D., Dai, Z., Cao, C., Liu, L., & Chen, T. (2019). Adsorption properties of pyrene-functionalized nano-Fe3O4 mesoporous materials for uranium. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 270, 666–673.
Ma, L., Du, Y., Niu, X., Zheng, S., & Zhang, W. (2012). Thermal and kinetic analysis of the process of thermochemical decomposition of Phosphogypsum with CO and additives. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 51, 6680–6685.
Manjit, S. (2007). Treating waste phosphogypsum for cement and plaster manufacture. Cement and Concrete Research, 32(7), 1033–1038.
Marczenko, Z. (1976). spectrophotometric determination of elements. Harwood, New York: John Wiley and Sons. 1976
Mosai, A. K., Chimuka, L., Cukrowska, E. M., Kotzé, I. A., & Tutu, H. (2019). The recovery of rare earth elements (REEs) from aqueous solutions using natural zeolite and Bentonite. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 230, 188.
Newbury, D. E., & Ritchie, N. W. M. (2013). Is scanning Electron microscopy/energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (SEM/EDS) quantitative? Scanning, 35, 141–168. https://doi.org/10.1002/sca.21041
Nosov, V. N., Frolova, N. G., & Kamyshov, V. F. (1976). IR spectra of calcium sulfate semihydrates. Journal of Applied Spectroscopy, 24, 509.
Pacheco-Torgal, F., Jalali, S., & Fucic, A. (2012). Toxicity of building materials (p. 221). Woodhead Publishing Limited.
Pacheco-Torgal, F., Shi, C., & Sanchez, A. P. (2018). Carbon dioxide sequestration in Cementitious construction materials (p. 199). Elsevier.
Qi, D. (2018). Hydrometallurgy of Rare Earths: Extraction and Separation (p. 701). Elsevier.
Ramasamy, D. L., Puhakka, V., Doshi, B., Iftekhar, S., & Sillanpää, M. (2019). Fabrication of carbon nanotubes reinforced silica composites with improvedrare earth elements adsorption performance. Chemical Engineering Journal, 365, 291–304.
Rychkov, V. N., Kirillov, E. V., Kirillov, S. V., Semenishchev, V. S., Bunkov, G. M., Botalov, M. S., Smyshlyaev, D. V., & Malyshev, A. S. (2018). Recovery of rare earth elements from phosphogypsum. Journal of Cleaner Production, 196, 674–681.
Singh, B. P., Gupta V. K., and Passari, A. K. (2018). New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering Actinobacteria: Diversity and Biotechnological Applications,Chapter 18- Ashok Bankar and Geetha Nagaraja1, Elsevier B.V. Recent Trends in Biosorption of Heavy, Metals by Actinobacteria, Chapter 18, pp 265.
Siyal, A. A., Shamsuddin, M. R., Khan, M. I., Rabat, N. K., Zulfiqar, M., Man, Z., Siame, J., & Azizli, K. A. (2018). A review on geopolymers as emerging materials for the adsorption of heavy metals and dyes. Journal of Environmental Management, 224, 327.
Smith, Y. R., Bhattacharyya, D., Willhard, T., & Mano Misra, M. (2016). Adsorption of aqueous rare earth elements using carbon black derived from recycled tires. Chemical Engineering Journal, 296, 102–111.
Speight, J. G. (2017). Environmental Inorganic Chemistry for Engineers , Elsevier Inc., pp 149.
Szpadt, R., & Augustyn, Z. (1991). Environmental Pollution in the Vicinity of a Waste-Gypsum Landfill. In L. Pawlowski, W. J. Lacy, & J. J. Dlugosz (Eds.), Chemistry for the Protection of the Environment. Environmental Science Research (Vol. 42, pp. 387–399). Springer.
Tanabe, S. (2015). Glass and Rare-Earth Elements: A Personal Perspective. International Journal of Applied Glass Science, 6(4), 305–328.
Ul-Hamid, A. (2018). A Beginners' guide to scanning electron microscopy (pp. 4–6). Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Vijayakumar, G., Dharmendirakumar, M., Renganathan, S., Sivanesan, S., Baskar, G., & Elango, P. (2009). Removal of Congo red from aqueous solutions by perlite. CLEAN - Soil Air Water, 37(4–5), 355–364.
Wu, S., Zhao, L., Wang, L., Huang, X., Zhang, Y., Feng, Z., & Cui, D. (2019). Simultaneous Recovery of Rare Earth Elements and Phosphorus from Phosphate rock. Phosphoric Acid Leaching and Selective Precipitation: Towards Green Process, 37(6), 652–658.
Xu, X., Jiang, X., Jiao, F., Chen, X., & Yu, J. (2018). Tunable assembly of porous three-dimensional graphene oxide-corn zein composites with strong mechanical properties for adsorption of rare earth elements. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 85, 106–114.
Yaoguang, Y. U., Chen, G., Zhou, Y., & Han, Z. (2015). Recent advances in rare-earth elements modification of inorganic semiconductor-based photocatalysts for efficient solar energy conversion: A review. Journal of Rare Earths, 33(5), 453–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0721(14)60440-3.
Youssef, W. M., Hagag, M. S., & Ali, A. H. (2018). Synthesis, characterization and application of composite derived from rice husk ash with aluminium oxide for sorption of uranium. Adsorption Science and Technology, 36(5–6), 1274–1293. https://doi.org/10.1177/026361741876892.
Youssef, L., Morci, A., & Hagag, M. S. (2019). Uranium ions adsorption from acid leach liquor using acid cured phosphate rock: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Separation Science and Technology.
Yu, Z., Meng, X., Zheng, Z., Lu, Chen, H., Huang, C., Sun, H., Liang, K., Ma, Z., Qia, Y., & Zhang, T. (2019). Room temperature multiferroic properties of rare-earth-substituted Aurivillius phase Bi5Ti3Fe0.7Co0.3O15. Materials Research Bulletin, 115, 235–241.
Zhao, F., Repo, E., Meng, Y., Wang, X., Yin, D., & Sillanpää, M. (2016). An EDTA-b-cyclodextrin material for the adsorption of rare earth elements and its application in preconcentration of rare earth elements in seawater. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 465, 215–224.
Zhou, J., Yi, Y., Shu, Z., Wang, Y., Yakubu, Y., Zhao, Y., & Li, X. (2019). Enhancing waterproof performance of phosphogypsum non-fired ceramics by coating silane-coupled unsaturated polyester resin. Materials Letters, 252, 52–55.
Znajdek, K., Szczecińska, N., Sibiński, M., Wiosna-Sałyga, G., & Przymęcki, K. (2018). Luminescent layers based on rare earth elements for thin-film flexible solar cells applications. Optik, 165, 200–209.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hagag, M.S., Morsy, A.M.A., Ali, A.H. et al. Adsorption of Rare Earth Elements onto the Phosphogypsum a Waste Byproduct. Water Air Soil Pollut 230, 308 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4362-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4362-z