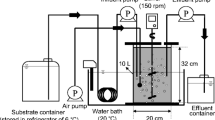
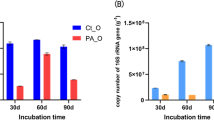
Abstract
Contamination with fluoroaromatics (FAs), particularly polyfluorinated aniline, is becoming a serious environmental problem worldwide. To shorten the start-up time, and increase the stability of treatment systems, this work focused on the effects of three seeding sources on treatment performances of 2,3,4-trifluoroaniline (2,3,4-TFA) during start-up and shock, as well as the acclimated strategy. After 246–323 days of acclimation in a stepwise feeding according to the inhibition degree, three sequencing batch reactors (SBRs) successfully achieved efficient removal, i.e., 300.00 mg/L of 2,3,4-TFA, with over 95.00% of degradation efficiency and 60.00–80.00% of defluorination rates. The sludge obtained from the fluorizated hydrocarbon wastewater treatment plant(FHS) without prior exposure to fluoroaniline was determined to be optimal, based on the observed shortest start-up time of 246 days, the highest defluorination rate of 70.00–80.00%, the fastest recovery time of 7 days after shock, and the highest microbial diversity with nine dominant bacterial groups. Furthermore, compared with the sludge obtained from pharmaceutical wastewater containing part of municipal wastewater treatment plant(PMS), the seeding source used in treating the comprehensive wastewater in industrial park (CIS) exhibited earlier defluorination reaction, higher defluorination rate and microbial diversity, but lower shock resistance. High-throughput sequencing demonstrated that microbial diversity was dependent on the origin of the inoculum after acclimation. We identified two predominant phyla in PMS, namely, Deinococcus-Thermus (24.43%) and Bacteroidetes (18.44%), whereas these were Acidobacteria and Chloroflexi in FHS and CIS. During the shock of 400 mg/L 2,3,4-TFA, the predominant bacteria norank_f_Blastocatellaceae and norank_f_Methylobacteriaceae disappeared, and the defluorination reaction hardly occurred, indicating that the bacterial genera could contribute to the defluorination reaction.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, D. E. C., & Halden, R. U. (2010). Fluorinated chemicals and the impacts of anthropogenic use. Contaminants of Emerging Concern in the Environment: Ecological and Human Health Considerations, 1048, 539–560.
Alexandrino, D. A. M., Ribeiro, I., Pinto, L. M., Cambra, R., Oliveira, R. S., Pereira, F., & Carvalho, M. F. (2018). Biodegradation of mono-, di- and trifluoroacetate by microbial cultures with different origins. New Biotechnology, 43, 23–29.
Alves, A. P. A., Lima, P. S., Dezotti, M., & Bassin, J. P. (2017). Impact of phenol shock loads on the performance of a combined activated sludge-moving bed biofilm reactor system. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 123, 146–155.
Amorim, C. L., Carvalho, M. F., Afonso, C. M. M., & Castro, P. M. L. (2013). Biodegradation of fluoroanilines by the wild strain Labrys portucalensis. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 80, 10–15.
APHA (American Public Health Association) (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water.Washington, USA.
Bai, N. L., Abuduaini, R., Wang, S., Zhang, M. N., Zhu, X. F., & Zhao, Y. H. (2017). Nonylphenol biodegradation characterizations and bacterial composition analysis of an effective consortium NP-M2. Environmental Pollution, 220, 95–104.
Blanco-Enriquez, E. G., de la Serna, F. J. Z. D., Peralta-Perez, M. D., Ballinas-Casarrubias, L., Salmeron, I., Rubio-Arias, H., & &Rocha-Gutierrez, B.A. (2018). Characterization of a microbial consortium for the bioremoval of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in water. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(5).
Cai, B. J., Xie, L., Yang, D. H., & Arcangeli, J. P. (2010). Toxicity evaluation and prediction of toxic chemicals on activated sludge system. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 177(1-3), 414–419.
Caporaso, J. G., Kuczynski, J., Stombaugh, J., Bittinger, K., Bushman, F. D., Costello, E. K., Fierer, N., Pena, A. G., Goodrich, J. K., Gordon, J. I., Huttley, G. A., Kelley, S. T., Knights, D., Koenig, J. E., Ley, R. E., Lozupone, C. A., McDonald, D., Muegge, B. D., Pirrung, M., Reeder, J., Sevinsky, J. R., Tumbaugh, P. J., Walters, W. A., Widmann, J., Yatsunenko, T., Zaneveld, J., & Knight, R. (2010). QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nature Methods, 7(5), 335–336.
Carvalho, G., Marques, R., Lopes, A. R., Faria, C., Noronha, J. P., Oehmen, A., Nunes, O. C., & Reis, M. A. M. (2010). Biological treatment of propanil and 3,4-dichloroaniline: kinetic and microbiological characterisation. Water Research, 44(17), 4980–4991.
Chen, S. C., Peng, J. J., & Duan, G. L. (2016). Enrichment of functional microbes and genes during pyrene degradation in two different soils. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 16(2), 417–426.
Chen, X. J., Xu, Y., Fan, M. J., Chen, Y. W., & Shen, S. B. (2019). The stimulatory effect of humic acid on the co-metabolic biodegradation of tetrabromobisphenol A in bioelectrochemical system. Journal of Environmental Management, 235, 350–356.
Choi, M., Cho, K., Lee, S., Chung, Y. C., Park, J., & Bae, H. (2018). Effective seeding strategy using flat type poly (vinyl alcohol) cryogel for anammox enrichment. Chemosphere, 205, 88–97.
Chong, N. M., & Chen, Y. S. (2007). Activated sludge treatment of a xenobiotic with or without a biogenic substrate during start-up and shocks. Bioresource Technology, 98(18), 3611–3616.
Cortes-Tolalpa, L., Jimenez, D. J., Brossi, M. J. D., Salles, J. F., & van Elsas, J. D. (2016). Different inocula produce distinctive microbial consortia with similar lignocellulose degradation capacity. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 100(17), 7713–7725.
Cui, D. Z., Shen, D., Wu, C. R., Li, C., Leng, D. J., & Zhao, M. (2017). Biodegradation of aniline by a novel bacterial mixed culture AC. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 125, 86–96.
Dionisi, D., Beccari, M., Di Gregorio, S., Majone, M., Papini, M. P., & Vallini, G. (2005). Storage of biodegradable polymers by an enriched microbial community in a sequencing batch reactor operated at high organic load rate. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 80(11), 1306–1318.
Duque, A. F., Hasan, S. A., Bessa, V. S., Carvalho, M. F., Samin, G., Janssen, D. B., & Castro, P. M. L. (2012). Isolation and characterization of a Rhodococcus strain able to degrade 2-fluorophenol. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 95(2), 511–520.
Duque, A. F., Bessa, V. S., & Castro, P. M. L. (2014). Bacterial community dynamics in a rotating biological contactor treating 2-fluorophenol-containing wastewater. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 41(1), 97–104.
Edgar, R. C. (2010). Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics, 26(19), 2460–2461.
Franco, A. R., Ferreira, A. C., & Castro, P. M. L. (2014). Co-metabolic degradation of mono-fluorophenols by the ectomycorrhizal fungi Pisolithus tinctorius. Chemosphere, 111, 260–265.
Gui, X. F., Xu, W. C., Cao, H. B., Ning, P. G., Zhang, Y. X., Li, Y. P., & Sheng, Y. X. (2019). A novel phenol and ammonia recovery process for coal gasification wastewater altering the bacterial community and increasing pollutants removal in anaerobic/anoxic/aerobic system. Science of the Total Environment, 661, 203–211.
Hou, L. F., Wu, Q. P., Gu, Q. H., Zhou, Q., & Zhang, J. M. (2018). Community structure analysis and biodegradation potential of aniline-degrading bacteria in biofilters. Current Microbiology, 75(7), 918–924.
ISO (1998) ISO 11348-3 Water quality: determination of the inhibitory effect of water samples on the light emission of Vibrio fischeri (Luminescent bacteria test)—part 3: method using freeze-dried bacteria. International Standardization Organization, Geneva(Comparison of experimental methods for determination of toxicity and biodegradability of xenobiotic compounds).
Jiang, Y., Wei, L., Yang, K., & Wang, H. Y. (2019). Investigation of rapid granulation in SBRs treating aniline-rich wastewater with different aniline loading rates. Science of the Total Environment, 646, 841–849.
Jiao, S., Chen, W. M., Wang, E. T., Wang, J. M., Liu, Z. S., Li, Y. N., & Wei, G. H. (2016). Microbial succession in response to pollutants in batch-enrichment culture. Scientific Reports, 6, 1–11.
Kiel, M., & Engesser, K. H. (2015). The biodegradation vs. biotransformation of fluorosubstituted aromatics. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 99(18), 7433–7464.
Lepik, R., & Tenno, T. (2012). Determination of biodegradability of phenolic compounds, characteristic to wastewater of the oil-shale chemical industry, on activated sludge by oxygen uptake measurement. Environmental Technology, 33(3), 329–339.
Moreira, I. S., Amorim, C. L., Carvalho, M. F., & Castro, P. M. L. (2012). Degradation of difluorobenzenes by the wild strain Labrys portucalensis. Biodegradation, 23(5), 653–662.
Moreno, G., & Buitron, G. (2004). Influence of the origin of the inoculum and the acclimation strategy on the degradation of 4-chlorophenol. Bioresource Technology, 94(2), 215–218.
Movahedyan, H., Assadi, A., & Amin, M. M. (2008). Effects of 4-chlorophenol loadings on acclimation of biomass with optimized fixed time sequencing batch reactor. Iranian Journal of Environmental Health Science & Engineering, 5(4), 225–234.
Nzila, A., Sankara, S., Al-Momani, M., & Musa, M. M. (2018). Isolation and characterisation of bacteria degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: phenanthrene and anthracene. Archives of Environmental Protection, 44(2), 43–54.
Orozco, A. M. F., Lobo, C. C., Contreras, E. M., & Zaritzky, N. E. (2013). Biodegradation of bisphenol-A (BPA) in activated sludge batch reactors: analysis of the acclimation process. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 85, 392–399.
Osuna, M. B., Sipma, J., Emanuelsson, M. A. E., Carvalho, M. F., & Castro, P. M. L. (2008). Biodegradation of 2-fluorobenzoate and dichloromethane under simultaneous and sequential alternating pollutant feeding. Water Research, 42(14), 3857–3869.
Perez-Lara, L. F., Vargas-Suarez, M., Lopez-Castillo, N. N., Cruz-Gomez, M. J., & &Loza-Tavera, H. (2016). Preliminary study on the biodegradation of adipate/phthalate polyester polyurethanes of commercial-type by Alicycliphilus sp BQ8. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 133(6).
Polo, A. M., Tobajas, M., Sanchis, S., Mohedano, A. F., & Rodriguez, J. J. (2011). Comparison of experimental methods for determination of toxicity and biodegradability of xenobiotic compounds. Biodegradation, 22(4), 751–761.
Ramos, C., Amorim, C. L., Mesquita, D. P., Ferreira, E. C., Carrera, J., & Castro, P. M. L. (2017). Simultaneous partial nitrification and 2-fluorophenol biodegradation with aerobic granular biomass: Reactor performance and microbial communities. Bioresource Technology, 238, 232–240.
Rezouga, F., Hamdi, M., & Sperandio, M. (2009). Variability of kinetic parameters due to biomass acclimation: case of para-nitrophenol biodegradation. Bioresource Technology, 100(21), 5021–5029.
Singleton, D. R., Adrion, A. C., & Aitken, M. D. (2016). Surfactant-induced bacterial community changes correlated with increased polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation in contaminated soil. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 100(23), 10165–10177.
Song, E. X., Wang, M. Z., & Shen, D. S. (2014). Isolation, identification and characterization of a novel Ralstonia sp FD-1, capable of degrading 4-fluoroaniline. Biodegradation, 25(1), 85–94.
Song, M., Zhang, L., Sun, B., Zhang, H., Ding, H., Li, Q., Guo, S. H., & Huang, X. (2015a). Ferrovibrio xuzhouensis sp nov., a cyhalothrin-degrading bacterium isolated from cyhalothrin contaminated wastewater. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek International Journal of General and Molecular Microbiology, 108(2), 377–382.
Song, Z. W., Li, T., Wang, Q. X., Pan, Y., & Li, L. X. (2015b). Influence of microbial community structure of seed sludge on the properties of aerobic nitrifying granules. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 35, 144–150.
Song, J. X., Chen, L. J., Chen, H. D., Sheng, F. F., Xing, D. F., Li, L., Zhang, Y. M., & Rittmann, B. (2018). Characterization and high-throughput sequencing of a trichlorophenol-dechlorinating microbial community acclimated from sewage sludge. Journal of Cleaner Production, 197, 306–313.
Strunk, N., & Engesser, K. H. (2013). Degradation of fluorobenzene and its central metabolites 3-fluorocatechol and 2-fluoromuconate by Burkholderia fungorum FLU100. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 97(12), 5605–5614.
Sun, W. M., Li, Y., McGuinness, L. R., Luo, S. A., Huang, W. L., Kerkhof, L. J., Mack, E. E., Haggblom, M. M., & Fennell, D. E. (2015). Identification of anaerobic aniline-degrading bacteria at a contaminated industrial site. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(18), 11079–11088.
Sun, Z. R., Zhang, J. W., Yang, J., Li, J. Y., Wang, J. G., & Hu, X. (2018). Acclimation of 2-chlorophenol-biodegrading activated sludge and microbial community analysis. Water Environment Research, 90(12), 2083–2089.
Van der Waals, M. J., Plugge, C., Meima-Franke, M., de Waard, P., Bodelier, P. L. E., Smidt, H., & Gerritse, J. (2019). Ethyl tert-butyl ether (EtBE) degradation by an algal-bacterial culture obtained from contaminated groundwater. Water Research, 148, 314–323.
Vasiliadou, I. A., Molina, R., Martinez, F., Melero, J. A., Stathopoulou, P. M., & Tsiamis, G. (2018). Toxicity assessment of pharmaceutical compounds on mixed culture from activated sludge using respirometric technique: The role of microbial community structure. Science of the Total Environment, 630, 809–819.
Vasquez, J., & Nakasaki, K. (2016). Effects of shock loading versus stepwise acclimation on microbial consortia during the anaerobic digestion of glycerol. Biomass & Bioenergy, 86, 129–135.
Wang, M. Z., Xu, J. J., Wang, J. H., Wang, S., Feng, H. J., Shentu, J. L., & Shen, D. S. (2013). Differences between 4-fluoroaniline degradation and autoinducer release by Acinetobacter sp TW: implications for operating conditions in bacterial bioaugmentation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(9), 6201–6209.
Wang, R. F., Chen, X. Y., & Yang, Q. X. (2018). Evolution of functional bacteria in a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH)-degrading bioreactor. Water Environment Research, 90(12), 2090–2099.
Wosman, A., Lu, Y. H., Sun, S. P., Liu, X., Wan, C. L., Zhang, Y., Lee, D. J., & Tay, J. (2016). Effect of operational strategies on activated sludge’s acclimation to phenol, subsequent aerobic granulation, and accumulation of polyhydoxyalkanoates. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 317, 221–228.
Yang, H., Yu, H. X., Hang, Q. G., Han, S. K., Wang, L. S., & Zhang, Z. (1997). Quantitative structure-toxicity relationships for fluorine-contained aromatics to Photobacterium phosphoreum. Chemosphere, 35(11), 2657–2663.
Zhao, Z. Q., Tian, B. H., Zhang, X., Ghulam, A., Zheng, T. C., & Shen, D. S. (2015). Aerobic degradation study of three fluoroanilines and microbial community analysis: the effects of increased fluorine substitution. Biodegradation, 26(1), 1–14.
Zhao, J. G., Li, Y. H., Chen, X. R., & Li, Y. (2018). Effects of carbon sources on sludge performance and microbial community for 4-chlorophenol wastewater treatment in sequencing batch reactors. Bioresource Technology, 255, 22–28.
Zilouei, H., Soares, A., Murto, M., Guieysse, B., & Mattiasson, B. (2006). Influence of temperature on process efficiency and microbial community response during the biological removal of chlorophenols in a packed-bed bioreactor. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 72(3), 591–599.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the editor and all the anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments and suggestions.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 21607092); the Public Technology Research Program of Zhejiang Province (no. 2017C33229); and the Talent Project of Qu Zhou University (no. XNZQN201506; BSJX201601).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, ZQ., Shen, XL., Zheng, TC. et al. Evaluation of Inoculum Sources for Aerobic Treatment of 2,3,4-Trifluoroaniline During Start-up and Shock. Water Air Soil Pollut 230, 283 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4346-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4346-z