Abstract
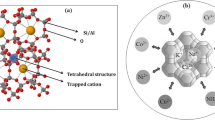
The efficiency and mechanism of modified clinoptilolites immobilizing Cu from aqueous solutions and contaminated sediments were investigated. The results showed that the clinoptilolite modified by lanthanum chloride (LaCl3) at a particle size of 0.5–1.0 mm could remove 65% of Cu2+ from 100 mg L−1 of Cu2+ solutions at the sorbent:solution mass ratio of 1:100. The equilibrium data fitted well to the Langmuir isotherm model with a maximum adsorption capacity of 21.09 mg Cu2+ g−1 at 25 °C. The Dubinin–Radushkevich adsorption model indicated that the adsorption of Cu2+ by modified clinoptilolite can be identified as chemisorption. The pseudo-second-order model could well represent the kinetics of the adsorption. The results of toxicity characteristic leaching procedure (TCLP) and Community Bureau of Reference (BCR) sequential extraction procedure showed that the modified clinoptilolite could reduce the leaching of Cu in the sediment and effectively transform Cu from the acid extractable or reducible fractions to the oxidizable or residual fractions. The presented work showed that the modified clinoptilolite holds great potential to remove Cu2+ from water, and to stabilize Cu-contaminated sediment.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriano, D., Page, A., Elseewi, A., Chang, A., & Straughan, I. (1980). Utilization and disposal of fly ash and other coal residues in terrestrial ecosystems: a review 1. Journal of Environmental Quality, 9(3), 333–344.
Agouborde, L., & Navia, R. (2009). Heavy metals retention capacity of a non-conventional sorbent developed from a mixture of industrial and agricultural wastes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 167(1), 536–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.01.027.
Aljerf, L. (2018). High-efficiency extraction of bromocresol purple dye and heavy metals as chromium from industrial effluent by adsorption onto a modified surface of zeolite: kinetics and equilibrium study. Journal of Environmental Management, 225, 120–132.
Andrejkovičová, S., Sudagar, A., Rocha, J., Patinha, C., Hajjaji, W., da Silva, E. F., Velosa, A., & Rocha, F. (2016). The effect of natural zeolite on microstructure, mechanical and heavy metals adsorption properties of metakaolin based geopolymers. Applied Clay Science, 126, 141–152.
Bao, J., Wang, L., & Xiao, M. (2016). Changes in speciation and leaching behaviors of heavy metals in dredged sediment solidified/stabilized with various materials. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(9), 8294–8301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6184-5.
Barjoveanu, G., De Gisi, S., Casale, R., Todaro, F., Notarnicola, M., & Teodosiu, C. (2018). A life cycle assessment study on the stabilization/solidification treatment processes for contaminated marine sediments. Journal of Cleaner Production, 201 391–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.053.
Bi, J., Liu, M., Song, C., Wang, X., & Guo, X. (2011). C2–C4 light olefins from bioethanol catalyzed by Ce-modified nanocrystalline HZSM-5 zeolite catalysts. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 107(1), 68–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.06.038.
Bouhamed, F., Elouear, Z., & Bouzid, J. (2012). Adsorptive removal of copper(II) from aqueous solutions on activated carbon prepared from Tunisian date stones: equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 43(5), 741–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2012.02.011.
Cao, C. Y., Liang, C. H., Yin, Y., & Du, L. Y. (2017). Thermal activation of serpentine for adsorption of cadmium. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 329, 222–229.
Chabukdhara, M., & Nema, A. K. (2012). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in Hindon River sediments: a chemometric and geochemical approach. Chemosphere, 87(8), 945–953.
Chen, Q. Y., Tyrer, M., Hills, C. D., Yang, X. M., & Carey, P. (2009). Immobilisation of heavy metal in cement-based solidification/stabilisation: a review. Waste Management, 29(1), 390–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2008.01.019.
Chen, Y. M., Gao, J. b., Yuan, Y. Q., Ma, J., & Yu, S. (2016). Relationship between heavy metal contents and clay mineral properties in surface sediments: implications for metal pollution assessment. Continental Shelf Research, 124, 125–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2016.06.002.
De Witte, B., Ruttens, A., Ampe, B., Waegeneers, N., Gauquie, J., Devriese, L., Cooreman, K., & Parmentier, K. (2016). Chemical analyses of dredged spoil disposal sites at the Belgian part of the North Sea. Chemosphere, 156, 172–180.
Demiral, H., & Güngör, C. (2016). Adsorption of copper(II) from aqueous solutions on activated carbon prepared from grape bagasse. Journal of Cleaner Production, 124, 103–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.02.084.
Demirbas, E., Dizge, N., Sulak, M. T., & Kobya, M. (2009). Adsorption kinetics and equilibrium of copper from aqueous solutions using hazelnut shell activated carbon. Chemical Engineering Journal, 148(2), 480–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.09.027.
Egashira, R., Tanabe, S., & Habaki, H. (2012). Adsorption of heavy metals in mine wastewater by Mongolian natural zeolite. Procedia Engineering, 42, 49–57.
Erdem, E., Karapinar, N., & Donat, R. (2004). The removal of heavy metal cations by natural zeolites. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 280(2), 309–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.08.028.
Fathollahzadeh, H., Kaczala, F., Bhatnagar, A., & Hogland, W. (2014). Speciation of metals in contaminated sediments from Oskarshamn Harbor, Oskarshamn, Sweden. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21(4), 2455–2464.
Febrianto, J., Kosasih, A. N., Sunarso, J., Ju, Y. H., Indraswati, N., & Ismadji, S. (2009). Equilibrium and kinetic studies in adsorption of heavy metals using biosorbent: a summary of recent studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 162(2–3), 616–645.
Foo, K. Y., & Hameed, B. H. (2010). Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chemical Engineering Journal, 156(1), 2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.013.
Huang, H., Xiao, X., Yan, B., & Yang, L. (2010). Ammonium removal from aqueous solutions by using natural Chinese (Chende) zeolite as adsorbent. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 175(1), 247–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.156.
Huang, Y., Zeng, X., Guo, L., Lan, J., Zhang, L., & Cao, D. (2018). Heavy metal ion removal of wastewater by zeolite-imidazolate frameworks. Separation and Purification Technology, 194, 462–469.
Inglezakis, V., Fyrillas, M., & Stylianou, M. (2018). Two-phase homogeneous diffusion model for the fixed bed sorption of heavy metals on natural zeolites. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 266, 164–176.
Ismail, A., Kawde, A., Muraza, O., Sanhoob, M. A., Aziz, M. A., & Al-Betar, A. R. (2019). Modified lanthanum–zeolite for sensitive electrochemical detection of heavy metal ions. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 44(1), 217–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3486-6.
Ji, G., Ni, J., & Sun, T. (2004). Progresses in remediation technologies for persistent toxic substances polluted sediments. Acta Genetica Sinica, 23(4), 118–121.
Kadirvelu, K., Faur-Brasquet, C., & Cloirec, P. L. (2000). Removal of Cu(II), Pb(II), and Ni(II) by adsorption onto activated carbon cloths. Langmuir, 16(22), 8404–8409. https://doi.org/10.1021/la0004810.
Leinonen, H., & Lehto, J. (2001). Purification of metal finishing waste waters with zeolites and activated carbons. Waste Management & Research, 19(1), 45–57. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242x0101900106.
Lin, J., Wang, H., Zhan, Y., & Chen, D. (2016). Adsorption of phosphate by lanthanum hydroxide/natural zeolite composites from low concentration phosphate solution. Environmental Science (in Chinese with English Abstract), 37(1), 208–219.
Liu, X., & Wang, R. (2017). Effective removal of hydrogen sulfide using 4A molecular sieve zeolite synthesized from attapulgite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 326, 157–164.
Matouq, M., Jildeh, N., Qtaishat, M., Hindiyeh, M., & Al Syouf, M. Q. (2015). The adsorption kinetics and modeling for heavy metals removal from wastewater by Moringa pods. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 3(2), 775–784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.03.027.
Motsi, T., Rowson, N., & Simmons, M. (2009). Adsorption of heavy metals from acid mine drainage by natural zeolite. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 92(1–2), 42–48.
Nguyen, T. C., Loganathan, P., Nguyen, T. V., Kandasamy, J., Naidu, R., & Vigneswaran, S. (2018). Adsorptive removal of five heavy metals from water using blast furnace slag and fly ash. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(21), 20430–20438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9610-4.
Pan, Y., Yang, L., Zhou, J., Liu, J., Qian, G., Ohtsuka, N., Motegi, M., Oh, K., et al. (2013). Characteristics of dioxins content in fly ash from municipal solid waste incinerators in China. Chemosphere, 92(7), 765–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.04.003.
Peng, J., Song, Y., Yuan, P., Cui, X., & Qiu, G. (2009). The remediation of heavy metals contaminated sediment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161(2–3), 633–640.
Petrus, R., & Warchoł, J. (2003). Ion exchange equilibria between clinoptilolite and aqueous solutions of Na+/Cu2+, Na+/Cd2+ and Na+/Pb2+. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 61(1), 137–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1387-1811(03)00361-5.
Pizarro, J., Castillo, X., Jara, S., Ortiz, C., Navarro, P., Cid, H., Rioseco, H., Barros, D., et al. (2015). Adsorption of Cu2+ on coal fly ash modified with functionalized mesoporous silica. Fuel, 156, 96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.04.030.
Shilina, A., Bakhtin, V., Burukhin, S., & Askhadullin, S. (2017). Sorption of cations of heavy metals and radionuclides from the aqueous media by new synthetic zeolite-like sorbent. Nuclear Energy and Technology, 3(4), 249–254.
Sounthararajah, D., Loganathan, P., Kandasamy, J., & Vigneswaran, S. (2015). Effects of humic acid and suspended solids on the removal of heavy metals from water by adsorption onto granular activated carbon. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 12(9), 10475–10489. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120910475.
Sun, C., Qiu, J., Zhang, Z., Marhaba, T. F., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, W. (2016). Characterization of citric acid-modified clam shells and application for aqueous lead (II) removal. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 227(9), 298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2975-z.
Tomasevic, D. D., Dalmacija, M. B., Prica, M. D., Dalmacija, B. D., Kerkez, D. V., Bečelić-Tomin, M. R., & Roncevic, S. D. (2013). Use of fly ash for remediation of metals polluted sediment–green remediation. Chemosphere, 92(11), 1490–1497.
Visa, M. (2016). Synthesis and characterization of new zeolite materials obtained from fly ash for heavy metals removal in advanced wastewater treatment. Powder Technology, 294, 338–347.
Wang, S. J., Salihu, M., Rushiti, F., Bala, L., & Modvig, J. (2010). Survivors of the war in the northern Kosovo: violence exposure, risk factors and public health effects of an ethnic conflict. Conflict and Health, 4(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-1505-4-11.
Wang, W., Pan, M., Qin, Y., Wang, L., & Song, L. (2011a). Effects of surface acidity on the adsorption desulfurization of Cu(I) Y zeolites. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 27(5), 1176–1180.
Wang, X. J., Xu, X. M., Liang, X., Wang, Y., Liu, M., Wang, X., Xia, S. Q., Zhao, J. F., et al. (2011b). Adsorption of copper(II) onto sewage sludge-derived materials via microwave irradiation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 192(3), 1226–1233.
Wang, F., Wang, H., Jin, F., & Al-Tabbaa, A. (2015). The performance of blended conventional and novel binders in the in-situ stabilisation/solidification of a contaminated site soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 285, 46–52.
Wang, Y. S., Dai, J. G., Wang, L., Tsang, D. C., & Poon, C. S. (2018). Influence of lead on stabilization/solidification by ordinary Portland cement and magnesium phosphate cement. Chemosphere, 190, 90–96.
Wen, J., & Zeng, G. (2018). Chemical and biological assessment of Cd-polluted sediment for land use: the effect of stabilization using chitosan-coated zeolite. Journal of Environmental Management, 212, 46–53.
Wen, J., Yi, Y., & Zeng, G. (2016). Effects of modified zeolite on the removal and stabilization of heavy metals in contaminated lake sediment using BCR sequential extraction. Journal of Environmental Management, 178, 63–69.
Xie, J., Wang, Z., Fang, D., Li, C., & Wu, D. (2014). Green synthesis of a novel hybrid sorbent of zeolite/lanthanum hydroxide and its application in the removal and recovery of phosphate from water. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 423, 13–19.
Yan, M., Zeng, G., Li, X., He, J., Chen, G., Huang, D., Tang, L., Lai, C., et al. (2017). Incentive effect of bentonite and concrete admixtures on stabilization/solidification for heavy metal-polluted sediments of Xiangjiang River. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(1), 892–901. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7527-y.
Yi, Y., Wen, J., Zeng, G., Zhang, T., Huang, F., Qin, H., & Tian, S. (2017). A comparative study for the stabilisation of heavy metal contaminated sediment by limestone, MnO2 and natural zeolite. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(1), 795–804.
Yu, G., Lei, H., Bai, T., Li, Z., Yu, Q., & Song, X. (2009). In-situ stabilisation followed by ex-situ composting for treatment and disposal of heavy metals polluted sediments. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 21(7), 877–883.
Yu, K., Xu, J., Jiang, X., Liu, C., McCall, W., & Lu, J. (2017). Stabilization of heavy metals in soil using two organo-bentonites. Chemosphere, 184, 884–891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.06.040.
Zanin, E., Scapinello, J., de Oliveira, M., Rambo, C. L., Franscescon, F., Freitas, L., de Mello, J. M. M., Fiori, M. A., et al. (2017). Adsorption of heavy metals from wastewater graphic industry using clinoptilolite zeolite as adsorbent. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 105, 194–200.
Zendelska, A., Golomeova, M., Blazev, K., Krstev, B., Golomeov, B., & Krstev, A. (2015). Adsorption of copper ions from aqueous solutions on natural zeolite. Environment Protection Engineering, 41(4), 17–36. https://doi.org/10.5277/epe150402.
Zhang, H., Li, A., Zhang, W., & Shuang, C. (2016). Combination of Na-modified zeolite and anion exchange resin for advanced treatment of a high ammonia–nitrogen content municipal effluent. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 468, 128–135.
Funding
This research was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2018MEE045), Foundation of remediation of contaminated sediment in Shandong Province (No. 2017-HCZBLY-003, No. SDHBYF-2012-14), Shandong Key Scientific and Technical Innovation Project (No. 2018YFJH0902), and Research Project of Shandong Environmental Protection Department (No. SDDPPS2018C(402001)006). Yanhao Zhang received support from the China Scholarship Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Cao, G., Zhang, Z. et al. Immobilization of Copper from Aqueous Solution and Contaminated Sediment Using Modified Clinoptilolite. Water Air Soil Pollut 230, 184 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4231-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4231-9