Abstract
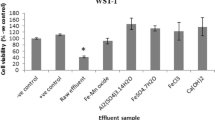
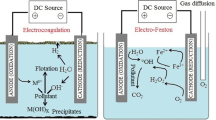
Exposure to complex organic substances present in textile wastewater has been considered a threat to human health and aquatic organisms. Development of appropriate treatment mechanisms, as well as sensitive monitoring assays, is considered important in order to safeguard and protect the delicate natural equilibrium in the environment. In this study, combined coagulation/flocculation and electrohydraulic discharge (EHD) system were explored for treatment of textile wastewater. Pre- and post-treatment samples were used to evaluate process efficiencies. Process efficiencies were evaluated using physicochemical characteristics, and cytotoxicity and inflammatory activities induced in macrophage RAW264.7 cell line. The RAW264.7 cell line was evaluated as an alternative to animals and human blood culture models, whose routine applications are hindered by stern ethical requirements. The toxicity of effluent was evaluated using WST-1 assay. The inflammatory activities were evaluated in RAW264.7 cell culture supernatant using nitric oxide (NO) and interleukin 6 (IL-6) as biomarkers of inflammation. The levels of NO and IL-6 were determined using the Griess reaction assay and double-antibody sandwich enzyme-linked immunoassay (DAS ELISA), respectively. Overall, the results of this study show that combined approaches and not the single EHD system are sufficient for complete removal of chemical oxygen demand (COD) and total organic carbon (TOC), toxicity and inflammatory activities in textile wastewater. The study shows that induction of NO and IL-6 secretions in macrophage RAW264.7 cells is a very sensitive model system to monitor the efficiency of textile effluent treatment processes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebayo, S. A., Shai, L. J., Cholo, M. C., Anderson, R., & du Toit, D. (2014). Assessment of the pro-inflammatory activity of water sampled from major water treatment facilities in the greater Pretoria region. Water SA, 40(2), 379–384.
Al-Hemiri, A., Al-Anbari, H., & Shakir, I. K. (2007). Dye removal from wastewater using iron salts. Iraqi Journal of Chemical and Petrolium Engineering, 9(3), 17–24.
American Public Health Association (APHA) (1999). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 20th Edition, APHA, Washington DC, p 1268.
Anvari, F., Kheirkhah, M., & Amraei, A. (2014). Treatment of synthetic textile wastewater by combination of coagulation/flocculation process and electron beam irradiation. Journal of Community Health Research., 3(1), 31–38.
Bacardit, J., Stötzner, J., Chamarro, E., & Esplugas, S. (2007). Effect of salinity on the photo-Fenton process. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 46, 7615–7619.
Bruggeman, P. J., & Locke, B. R. (2013). Assessment of potential applications of plasma with liquid water. In P. Chu & X. Lu (Eds.), Low temperature plasma technology: methods and applications (pp. 368–369). New York: CRC Press.
Chequer, F. M. D., de Oliveira, G. A. R., Ferraz, E. R. A., Cardoso, J. C., Zanoni, M. V. B., & de Oliveira, D. P. (2013). Textile dyes: dyeing process and environmental impact. In Eco-friendly textile dyeing and finishing. InTech.
Enjarlis (2013). Application of coagulation-advanced oxidation process by O3/GAC in the fan belt wastewater treatment. Asia-Pacific Chemical, Biological & Environmental Engineering Society (APCBEE). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcbee.2014.01.026.
Faul, A. K., Julies, E., & Pool, E. J. (2014). Steroid hormone concentrations and physiological toxicity of water from selected dams in Namibia. African Journal of Aquatic Science, 39(2), 189–198.
Hnizdo, E., & Vallyathan, V. (2003). Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease due to occupational exposure to silica dust: a review of epidemiological and pathological evidence. Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 60(4), 237–243.
Hoesel, B., & Schmid, J. A. (2013). The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Molecular Cancer, 12, 86.
Jiang, B., Zheng, J., Qiu, S., Wu, M., Zhang, Q., Yan, Z., & Xue, Q. (2014). Review on electrical discharge plasma technology for wastewater remediation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 236, 348–368.
Jung, Y. J., Kim, W. G., Yoon, Y., Hwang, T. M., & Kang, J. W. (2012). pH effect on ozonation of ampicillin: kinetic study and toxicity assessment. Ozone: Science & Engineering, 34(3), 156–162.
Kang, Y. H., & Biswas, S. K. (2013). Basophil-macrophage dialog in allergic inflammation. Immunity, 38(3), 408–410.
Kasprzyk-Hordern, B., Dinsdale, R. M., & Guwy, A. J. (2009). The removal of pharmaceuticals, personal cares products, endocrine disruptors and illicit drugs during wastewater treatment and its impact on the quality of receiving waters. Water Research, 43(2), 363–380.
Kim, H. G., Yeon, S. M., Kim, K. H., Kim, H., Park, J. I., Kang, H. J., Cha, E. J., Park, H. D., Kang, H. J., Park, T. W., Jeon, Y. H., Park, Y., Chang, K. T., & Jung, Y. W. (2014). Estrogenic endocrine-disrupting chemicals modulate the production of inflammatory mediators and cell viability of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Inflammation. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9966-2.
Kirkham, P. (2007). Oxidative stress and macrophage function: a failure to resolve the inflammatory response. Biochemical Society Transactions, 35(Pt 2), 284–287.
Kiwi, J., Lopez, A., & Nadtochenko, V. (2000). Mechanism and kinetics of the OH-radical intervention during Fenton oxidation in the presence of a significant amount of radical scavenger (Cl−). Environmental Science & Technology, 34, 2162–2168.
Klemola, K., Pearson, J., & Lindstrom-Seppä, P. (2007). Evaluating the toxicity of reactive dyes and dyed fabrics with the HacaT cytotoxicity test. Autex Research Journal, 7, 217–223.
Lacasse, K., & Baumann, W. (2004). Textile chemicals: environmental data and facts. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3642-18898-5.
Leme, D. M., de Oliveira, G. A. R., Meireles, G., dos Santos, T. C., Zanoni, M. V. B., & de Oliveira, D. P. (2014). Genotoxicological assessment of two reactive dyes extracted from cotton fibres using artificial sweat. Toxicology In Vitro, 28(1), 31–38.
Li, O. L., Takeuchi, N., He, Z., Guo, Y., Yasuoka, K., Chang, J. S., & Saito, N. (2012). Active species generated by a pulsed arc electrohydraulic discharge plasma channel in contaminated water treatments. Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing, 32(2), 343–358.
Maletz, S., Floehr, T., Beier, S., Klumper, C., Brouwer, A., Behnisch, P., Higley, E., Giesy, J. P., Hecker, M., Gebhardt, L. V., Pinnekamp, J., & Hollert, H. (2013). In vitro characterization of the effectiveness of enhanced sewage treatment processes to eliminate endocrine activity of hospital effluents. Water Research, 47, 1545–1557.
Malik, M. A. (2010). Water purification by plasmas: which reactors are most energy efficient? Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing, 30, 21–31.
Malinauskiene, L., Zimerson, E., Bruze, M., Ryberg, K., & Isaksson, M. (2012). Are allergenic disperse dyes used for dyeing textiles? Contact Dermatitis, 67(3), 141–148. Online. https://doi.org/10.1159/000357021.
Meriç, S., Selçuk, H., & Belgiorno, V. (2005). Acute toxicity removal in textile finishing wastewater by Fenton’s oxidation, ozone and coagulation–flocculation processes. Water Research, 39(6), 1147–1153.
Muruganandham, M., Suri, R. P. S., Jafari, S., Sillanpää, M., Gang-Juan, L., Wu, J. J. & Swaminathan, M. (2014). Recent developments in homogeneous advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment. International Journal of Photoenergy, 2014, 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/821674.
Nagel-Hassemer, M. E., Carvalho-Pinto, C. R. S., Matias, W. G., & Lapolli, F. R. (2011). Removal of coloured compounds from textile industry effluents by UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation and toxicity evaluation. Environmental Technology, 32(16), 1867–1874.
Nygaard, U., Kralund, H. H., & Sommerlund, M. (2013). Allergic contact dermatitis induced by textile necklace. Case Reports in Dermatology, 5(3), 336–339.
Olivier, L., Laurent, F., Michael, T., Diego, M., & Stéphanie, O. (2013). Treatment of 4-chlorobenzoic acid by plasma-based advanced oxidation processes. Chemical Engineering and Processing Process Intensification. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2013.06.008.
Oller, I., Malato, S., & Sánchez-Pérez, J. A. (2011). Combination of advanced oxidation processes and biological treatments for wastewater decontamination - a review. Science of the Total Environment, 409(20), 4141–4166.
Osuolale, O., & Okoh, A. (2015). Assessment of the physicochemical qualities and prevalence of Escherichia coli and Vibrios in the final effluents of two wastewater treatment plants in South Africa: ecological and public health implications. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 12(10), 13399–13412.
Pool, E. J., & Magcwebeba, T. U. (2009). The screening of river water for immunotoxicity using an in vitro whole blood culture assay. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 200(1–4), 25–31.
Puvaneswari, N., Muthukrishnan, J., & Gunasekaran, P. (2006). Toxicity assessment and microbial degradation of azo dyes. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology, 44(8), 618.
Rizzo, L. (2011). Bioassays as a tool for evaluating advanced oxidation processes in water and wastewater treatment. Water Research, 45(15), 4311–4340.
Sacan, M. T., & Balcioglu, I. A. (2006). A case study on algal response to raw and treated effluents from an aluminum plating plant and a pharmaceutical plant. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 64, 234–243.
Savin, I.-I., & Butnaru, R. (2008). Wastewater characteristics in textile finishing mills. Environmental Engineering and Management Journal, 7, 859–864.
Sharma S, Ruparelia, J.P. and Manish, L P (2011). A general review on advanced oxidation processes for waste water treatment. Paper presented at the Institute of Technology, Nirma University, Ahmedabad, 382-481, 08–10 2011.
Soni, P., Sharma, S., Sharma, S., Kumar, S., & Sharma, K. P. (2006). A comparative study on the toxic effects of textile dye wastewaters (untreated and treated) on mortality and RBC of a freshwater fish Gambusia affinis(Baird and Gerard). Journal of Environmental Biology, 27(4), 623–628.
Sonune, N. A., Mungal, N. A., & Kamble, S. P. (2015). Study of physico-chemical characteristics of domestic wastewater in Vishnupuri, Nanded, India. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 4(1), 533–536.
Tahara, M., & Okubo, M. (2014). Detection of free radicals produced by a pulsed electrohydraulic discharge using electron spin resonance. Journal of Electrostatics, 72(3), 222–227.
Verma, Y. (2008). Acute toxicity assessment of textile dyes and textile and dye industrial effluents using Daphnia magna bioassay. Toxicology and Industrial Health, 24(7), 491–500.
Wichmann, G., Daegelmann, C., Herbarth, O., Strauch, G., Schirmer, K., Wöstemeyer, J., & Lehmann, I. (2004). Inflammatory activity in river-water samples. Environmental Toxicology, 19(6), 594–602.
Wu, J. J., Yang, J. S., Muruganandham, M., & Wu, C. C. (2008). The oxidation study of 2-propanol using ozone-based advanced oxidation processes. Separation and Purification Technology, 62(1), 39–46.
Xu, X., Wu, X., Wang, Q., Cai, N., Zhang, H., Jiang, Z., Wan, M., & Oda, T. (2014). Immunomodulatory effects of alginate oligosaccharides on murine macrophage RAW264. 7 cells and their structure–activity relationships. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 62(14), 3168–3176.
Yang, D. M., Wan, B., Ren, H. Y., & Yuan, J. M. (2012). Effects and mechanism of ozonation for degradation of sodium acetate in aqueous solution. Water Science and Engineering, 5, 155–163.
Zayas, P. T., Geissler, G., & Hernandez, F. (2007). Chemical oxygen demand reduction in coffee wastewater through chemical flocculation and advanced oxidation processes. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 19, 300–305.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Makene, V.W., Tijani, J.O., Massima, E. et al. Toxicity Study of a Textile Effluent Treated with Electrohydraulic Discharge and Coagulant/Flocculants. Water Air Soil Pollut 230, 167 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4212-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4212-z