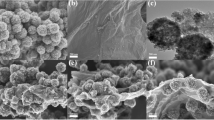
Abstract
In order to improve the catalytic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles in wastewater treatment, the Cu-doped Fe3O4/graphene oxide (Fe3−xCuxO4/GO) nanocomposites were prepared by a modified co-precipitation method and used as heterogeneous catalyst for p-Nitrophenol (p-NP) degradation. The effect of the GO and Cu contents in the nanocomposites was investigated. Compared with the unsupported Fe3O4 nanoparticles, the Fe3O4/GO nanocomposites have obviously improved catalytic performance, especially for the nanocomposite with 6.25 wt.% of the GO content. Furthermore, the catalytic efficiency is greatly improved by doping Cu in the nanocomposite. The Fe3−xCuxO4/GO nanocomposite achieves the best catalytic property in our catalyst system when the x value is about 0.075. Under the optimal reaction condition (0.8 g L−1 of catalyst dosage, 15 mmol L−1 of initial H2O2 concentration, 3.0 of pH value, and 30 °C of temperature), the p-NP conversion and chemical oxygen demand removal efficiencies in 120 min for the Fe2.925Cu0.075O4/GO nanocomposite are about 98.4% and 74.7%, respectively. And the p-NP conversion efficiency is still as high as 96.2% after four recycles under the optimum condition. The results clearly show that the Fe2.925Cu0.075O4/GO nanocomposite has outstanding catalytic properties for the p-NP degradation.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahadur, A., Saeed, A., Shoaib, M., Lqbal, S., Bashir, M. I., Waqas, M., Hussain, M. N., & Abbas, N. (2017). Eco-friendly synthesis of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles with tunable size: Dielectric, magnetic, thermal and optical studies. Materials Chemistry & Physics, 198, 229–235.
Barros, W. R. P., Steter, J. R., Lanza, M. R. V., & Tavares, A. C. (2016). Catalytic activity of Fe3−xCuxO4, (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.25) nanoparticles for the degradation of Amaranth food dye by heterogeneous electro-Fenton process. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 180, 434–441.
Bokare, A. D., & Choi, W. Y. (2014). Review of iron-free Fenton-like systems for activating H2O2 in advanced oxidation processes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 275, 121–135.
Chen, H. H., Yang, M., Tao, S., & Chen, G. W. (2017). Oxygen vacancy enhanced catalytic activity of reduced Co3O4 towards p-nitrophenol reduction. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 209, 648–656.
Costa, R. C., Lelis, M. F., Oliveira, L. C., Fabris, J. D., Ardisson, J. D., Rios, R. R., Silva, C. N., & Lago, R. M. (2006). Novel active heterogeneous Fenton system based on Fe3-xMxO4 (Fe, Co, Mn, Ni): The role of M2+ species on the reactivity towards H2O2 reactions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 129, 171–178.
Gao, Y. W., Wang, Y., & Zhang, H. (2015). Removal of rhodamine B with Fe-supported bentonite as heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyst under visible irradiation. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 178, 29–36.
Gonzalez-Olmos, R., Martin, M. J., Georgi, A., Kopinke, F. D., Oller, I., & Malato, S. (2012). Fe-zeolites as heterogeneous catalysts in solar Fenton-like reactions at neutral pH. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 125(3), 51–58.
Guo, S., Zhang, G. K., Guo, Y. D., & Yu, J. C. (2013). Graphene oxide–Fe2O3 hybrid material as highly efficient heterogeneous catalyst for degradation of organic contaminants. Carbon, 60(14), 437–444.
He, G. Y., Liu, W. F., Sun, X. Q., Chen, Q., Wang, X., & Chen, H. Q. (2013). Fe3O4@graphene oxide composite: A magnetically separable and efficient catalyst for the reduction of nitroarenes. Materials Research Bulletin, 48(5), 1885–1890.
Huang, H. H., Lu, M. C., & Chen, J. N. (2001). Catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide and 2-chlorophenol with iron oxides. Water Research, 35(9), 2291–2299.
Kakavandi, B., Takdastan, A., Jaafarzadeh, N., Azizi, M., Mirzaei, A., & Azari, A. (2016). Application of Fe3O4@C catalyzing heterogeneous UV-Fenton system for tetracycline removal with a focus on optimization by a response surface method. Journal of Photochemisrty & Photobiology A Chemistry, 314(1), 178–188.
Kwan, W. P., & Voelker, B. M. (2003). Rates of hydroxyl radical generation and organic compound oxidation in mineral-catalyzed Fenton-like systems. Environ Science & Technology, 37(6), 1150–1158.
Magalhães, F., Pereira, M. C., Botrel, S. E. C., Fabris, J. D., Macedo, W. A., Mendonca, R., Lago, R. M., & Oliveira, L. C. A. (2007). Cr-containing magnetites Fe3−xCrxO4: The role of Cr3+ and Fe2+ on the stability and reactivity towards H2O2 reactions. Applied Catalysis A General, 332(1), 115–123.
Malik, P. K., & Saha, S. K. (2003). Oxidation of direct dyes with hydrogen peroxide using ferrous ion as catalyst. Separation and Purification Technology, 31, 241–250.
Matta, R., Hanna, K., & Chiron, S. (2007). Fenton-like oxidation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene using different iron minerals. Science of the Total Environment, 385(1), 242–251.
Menini, L., Pereira, M. C., Parreira, L. A., Fabris, J. D., & Gusevskaya, E. V. (2008). Cobalt-and manganese-substituted ferrites as efficient single-site heterogeneous catalysts for aerobic oxidation of monoterpenic alkenes under solvent-free conditions. Journal of Catalysis, 254(2), 355–364.
Moura, F. C., Araujo, M. H., Costa, R. C., Fabris, J. D., Ardisson, J. D., Macedo, W. A., & Lago, R. M. (2005). Efficient use of Fe metal as an electron transfer agent in a heterogeneous Fenton system based on Fe0/Fe3O4 composites. Chemosphere, 60(8), 1118–1123.
Nejad, M. A., & Jonsson, M. (2004). Reactivity of hydrogen peroxide towards Fe3O4, Fe2CoO4, and Fe2NiO4. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 334(1), 28–34.
Pereira, M. C., Oliveira, L. C. A., & Murad, E. (2012). Iron oxide catalysts: Fenton and Fenton-like reactions—A review. Clay Minerals, 47(3), 285–302.
Pugazhenthiran, N., Sathishkumar, P., Murugesan, S., & Anandan, S. (2011). Effective degradation of acid orange 10 by catalytic ozonation in the presence of Au-Bi2O3 nanoparticles. Chemical Engineering Journal, 168(3), 1227–1233.
Sun, L., & Fugetsu, B. (2013). Mass production of graphene oxide from expanded graphite. Materials Letters, 109(1), 207–210.
Tian, X. J., Liu, Y. F., Chi, W. D., Wang, Y., Yue, X. Z., Huang, Q. G., & Yu, C. Y. (2017). Catalytic degradation of phenol and p-Nitrophenol using Fe3O4/MWCNT nanocomposites as heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 228, 297.
Ullah, K., Ye, S., Zhu, L., Meng, Z. D., Sarkar, S., & Oh, W. C. (2014). Microwave assisted synthesis of a noble metal-graphene hybridphotocatalyst for high efficient decomposition of organicdyes under visible light. Materials Science and Engineering B, 180, 20–26.
Wan, D., Li, W. B., Wang, G. H., Lu, L. L., & Wei, X. B. (2016). Degradation of p-Nitrophenol using magnetic Fe0/Fe3O4/coke composite as a heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst. Science of the Total Environment, 574, 1326–1334.
Wang, S. B. (2008). A comparative study of Fenton and Fenton-like reaction kinetics in decolourisation of wastewater. Dyes & Pigments, 76, 714–720.
Wang, N. N., Chen, J. Q., Zhao, Q., & Xu, H. (2017a). Study on preparation conditions of coal fly ash catalyst and catalytic mechanism in a heterogeneous Fenton-like process. RSC Advances, 7(83), 52524–52532.
Wang, N. N., Zhao, Q., & Zhang, A. L. (2017b). Catalytic oxidation of organic pollutants in wastewater via a Fenton-like process under the catalysis of HNO3-modified coal fly ash. RSC Advances, 7(44), 27619–27628.
Wu, Y., Luo, H. J., Wang, H., Zhang, L., Liu, P. P., & Feng, L. Q. (2014). Fast adsorption of nickel ions by porous graphene oxide/sawdust composite and reuse for phenol degradation from aqueous solutions. Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 436, 90–98.
Xu, H. Y., Shi, T. N., Zhao, H., Jin, L. G., Wang, F. C., Wang, C. Y., & Qi, S. Y. (2016). Heterogeneous Fenton-like discoloration of methyl orange using Fe3O4/MWCNTs as catalyst: Process optimization by response surface methodology. Frontiers of Materials Science, 10(1), 45–55.
Yang, S. J., He, H. P., Wu, D. Q., Chen, D., Liang, X. L., Qin, Z. H., Fan, M. D., & Zhu, J. X. (2009). Decolorization of methylene blue by heterogeneous Fenton reaction using Fe3−xTixO4 (0≤x ≤0.78) at neutral pH values. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 89, 527–535.
Yu, L., Chen, J. D., Liang, Z., Xu, W. C., Chen, L. M., & Ye, D. Q. (2016). Degradation of phenol using Fe3O4-GO nanocomposite as a heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyst. Separation & Purification Technology, 171, 80–87.
Zhang, S. X., Zhao, X. L., Niu, H. Y., Shi, Y. L., Cai, Y. Q., & Jiang, G. B. (2009). Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles as catalysts for the catalytic oxidation of phenolic and aniline compounds. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 167, 560–566.
Zhao, S. F., Ma, H. J., Wang, M., Cao, C. Q., Xiong, J., Xu, Y. S., & Yao, S. D. (2010). Role of primary reaction initiated by 254 nm UV light in the degradation of p-nitrophenol attacked by hydroxyl radicals. Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences: Official Journal of the European Photochemistry Association and the European Society for Photobiology, 9(5), 710–715.
Zhu, S. M., Dong, B. Z., Yu, Y. H., Bu, L. J., Deng, J., & Zhou, S. Q. (2017). Heterogeneous catalysis of ozone using ordered mesoporous Fe3O4 for degradation of atrazine. Chemical Engineering Journal, 328, 527–535.
Zubir, N. A., Yacou, C., Motuzas, J., Zhang, X., & Costa, J. C. D. D. (2014). Structural and functional investigation of graphene oxide-Fe3O4 nanocomposites for the heterogeneous Fenton-like reaction. Scientific Reports, 4, 1–8.
Funding
This study is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21174011 and U1462102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2612 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Jia, Z., Li, P. et al. High Catalytic Activity of Fe3−xCuxO4/Graphene Oxide (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.1) Nanocomposites as Heterogeneous Fenton Catalysts for p-Nitrophenol Degradation. Water Air Soil Pollut 230, 64 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4121-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4121-1