Abstract
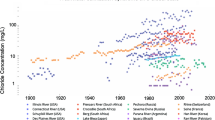
We use a 32-year dataset from a rural, southeastern New York stream to describe the effect of long-term road salt use on concentrations of sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−). Mean annual stream Na+ and Cl− concentrations initially increased, reached a plateau, and then increased again. Trends in summer and winter stream concentrations were similar but summer concentrations were higher than winter, indicating that salt entered the stream via groundwater discharge. Seasonal and inter-annual variability in stream Na+ and Cl− concentrations and export were high in the latter years of the study and can be explained by increased variability in stream discharge. Stream water Na+ and Cl− concentrations were positively correlated with conductivity, and conductivity was negatively correlated with discharge during all seasons (p < 0.001). We used road salt application data from a local agency to examine effects of best management practices. Despite reductions in salt application, there was no commensurate decrease in stream water Na+ and Cl− concentrations. We estimate that the legacy of long-term salt accumulation in groundwater and soils may delay a decline in stream water Na+ and Cl− concentrations by 20–30 years. Continued research to develop road salt reduction practices is important to mitigate impacts on freshwater ecosystems and drinking water supplies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger, E., Haase, P., Kuemmerlen, M., Leps, M., Schäfer, R. B., & Sundermann, A. (2017). Water quality variables and pollution sources shaping stream macroinvertebrate communities. The Science of the Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.031.
Cantafio, L. J., & Ryan, M. C. (2014). Quantifying baseflow and water-quality impacts from a gravel-dominated alluvial aquifer in an urban reach of a large Canadian river. Hydrogeology Journal, 22(4), 957–970. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-013-1088-7.
Cassanelli, J. P., & Robbins, G. A. (2013). Effects of road salt on Connecticut’s groundwater: a statewide centennial perspective. Journal of Environmental Quality, 42(3), 737–748. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2012.0319.
Cooper, C. A., Mayer, P. M., & Faulkner, B. R. (2014). Effects of road salts on groundwater and surface water dynamics of sodium and chloride in an urban restored stream. Biogeochemistry, 121(1), 149–166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-014-9968-z.
Corsi, S. R., De Cicco, L. A., Lutz, M. A., & Hirsch, R. M. (2015). River chloride trends in snow-affected urban watersheds: increasing concentrations outpace urban growth rate and are common among all seasons. Science of the Total Environment, 508, 488–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.12.012.
Daley, M. L., Potter, J. D., & McDowell, W. H. (2009). Salinization of urbanizing New Hampshire streams and groundwater: effects of road salt and hydrologic variability. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 28(4), 929–940. https://doi.org/10.1899/09-052.1.
Dugan, H. A., Bartlett, S. L., Burke, S. M., Doubek, J. P., Krivak-Tetley, F. E., Skaff, N. K., et al. (2017). Salting our freshwater lakes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 114(17), 4453–4458.
Fay, L., Nazari, M. H., Jungwirth, S., & Muthumani, A. (2015). Snow and ice control environmental best management practices (pp. 147–161). Reston: American Society of Civil Engineers. https://doi.org/10.1061/9780784479285.013.
Findlay, S. E. G., & Kelly, V. R. (2011). Emerging indirect and long-term road salt effects on ecosystems. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences., 1223, 58–68. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05942.x.
Guesdon, G., de Santiago-Martín, A., Raymond, S., Messaoud, H., Michaux, A., Roy, S., & Galvez, R. (2016). Impacts of salinity on Saint-Augustin Lake, Canada: remediation measures at watershed scale. Water, 8(7), 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8070285.
Gutchess, K., Jin, L., Lautz, L., Shaw, S. B., Zhou, X., & Lu, Z. (2016). Chloride sources in urban and rural headwater catchments, Central New York. Science of the Total Environment, 565, 462–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.181.
Hamilton, S. K. (2012). Biogeochemical time lags may delay responses of streams to ecological restoration: time lags in stream restoration. Freshwater Biology, 57, 43–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2011.02685.x.
Herbert, E. R., Boon, P., Burgin, A. J., Neubauer, S. C., Franklin, R. B., Ardón, M., et al. (2015). A global perspective on wetland salinization: ecological consequences of a growing threat to freshwater wetlands. Ecosphere, 6(10), art206. https://doi.org/10.1890/ES14-00534.1.
Hill, A. R., & Sadowski, E. K. (2016). Chloride concentrations in wetlands along a rural to urban land use gradient. Wetlands, 36(1), 73–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-015-0717-4.
Hubbart, J. A., Kellner, E., Hooper, L. W., & Zeiger, S. (2017). Quantifying loading, toxic concentrations, and systemic persistence of chloride in a contemporary mixed-land-use watershed using an experimental watershed approach. Science of The Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.019.
Kelly, V. R., Lovett, G. M., Weathers, K. C., Findlay, S. E. G., Strayer, D. L., Burns, D. J., & Likens, G. E. (2008). Long-term sodium chloride retention in a rural watershed: Legacy effects of road salt on streamwater concentration. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(2), 410–415. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0713911.
Kelly, W. R., Panno, S. V., Hackley, K. C., Hwang, H.-H., Martinsek, A. T., & Markus, M. (2010). Using chloride and other ions to trace sewage and road salt in the Illinois waterway. Applied Geochemistry, 25(5), 661–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.01.020.
Kilgour, B. W., Gharabaghi, B., & Perera, N. (2014). Ecological benefit of the road salt code of practice. Water Quality Research Journal of Canada, 49(1), 43. https://doi.org/10.2166/wqrjc.2013.129.
Ledford, S. H., Lautz, L. K., & Stella, J. C. (2016). Hydrogeologic processes impacting storage, fate, and transport of chloride from road salt in urban riparian aquifers. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(10), 4979–4988. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b00402.
Meriano, M., Eyles, N., & Howard, K. W. F. (2009). Hydrogeological impacts of road salt from Canada’s busiest highway on a Lake Ontario watershed (Frenchman’s bay) and lagoon, City of Pickering. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 107(1–2), 66–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2009.04.002.
Mueller, B., & Gaechter, R. (2012). Increasing chloride concentrations in Lake Constance: characterization of sources and estimation of loads. Aquatic Sciences, 74(1), 101–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-011-0200-0.
Nimiroski, M. T., & Waldron, M. C. (2006). Sources of sodium and chloride in the Scituate Reservoir drainage basin, Rhode Island (No. WRIR 02–4149). USGS.
Novotny, E. V., Sander, A. R., Mohseni, O., & Stefan, H. G. (2009). Chloride ion transport and mass balance in a metropolitan area using road salt. Water Resources Research, 45, W12410. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009wr008141.
Ostendorf, D. W. (2013). Hydrograph and chloride pollutograph analysis of Hobbs Brook reservoir subbasin in eastern Massachusetts. Journal of Hydrology, 503(0), 123–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.09.003.
Perera, N., Gharabaghi, B., & Howard, K. (2013). Groundwater chloride response in the Highland Creek watershed due to road salt application: a re-assessment after 20 years. Journal of Hydrology, 479, 159–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.11.057.
Rhodes, A. L., & Guswa, A. J. (2016). Storage and release of road-salt contamination from a calcareous lake-basin fen, western Massachusetts, USA. Science of the Total Environment, 545, 525–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.12.060.
Salminen, J. M., Nysten, T. H., & Tuominen, S. M. (2011). Review of approaches to reducing adverse impacts of road deicing on groundwater in Finland. Water Quality Research Journal of Canada, 46(2), 166–173. https://doi.org/10.2166/wqrjc.2011.002.
Schalk, C. W., & Stasulis, N. W. (2012). Relations among water levels, specific conductance, and depths of bedrock fractures in four road-salt-contaminated wells in Maine, 2007-9. USGS Scientific Investigations Report 2012–5205.
USGS. 2018. U.S. Department of the Interior | U.S. Geological Survey, minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/commodity/salt/index.html, page maintained by: rcallaghan@usgs.gov, page last modified: Thursday, 08-Feb-2018 12:49:01 EST. Accessed 4 April 2018.
Zuidema, S., Wollheim, W. M., Mineau, M. M., Green, M. B., & Stewart, R. J. (2018). Controls of chloride loading and impairment at the river network scale in New England. Journal of Environment Quality, 47(4), 839. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2017.11.0418.
Acknowledgments
We greatly appreciate the assistance and contribution of valuable comments and suggestions from Michael Lashmet of the New York State Department of Transportation (NYDOT), and AJ Reisinger and David Strayer of Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the NYDOT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 138 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kelly, V.R., Findlay, S.E., Hamilton, S.K. et al. Seasonal and Long-Term Dynamics in Stream Water Sodium Chloride Concentrations and the Effectiveness of Road Salt Best Management Practices. Water Air Soil Pollut 230, 13 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-4060-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-4060-2