Abstract
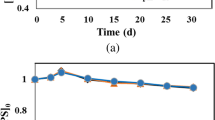
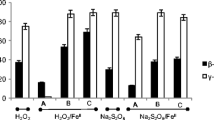
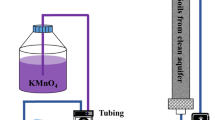
Accurate estimation of oxidant consumption during in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) is the key to determining the treatment effectiveness in contaminated sites. We established the estimation model of soil oxidant demand (SOD) and simulation equations of potassium permanganate (KMnO4) dynamic consumption based on the reaction equation of KMnO4 with reductive minerals and the estimation model of SOD. Model validation, model application, and simulation assessment had been accomplished. Results indicated that the simulations are in good agreement with measured data. The confidence level of the SOD estimation model of KMnO4 was over 80%, with sensitivity in decreasing order as follows: organic matter content > initial KMnO4 concentration > reductive minerals (RMs). Particularly, the organic matter played a dominate role in the SOD model estimation. The coefficient of determination (R2) of the SOD dynamic consumption simulation equation was above 0.9. Among the various types of soils, the overall trend of SOD value and reaction period decreased as follows: clay > loam > sand. However, the consumption rate of KMnO4 decreased in the order of clay > sand > loam. In addition, SOD value, reaction period, and reaction rate all increased as the initial concentration of KMnO4 went up. This work can provide a methodology and reference for selecting and estimating of the optimal oxidant doses and reaction period during field application.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, Y., Feng, S., Yang, T., Zhang, W., & Wang, S. (2013). Statistical property of soil organic matter in different soil types in China. Journal of Fudan University (Nature Science), 52(2), 220–224 (in Chinese).
Cheng, H., Li, K., Li, M., Yang, K., Liu, F., & Cheng, X. (2014). Geochemical background and baseline values of chemical elements of urban soil in China. Earth Science Frontiers, 21(3), 265–306 (in Chinese).
Dong, G., Liu, D., Jiang, Y., & Tao, Y. (2003). The content and effectiveness evaluation of soil trace elements in Huzhou. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 35(4), 474–478 (in Chinese).
Fang, G., Wu, W., Liu, C., Dionysiou, D. D., Deng, Y., & Zhou, D. (2017). Activation of persulfate with vanadium species for PCBs degradation: A mechanistic study. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 202, 1–11.
Haselow, J. S., Siegrist, R. L., Crimi, M., & Jarosch, T. (2003). Estimating the total oxidant demand for in situ chemical oxidation design. Remediation Journal, 13, 5–16.
Hønning, J., Broholm, M. M., & Bjerg, P. L. (2007). Quantification of potassium permanganate consumption and PCE oxidation in subsurface materials. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 90(3), 221–239.
Innocenti, I., Verginelli, I., Massetti, F., Piscitelli, D., Gavasci, R., & Baciocchi, R. (2014). Pilot-scale ISCO treatment of a MtBE contaminated site using a Fenton-like process. Science of the Total Environment, 485-486, 726–738.
Kao, C. M., Huang, K. D., Wang, J. Y., Chen, T. Y., & Chien, H. Y. (2008). Application of potassium permanganate as an oxidant for in situ oxidation of trichloroethylene-contaminated groundwater: A laboratory and kinetics study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 153(3), 919–927.
Kumpiene, J., Lagerkvist, A., & Maurice, C. (2008). Stabilization of As, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn in soil using amendments-a review. Waste Management, 28(1), 215–225.
Lemaire, J., Bues, M., Kabeche, T., Hanna, K., & Simonnot, M. O. (2013). Oxidant selection to treat an aged PAH contaminated soil by in situ chemical oxidation. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 1(4), 1261–1268.
Liao, X. Y., Zhao, D., & Yan, X. L., (2011). Determination of potassium permanganate demand variation with depth for oxidation-remediation of soils from a PAHs-contaminated coking plant. Journal of hazardous materials, 193, 164-170.
Matera, V., Le Hecho, I., Laboudigue, A., Thomas, P., Tellier, S., & Astruc, M. (2003). A methodological approach for the identification of arsenic bearing phases in polluted soils. Environmental Pollution, 126(1), 51–64.
Mumford, K. G., Thomson, N. R., & Allen-King, R. M. (2005). Bench-scale investigation of permanganate natural oxidant demand kinetics. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(8), 2835–2840.
Mundle, K., Reynolds, D. A., West, M. R., & Kueper, B. H. (2007). Concentration rebound following in situ chemical oxidation in fractured clay. Groundwater, 45(6), 692–702.
Petri, B. G., Thomson, N. R., & Urynowicz, M. A. (2011). Fundamentals of ISCO using permanganate. In Situ chemical oxidation for groundwater remediation (pp. 89–146). New York: Springer.
Ranc, B., Faure, P., Croze, V., & Simonnot, M. O. (2016). Selection of oxidant doses for in situ chemical oxidation of soils contaminated by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 312, 280–297.
Shu, Z., Wu, H., Lin, H., Li, T., Liu, Y., Ye, F., Mu, X., Li, X., Jiang, X., & Huang, J. (2016). Decolorization of Remazol Brilliant Blue R using a novel acyltransferase-ISCO (in situ chemical oxidation) coupled system. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 115, 56–63.
Siegrist, R. L. (Ed.). (2001). Principles and practices of in situ chemical oxidation using permanganate. Battelle Press.
Siegrist, R. L., Petri, B., Krembs, F., Crimi, M. L., Ko, S., Simpkin, T., & Palaia, T. (2007). In situ chemical oxidation for remediation of contaminated ground water. In Summary Proceedings, ISCO Technology Practices Workshop (ESTCP ER-0623), Golden, CO, USA.
Siegrist, R. L., Crimi, M., & Simpkin, T. J. (Eds.). (2011). In situ chemical oxidation for groundwater remediation (Vol. 3). Springer Science & Business Media.
Teel, A. L., Elloy, F. C., & Watts, R. J. (2016). Persulfate activation during exertion of total oxidant demand. Chemosphere, 158, 184–192.
Tsitonaki, A., Petri, B., Crimi, M., Mosbæk, H., Siegrist, R. L., & Bjerg, P. L. (2010). In situ chemical oxidation of contaminated soil and groundwater using persulfate: A review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 40(1), 55–91.
Urynowicz, M. A., Balu, B., & Udayasankar, U. (2008). Kinetics of natural oxidant demand by permanganate in aquifer solids. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 96(1–4), 187–194.
Verschueren, K. (1985). Handbook of environmental data on organic chemicals, 2nd Ed. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold.
Xu, X., & Thomson, N. R. (2008). Estimation of the maximum consumption of permanganate by aquifer solids using a modified chemical oxygen demand test. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 134(5), 353–361.
Xu, X., & Thomson, N. R. (2009). A long-term bench-scale investigation of permanganate consumption by aquifer materials. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 110(3–4), 73–86.
Yang, Y., Jiang, T., Wei, S., He, R., & Liu, L. (2012). Chemical stability of organic matter in typical farmland soil of Chongqing. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 26(6), 180–184 (in Chinese).
Yang, L., Jin, M., Tong, C., & Xie, S. (2013). Study of dynamic sorption and desorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in silty-clay soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 244-245, 77–85.
Zhang, Y., Wang, R., & Jin, S. (2005). The study of the content of soil trace element and its influence factor. Soil Fertilizer, 5, 35–37 (in Chinese).
Zhao, D., Liao, X., Yan, X., Huling, S. G., Chai, T., & Tao, H. (2013). Effect and mechanism of persulfate activated by different methods for PAHs removal in soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 254, 228–235.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Key Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (ZDRW-ZS-2016-5-5) and the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA19040302).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highlights
• An estimation model of SOD was established for ISCO with KMnO4.
• Model of SOD consumption dynamic were successful applied under various condition.
• The major contribution to NOD came from TOC and OM.
• The SOD value was higher in clay than in loam or sandy soils.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 21.4 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Yang, K., Liao, X. et al. Quantification of Oxidant Demand and Consumption for In Situ Chemical Oxidation Design: in the Case of Potassium Permanganate. Water Air Soil Pollut 229, 375 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3982-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3982-z