Abstract
The degradation of two sulfonylurea herbicides, nicosulfuron and thifensulfuron methyl in water by chlorine dioxide, was studied for the first time in this paper. In order to examine the optimal parameters for degradation of both herbicides, degradation was investigated under light or dark conditions with different amount of chlorine dioxide, different degradation periods, and at different pH values. Degradation efficiency of herbicides was monitored using high-performance liquid chromatography with photodiode array detection (HPLC-DAD). The degradation products were analyzed by gas chromatography with triple quadrupole mass detector (GC–QQQ). Three products were identified after degradation of nicosulfuron and two products after degradation of thifensulfuron methyl. Total organic analysis (TOC) gave insight into some differences in degradation mechanisms and degrees of mineralization after degradation of the herbicides using chlorine dioxide. A simple mechanism of herbicide degradation was proposed. Acute toxicity tests were performed on the products produced after degradation with chlorine dioxide, and the results showed that the degradation products were less toxic than the parent compounds. The findings of the present study are very useful for the treatment of wastewaters contaminated with herbicides.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
03 September 2018
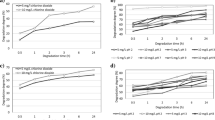
During typesetting, the image of figure 4 was also used in figure 5. The mistake was discovered after the original article was published online.
References
Ahmed, S., Rasul, M. G., Brown, R., & Hashib, M. A. (2011). Influence of parameters on the heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of pesticides and phenolic contaminants in wastewater: A short review. Journal of Environmental Management, 92(3), 310–330.
APHA (American Public Health Association). (1998). American Water Works Association, and water environment federation, standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington DC: American Public Health Association.
Battaglin, W. A., Furlong, E. T., Burkhardt, M. R., & Peter, C. J. (2000). Occurrence of sulfonylurea, sulfonamide, Imidazolinone, and other herbicides in rivers, reservoirs and ground water in the Midwestern United States, 1998. Science of the Total Environment, 248(2–3), 123–133.
Ben, W., Shi, Y., Li, W., Zhang, Y., & Qiang, Z. (2017). Oxidation of sulfonamide antibiotics by chlorine dioxide in water: Kinetics and reaction pathways. Chemical Engineering Journal, 327(11), 743–750.
Benzi, M., Robotti, E., & Gianotti, V. (2011). HPLC-DAD-MSn to investigate the Photodegradation pathway of Nicosulfuron in aqueous solution. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 399(4), 1705–1714.
Berger, B. M., & Wolfe, N. (1996). Hydrolysis and biodegradation of sulfonylurea herbicides in aqueous buffers and anaerobic water sediment systems: Assessing fate pathways using molecular descriptors. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 15(9), 1500–1507.
Carles, L., Joly, M., Bonnemoy, F., Leremboure, M., Batisson, I., & Besse-Hoggan, P. (2017). Identification of sulfonylurea biodegradation pathways enabled by a novel Nicosulfuron-transforming strain Pseudomonas fluorescens SG-1: Toxicity assessment and effect of formulation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 324(2), 184–193.
Chamberlain, E., Shi, H., Wang, T., Ma, Y., Fulmer, A., & Adams, C. (2012). Comprehensive screening study of pesticide degradation via oxidation and hydrolysis. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 60(6), 354–363.
Chen, Q., Wang, Y., Chen, F., Zhang, Y., & Liao, X. (2014). Chlorine dioxide treatment for the removal of pesticide residues on fresh lettuce and in aqueous solution. Food Control, 40(6), 106–112.
Djorđević, J. S., Vladisavljević, G. T., & Trtić-Petrović, T. M. (2014). Removal of the selected pesticides from a water solution by applying hollow Fiber liquid−liquid membrane extraction. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 53(12), 4861–4870.
Dugandžić, A. M., Tomašević, A. V., Radišić, M. M., Šekuljić, N. Ž., Mijin, D. Ž., & Petrović, S. D. (2017). Effect of inorganic ions, Photosensitisers and scavengers on the photocatalytic degradation of Nicosulfuron. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry. A, 336(3), 146–155.
Fan, J., Wei, Z., Ming, Z. Z., Xiang, X., Jun, W. J., Zhen, Q., Ke, L., & Ming, L. L. (2008). Desorption character of Nicosulfuron and effect of pH on adsorption of Nicosulfuron in soils. Journal of Agricultural Science, 21, 702–708.
Fenoll, J., Hellín, P., Flores, P., Martínez, C. M., & Navarro, S. (2012). Photocatalytic degradation of five sulfonylurea herbicides in aqueous semiconductor suspensions under natural sunlight. Chemosphere, 87(8), 954–961.
Fenoll, J., Sabater, P., Navarro, G., Vela, N., Pérez-Lucas, G., & Navarro, S. (2013). Abatement kinetics of 30 sulfonylurea herbicide residues in water by photocatalytic treatment with semiconductor materials. Journal of Environmental Management, 130(11), 361–368.
George, J., & Shukla, Y. (2011). Pesticides and Cancer: Insights into Toxicoproteomic-based findings. Journal of Proteomics, 74(12), 2713–2722.
Gonzalez, J. M., & Ukrainczyk, L. (1996). Adsorption and desorption of Nicosulfuron in soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 25(6), 1186–1192.
Halle, A., Lavieille, D., & Richard, C. (2010). The effect of mixing two herbicides Mesotrione and Nicosulfuron on their photochemical reactivity on Cuticular wax film. Chemosphere, 79(4), 482–487.
Hwang, E., Cash, J. N., & Zabik, M. J. (2002). Chlorine and chlorine dioxide treatment to reduce or remove EBDCs and ETU residues in a solution. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 50(16), 4734–4742.
Jia, X.-H., Feng, L., Liu, Y.-Z., Zhang, L.-Q., Jia, X.-H., Feng, L., Liu, Y.-Z., & Zhang, L.-Q. (2017). Oxidation of Antipyrine by chlorine dioxide: Reaction kinetics and degradation pathway. Chemical Engineering Journal, 309(2), 646–654.
Jović, M., Manojlović, D., Stanković, D., Dojčinović, B., Obradović, B., Gašić, U., & Roglić, G. (2013). Degradation of Triketone herbicides, Mesotrione and Sulcotrione, using advanced oxidation processes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 260(9), 1092–1099.
Klüttgen, B., Dülmer, U., Engels, M., & Ratte, T. H. (1994). ADaM, an artificial freshwater for the culture of zooplankton. Water Research, 28(3), 743–746.
Lanchote, V. L., Bonato, P. S., Cerdeira, A. L., Santos, N. A. G., de Carvalho, D., & Gomes, M. A. (2000). HPLC screening and GC-MS confirmation of Triazine herbicides residues in drinking water from sugar cane area in Brazil. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 118(3–4), 329–337.
Leboulanger, C., Rimet, F., de Lacotte, M. H., & Bérard, A. (2001). Effects of atrazine and Nicosulfuron on freshwater microalgae. Environmental International, 26(3), 131–135.
Lopez, A., Mascolo, G., Tiravanti, G., & Passino, R. (1997). Degradation of herbicides (Ametryn and Isoproturon) during water disinfection by means of two oxidants (hypochlorite and chlorine dioxide). Water Science and Technology, 35(4), 129–130 132-136.
Lu, X. H., Kang, Z. H., Tao, B., Wang, Y. N., Dong, J. G., & Zhang, J. L. (2012). Degradation of Nicosulfuron by Bacillus subtilis YB1 and aspergillus Niger YF1. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology, 48(5), 460–466.
Ma, X. L., Yu, P. B., Gao, H. N., & Zhang, H. (2011). Bioremediation of exogenous degrading Bacteria to the Nicosulfuron-contaminated soil. Journal of Safety and Environment, 11(4), 44–47.
Maurino, V., Minero, C., Pelizzetti, E., & Vincenti, M. (1999). Photocatalytic transformation of sulfonylurea herbicides over irradiated titanium dioxide particles. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 151(1–2), 329–338.
OECD Guideline for testing of chemicals (2004) Daphnia sp. Acute Immobilisation Test. OECD Guideline 202.
Otero, R., Fernandez, J. M., Gonzalez, M. A., Pavlovic, I., & Ulibarri, M. A. (2013). Pesticides adsorption–desorption on mg–Al mixed oxides. Kinetic modeling, Competing Factors and Recyclability. Chemical Engineering Journal, 221(4), 214–221.
Persoone, G., Marsalek, B., Blinova, I., Törökne, A., Zarina, D., Manusadzianas, L., Nalecz-Jawecki, G., Tofan, L., Stepanova, N., Tothova, L., & Kolar, B. (2003). A practical and user-friendly toxicity classification system with Microbiotests for natural waters and wastewaters. Environmental Toxicology, 18(6), 395–402.
Pileggi, M., Pileggi, S. A. V., Olchanheski, L. R., da Silva, P. A. G., Gonzalez, A. M. M., Koskinen, W. C., Barber, B., & Sadowsky, M. J. (2012). Isolation of Mesotrione-degrading Bacteria from aquatic environments in Brazil. Chemosphere, 86(11), 1127–1132.
Sabadie, J. (2002). Nicosulfuron: Alcoholysis, chemical hydrolysis, and degradation on various minerals. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 50(3), 526–531.
Sarmah, A. K., & Sabadie, J. (2002). Hydrolysis of sulfonylurea herbicides in soils and aqueous solutions: A review. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 50(22), 6253–6265.
Seguin, F., Leboulanger, C., Rimet, F., Druart, J. C., & Bérard, A. (2001). Effects of atrazine and Nicosulfuron on phytoplankton in Systems of Increasing Complexity. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 40(2), 198–208.
Sharma, V. K. (2008). Oxidative transformations of environmental pharmaceuticals by Cl2, ClO2, O3, and Fe (VI): Kinetics assessment. Chemosphere, 73(9), 1379–1386.
Shukla, G., Kumar, A., Bhanti, M., Joseph, P. E., & Taneja, A. (2006). Organochlorine pesticide contamination of ground water in the City of Hyderabad. Environmental International, 32(2), 244–247.
Song, J., Gu, J., Zhai, Y., Wu, W., Wang, H., Ruan, Z., Shi, Y., & Yan, Y. (2013). Biodegradation of Nicosulfuron by a Talaromyces Flavus LZM1. Bioresource Technology, 140(3), 243–248.
Tian, F., Qiang, Z., Liu, C., Zhang, T., & Dong, B. (2010). Kinetics and mechanism for Methiocarb degradation by chlorine dioxide in aqueous solution. Chemosphere, 79(6), 646–651.
Tian, F.-X., Xu, B., Zhang, T.-Y., & Gao, N.-Y. (2014). Degradation of Phenylurea herbicides by chlorine dioxide and formation of disinfection by-products during subsequent Chlor(am)ination. Chemical Engineering Journal, 258(12), 210–217.
Ukrainczyk, L., & Rashid, N. (1995). Irreversible sorption of Nicosulfuron on clay minerals. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 43(4), 855–857.
Vela, N., Navarro, G., Giménez, M. J., & Navarro, S. (2004). Gradual fall of s-Triazine herbicides in drinking and wastewater samples as influenced by light and temperature. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 158(1), 3–19.
Wang, Y., Liu, H., Xie, Y., Ni, T., & Liu, G. (2015). Oxidative removal of diclofenac by chlorine dioxide: Reaction kinetics and mechanism. Chemical Engineering Journal, 279(11), 409–415.
Wang, L., Zhang, X., & Li, Y. (2016). Degradation of Nicosulfuron by a novel Isolatedbacterial strain Klebsiella sp. Y1: Condition optimization, Kinetics and Degradation Pathway. Water Science and Technology, 73(12), 2896–2903.
Zhang, H., Mu, W., Hou, Z., Wu, X., Zhao, W., Zhang, X., Pan, H., & Zhang, S. (2012). Biodegradation of Nicosulfuron by the bacterium Serratia Marcescens N80. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part B, 47(3), 153–160.
Zhao, W., Wang, C., Xu, L., Zhao, C., Liang, H., & Qiu, L. (2015). Biodegradation of Nicosulfuron by a novel Alcaligenes Faecalis strain ZWS11. Journal of Environmental Science, 35(9), 151–162.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank TwinOxide-RS d.o.o. for providing components for the preparation of chlorine dioxide (“TWINS” preparation).
Funding
Financial support for this study was granted by the Ministry of Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia, Project Number 172030. DMS was supported by Magbiovin project (FP7-ERAChairs-Pilot Call-2013, Grant agreement: 621375).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The original version of this article was revised:During typesetting, the image of figure 4 was also used in figure 5. Figure 5 was updated with the correct image.
Electronic supplementary material
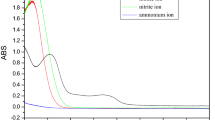
HPLC chromatograms of initial nicosulfuron (10 mg/L), initial thifensulfuron methyl (10 mg/L), their degradation products, and GC-QQQ chromatograms and mass spectra for degradation products of the sulfonylurea herbicides.
ESM 1
(DOCX 406 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pergal, M.V., Kodranov, I.D., Pergal, M.M. et al. Assessment of Degradation of Sulfonylurea Herbicides in Water by Chlorine Dioxide. Water Air Soil Pollut 229, 287 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3947-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3947-2