Abstract
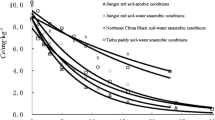
Ibuprofen is commonly detected in onsite wastewater systems. Such onsite systems are abundant in coastal plain areas, globally. Coastal plain soils have unique mineralogy. Rapid subsurface transport may occur in coastal plain soils due to their characteristic permeable soils and seasonally high water tables. Laboratory batch sorption studies were conducted on Norfolk, Goldsboro, and Lynchburg, three archetypical coastal plain soils, with varying physicochemical properties, to evaluate ibuprofen sorption. Sorption distribution coefficients (KD values) across all three soils ranged from 0.63 to 1.26 L kg−1. Sorption of ibuprofen to Norfolk and Goldsboro soils was able to be modeled using a Freundlich isotherm; however, the Lynchburg soil, was not, likely due to soil heterogeneity. In general, sorption of ibuprofen was influenced by soil organic carbon content.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avdeef, A., Box, K. J., Comer, J. E. A., Hibbert, C., & Tam, K. Y. (1998). Determination of liposomal membrane-water partition coefficients of ionizable drugs. Pharmaceutical Research, 15, 209–215.
Baker, J. R., Mihelcic, J. R., Luehrs, D. C., & Hickey, J. P. (1997). Evaluation of estimation methods for organic carbon normalized sorption coefficients. Water Environment Research, 69, 136–145.
Barnes, K. K., Kolpin, D. W., Furlong, E. T., Zaugg, S. D., Meyer, M. T., & Barber, L. B. (2008). A national reconnaissance of pharmaceuticals and other organic wastewater contaminants in the United States—I Groundwater. The Science of the Total Environment, 402, 192–200.
Becking, L. B., Kaplan, I. R., & Moore, D. (1960). Limits of the natural environment in terms of pH and oxidation-reduction potentials. The Journal of Geology, 68, 243–284.
Behera, S. K., Oh, S. Y., & Park, H. S. (2012). Sorptive removal of ibuprofen from water using selected soil minerals and activated carbon. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 9, 85–94.
Benfield, B. (2017). Sorption of ibuprofen to Coastal Plain Soils. MS Thesis. Department of Geological Sciences, East Carolina University, Greenville, NC.
Cho, H. H., Huang, H., & Schwab, K. (2011). Effects of solution chemistry on the adsorption of ibuprofen and triclosan onto carbon nanotubes. Langmuir, 27, 12960–12967.
Daniels, R. B., Gamble, E. E., & Cady, J. G. (1970). Some relations among Coastal Plain soils and geomorphic surfaces in North Carolina. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 34, 648–653.
Daughton, C. G., & Ternes, T. A. (1999). Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: agents of subtle change? Environmental Health Perspectives, 107, 907–938.
Del Rosario, K. L., Mitra, S., Humphrey, C. P., & O'Driscoll, M. A. (2014). Detection of pharmaceuticals and other personal care products in groundwater beneath and adjacent to onsite wastewater treatment systems in a coastal plain shallow aquifer. Science of the Total Environment, 487, 216–223.
Dougherty, J. A., Swarzenski, P. W., Dinicola, R. S., & Reinhard, M. (2010). Occurrence of herbicides and pharmaceutical and personal care products in surface water and groundwater around Liberty Bay, Puget Sound, Washington. Journal of Environmental Quality, 39, 1173–1180.
Duffera, M., White, J. G., & Weisz, R. (2007). Spatial variability of southeastern US Coastal Plain soil physical properties: implications for site-specific management. Geoderma, 137, 327–339.
Ericson, H., Thorsén, G., & Kumblad, L. (2010). Physiological effects of diclofenac, ibuprofen and propranolol on Baltic Sea blue mussels. Aquatic Toxicology, 99, 223–231.
Estevez, E., Hernandez-Moreno, J. M., Fernandez-Vera, J. R., & Palacios-Diaz, M. P. (2014). Ibuprofen adsorption in four agricultural volcanic soils. Science of the Total Environment, 468, 406–414.
Gerstl, Z. (1990). Estimation of organic chemical sorption by soils. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 6, 357–375.
Guedidi, H., Reinert, L., Lévêque, J. M., Soneda, Y., Bellakhal, N., & Duclaux, L. (2013). The effects of the surface oxidation of activated carbon, the solution pH and the temperature on adsorption of ibuprofen. Carbon, 54, 432–443.
Halling-Sørensen, B., Nielsen, S. N., Lanzky, P. F., Ingerslev, F., Lützhøft, H. H., & Jørgensen, S. E. (1998). Occurrence, fate and effects of pharmaceutical substances in the environment—a review. Chemosphere, 36, 357–393.
Han, S., Choi, K., Kim, J., Ji, K., Kim, S., Ahn, B., & Giesy, J. P. (2010). Endocrine disruption and consequences of chronic exposure to ibuprofen in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) and freshwater cladocerans Daphnia magna and Moina macrocopa. Aquatic Toxicology, 98, 256–264.
Hansch, C., Rockwell, S. D., Jow, P. Y., Leo, A., & Steller, E. E. (1977). Substituent constants for correlation analysis. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 20, 304–306.
Heath, R. C. (1983). Basic ground-water hydrology. US Geological Survey.
Humphrey Jr, C. P. (2009). Controls on septic system wastewater treatment and shallow groundwater quality in coastal North Carolina. East Carolina University.
Karickhoff, S. W. (1984). Organic pollutant sorption in aquatic systems. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 110, 707–735.
Karickhoff, S. W., Brown, D. S., & Scott, T. A. (1979). Sorption of hydrophobic pollutants on natural sediments. Water Research, 13, 241–248.
Katsoyiannis, A., & Samara, C. (2007). The fate of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in the wastewater treatment process and its importance in the removal of wastewater contaminants. Environmental Science and Pollution Research-International, 14, 284–292.
Kenaga, E. E., & Goring, C. A. I. (1980). Relationship between water solubility, soil sorption, octanol-water partitioning, and concentration of chemicals in biota. Aquatic Toxicology, 707, 78–115.
Kolpin, D. W., Furlong, E. T., Meyer, M. T., Thurman, E. M., Zaugg, S. D., Barber, L. B., & Buxton, H. T. (2002). Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in US streams, 1999− 2000: a national reconnaissance. Environmental Science & Technology, 36, 1202–1211.
Langenhoff, A., Inderfurth, N., Veuskens, T., Schraa, G., Blokland, M., Kujawa-Roeleveld, K., & Rijnaarts, H. (2013). Microbial removal of the pharmaceutical compounds ibuprofen and diclofenac from wastewater. BioMed Research International. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/325806.
Maamar, M. B., Lesné, L., Hennig, K., Desdoits-Lethimonier, C., Kilcoyne, K. R., Coiffec, I., & Antignac, J. P. (2017). Ibuprofen results in alterations of human fetal testis development. Scientific Reports, 7, 44184.
NC DEHNR (1996). On-site wastewater management: guidance manual. Division of Environmental Health, On-Site Wastewater Section, Raleigh, NC. https://ehs.ncpublichealth.com/oswp/resources.htm. Accessed 27 Mar 2018.
Richardson, M. L., & Bowron, J. M. (1985). The fate of pharmaceutical chemicals in the aquatic environment. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 37, 1–12.
Sangster, J. (1989). Octanol-water partition coefficients of simple organic compounds. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 18, 1111–1229.
Schaider, L. A., Rodgers, K. M. & Rudel, R. A. (2017). Environmental Science & Technology, 51, 7304–7317.
Scheytt, T., Mersmann, P., Lindstädt, R., & Heberer, T. (2005a). Determination of sorption coefficients of pharmaceutically active substances carbamazepine, diclofenac, and ibuprofen, in sandy sediments. Chemosphere, 60, 245–253.
Scheytt, T., Mersmann, P., Lindstädt, R., & Heberer, T. (2005b). 1-Octanol/water partition coefficients of 5 pharmaceuticals from human medical care: carbamazepine, clofibric acid, diclofenac, ibuprofen, and propyphenazone. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 165, 3–11.
Scheytt, T. J., Mersmann, P., & Heberer, T. (2006). Mobility of pharmaceuticals carbamazepine, diclofenac, ibuprofen, and propyphenazone in miscible-displacement experiments. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 83, 53–69.
Schwarzenbach, R. P., & Westall, J. (1981). Transport of non-polar organic pollutants in a river water–groundwater infiltration system: a systematic approach. Studies in Environmental Science, 17, 569–574.
Schwarzenbach, R. P., Gschwend, P. M., & Imboden, D. M. (1993). Organic acids and bases: acidity constant and partitioning behavior. Environmental Organic Chemistry, 245–274.
Soller, D. R., & Mills, H. H. (1991). Surficial geology and geomorphology. In: W.J. Horton, V.A. Zullo (Eds.), The geology of the Carolinas. Carolina geological society fifteenth anniversary volume. (pp. 290–308). KNoxville: University of Tennessee Press.
Stuckey, J. L. (1965). North Carolina: its geology and mineral resources. Department of Conservation and Development.
Styszko, K., Sosnowska, K., Wojtanowicz, P., Gołaś, J., Gorecki, J., & Macherzynski, M. (2010). Sorption of ibuprofen on sediments from the Dobczyce (Southern Poland) drinking water reservoir. Archives of Environmental Protection, 36, 81–91.
Ternes, T., Bonerz, M., & Schmidt, T. (2001). Determination of neutral pharmaceuticals in wastewater and rivers by liquid chromatography–electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 938, 175–185.
Tesoriero, A. J., Spruill, T. B., & Eimers, J. L. (2004). Geochemistry of shallow ground water in coastal plain environments in the southeastern United States: implications for aquifer susceptibility. Applied Geochemistry, 19, 1471–1482.
Tixier, C., Singer, H. P., Oellers, S., & Müller, S. R. (2003). Occurrence and fate of carbamazepine, clofibric acid, diclofenac, ibuprofen, ketoprofen, and naproxen in surface waters. Environmental science & technology, 37, 1061–1068.
USDA. (2005). https://soilseries.sc.egov.usda.gov. Accessed 27 Mar 2018.
US EPA. (2002). Onsite wastewater treatment systems manual. Report #EPA/625/R-00/008. Washington, DC: Office of Water and Office of Research and Development.
Vulava, V. M., Cory, W. C., Murphey, V. L., & Ulmer, C. Z. (2016). Sorption, photodegradation, and chemical transformation of naproxen and ibuprofen in soils and water. The Science of the Total Environment, 565, 1063–1070.
Warren, N., Allan, I. J., Carter, J. E., House, W. A., & Parker, A. (2003). Pesticides and other micro-organic contaminants in freshwater sedimentary environments—a review. Applied Geochemistry, 18, 159–194.
Xu, J., Wu, L., & Chang, A. C. (2009). Degradation and adsorption of selected pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in agricultural soils. Chemosphere, 77, 1299–1305.
Yalkowsky, S. H., & Dannenfelser, R. M. (1992). Aquasol database of aqueous solubility. Tucson: College of Pharmacy, University of Arizona.
Yamamoto, H., Nakamura, Y., Moriguchi, S., Nakamura, Y., Honda, Y., Tamura, I., & Sekizawa, J. (2009). Persistence and partitioning of eight selected pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment: laboratory photolysis, biodegradation, and sorption experiments. Water Research, 43, 351–362.
Acknowledgements
East Carolina University’s Division of Research, Economic Development, and Engagement is acknowledged for providing funding to BB as part of ECU’s East-West Collaborative Research Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 3009 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitra, S., Benfield, B. Ibuprofen Sorption to Coastal Plain Soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 229, 295 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3900-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3900-4