Abstract
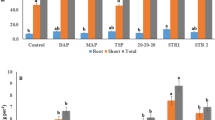
Water table depth manipulations as implemented in sugarcane fields of Southwestern Florida, USA, were hypothesized to influence the nutrient concentrations below the water table. Concentrations of phosphorus (P), potassium (K), nitrogen (N), and bromide (Br−) were monitored above and below the water table using a column leaching experiment. Three columns were packed with Immokalee soil (A, E, and Bh horizons) classified as a spodosol and fertilizers (NPK) were applied on the soil surface as solids using rates of 11 kg P ha−1, 166 kg K ha−1, and 200 kg N ha−1. A fourth column where fertilizer mixture and bromide were not added acted as a blank. Potassium was also applied as KBr with bromide used as tracer for water movement. Water table was maintained at 30 cm for 6 weeks and lowered to 50 cm deep for another 6 weeks. Samplers were placed in A, E, and Bh horizons and outlets were placed at 30 and 50 cm deep to obtain solutions for monitoring nutrients and tracer. Solution samplers placed in E and Bh horizons were located below the water table. Slightly elevated P, N, and K concentrations in E horizon for a 50-cm water table depth treatment were observed. For both water table treatments, minimal loss of applied N, P, and K below the water table was observed. The results of the study have shown that movement of nutrients below the water table is slow, and depends on the type of nutrients applied and the water table depth.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barber, S. A., Walker, J. M., & Vasey, E. H. (1963). Mechanisms for movement of plant nutrients from soil and fertilizer to plant root. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 11(3), 204–207.
Beigel, C., & Di Pietro, L. (1999). Transport of triticonazole in homogeneous soil columns: influence of nonequilibrium sorption. Soil Science Society of American Journal, 63, 1077–1086.
Bouldin, D. R., & Black, C. A. (1954). Phosphorus diffusion in soils. Soil Science Society of American Journal, 18(3), 255–259.
Divine, C. C., & McDonell, J. J. (2005). The future of applied tracers in hydrogeology. Hydrogeology Journal, 13, 255–258.
Elmi, A. A., Madramootoo, C., Egeh, M., Liu, A., & Hamel, C. (2002). Environmental and agronomic implications of water table and nitrogen fertilization management. Journal of Environmental Quality, 31, 1858–1867.
Fisher, L. H., & Healy, R. W. (2008). Water movement within the unsaturated zone in four agricultural areas of the United States. Journal of Environmental Quality, 37, 1051–1063.
Fortin, J., Gagnon-Batrand, E., Vezina, L., & Rompre, M. (2002). Preferential bromide and pesticide movement to tile drains under different cropping practices. Journal of Environmental Quality, 31, 1940–1952.
Glaz, B., & Morris, D. R. (2010). Sugarcane responses to water-table depth and periodic flood. Agronomy Journal, 102, 372–380.
Hefting, M., Clement, J. C., Dowrick, D., Cosandey, A. C., Bernal, S., Cimpian, C., Tatur, A., Burt, T. P., & Pinay, G. (2004). Water table elevation controls on soil nitrogen cycling in riparian wetlands along a European climatic gradient. Biogeochemistry, 67, 113–134.
Jellali, S., Diamantopoulos, E., Kallali, S., Bennaceur, S., Anane, M., & Jedid, N. (2010). Dynamic sorption of ammonium by sandy soil in fixed bed columns: evaluation of equilibrium and non-equilibrium transport processes. Journal of Environmental Management, 91, 897–905.
Kelly, W. R., & Wilson, S. D. (2000). Movement of bromide, nitrogen-15, and atrazine through flooded soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 29, 1085–1094.
Kliewer, B. A., & Gilliam, J. W. (1995). Water table management effects on denitrification and nitrous oxide evolution. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 59, 1694–1701.
Kookana, R. S., Schuller, R. D., & Aylmore, L. A. G. (1993). Simulation of simazine transport through soil columns using time-dependent sorption data measured under flow conditions. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 14, 93–115.
Lawrence, H. F., & Richard, W. H. (2008). Water movement within the unsaturated zone in four agricultural areas of the United States. Journal of Environmental Quality, 37, 1051–1063.
Li, Y. C., Alva, A. K., & Calvert, D. V. (1997). Transport of phosphorus and fractionation of residual phosphorus in various horizons of a Spodosol. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 109, 303–312.
Martin, H. W., Ivanoff, D. B., Graetz, D. A., & Reddy, K. R. (1997). Water table effects on Histosol drainage water carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus. Journal of Environmental Quality, 26(4), 1062–1071.
Obour, A. K., Silveira, M. L., Vendramini, J. M. B., Sollenberger, L. E., & O’Connor, G. A. (2011). Fluctuating water table effect on phosphorus release and availability from a Florida Spodosol. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 91, 207–217.
Obreza, T. A., Anderson, D. L., & Pitts, D. J. (1998). Water and nitrogen management of sugarcane growth on sandy, high-water-table soil. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 62, 992–999.
Pant, H. K., Nair, V. D., Reddy, K. R., Graetz, D. A., & Villapando, R. R. (2002). Influence of flooding on phosphorus mobility in manure-impacted soil. Journal of Environmental Quality, 31, 1399–1405.
Poulsen, T. G., Moldrup, P., de Jonge, L. W., & Komatsu, T. (2006). Colloid and bromide transport in undisturbed soil columns: application of two regional model. Vadose Zone Journal, 5, 649–656.
Reddy, K. R., Patrick, W. H., & Philips, R. E. (1976). Ammonium diffusion as a factor in nitrogen loss from flooded soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 40, 528–533.
Reddy, K. R., Patrick, W. H., & Broadbent, F. E. (1984). Nitrogen transformations and loss in flooded soils and sediments. CRC Critical Reviews in Environmental Control, 13(4), 273–309. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643388409381709.
Shackelford, C. D., & Daniel, D. E. (1991). Diffusion in saturated soil. I: Background. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 117(3), 467–484.
Shinde, D., Savabi, M. R., Nkedi-Kizza, P., & Vazquez, A. (2001). Modeling transport of atrazine through calcareous soils from South Florida. American Society of Agricultural Engineers, 44(2), 251–258.
Shokri, N., & Salvucci, G. D. (2011). Evaporation of porous media in the presence of a water table. Vadose Zone Journal, 10, 1309–1318.
USDA-NRCS. (1995). Soil survey laboratory manual. Washington, DC: USDA.
Villapando, R.R. (1997). Reactivity of inorganic phosphorus in the spodic horizon. PhD dissertation. University of Florida, Gainesville.
Villapando, R. R., & Graetz, D. A. (2001). Phosphorus and desorption properties of the spodic horizon from selected Florida Spodosols. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 65, 331–339.
Acknowledgements
We thank Florida Department of Environmental Regulation for funding the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muwamba, A., Nkedi-Kizza, P. & Morgan, K.T. Effect of Water Table Depth on Nutrient Concentrations Below the Water Table in a Spodosol. Water Air Soil Pollut 229, 83 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3727-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3727-z