Abstract
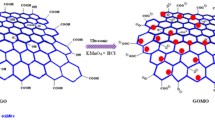
Nano zerovalent iron (nZVI) impregnated reduced graphene oxide (nZVI-rGO) hybrid was prepared via gaseous hydrogen reduction of anhydrous iron(III) chloride (FeCl3) on the surface of thermally exfoliated reduced graphene oxide (rGO) nanosheets without using any toxic reducing agent, surfactant, or stabilizing agent. Characterization of prepared samples was carried out using various techniques. Morphological study showed that prepared rGO possesses a few-layered wrinkled paper-like structures and nZVI particles of ~ 30 nm size were homogeneously dispersed on the surface of rGO nanosheets. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDS) analyses indicated that oxygen-containing functional groups decreased in the order of graphite oxide (GO) > rGO > nZVI-rGO. Removal studies of trinitrotoluene (TNT) were carried out using graphite (G), GO, rGO, and nZVI-rGO with the aid of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Kinetic models were applied to establish the rate and mechanism of adsorption of TNT on different adsorbents, and intraparticle diffusion model based on initial adsorption characteristics was employed to ascertain mechanism of film and intraparticle diffusion in the adsorption process. The removal rate and adsorption capacity was found to be highest for nZVI-rGO, which renders this adsorbent to be a potential futuristic adsorbent for removal of explosives.

ᅟ








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian, N. R., & Arnett, C. M. (2007). Anaerobic biotransformation of explosives in aquifer slurries amended with ethanol and propylene glycol. Chemosphere, 66, 1849–1856.
Agrawal, A., & Tratnyek, P. G. (1996). Reduction of nitro aromatic compounds by zero-valent iron metal. Environmental Science & Technology, 30, 153–160.
An, F., Feng, X., & Gao, B. (2009). Adsorption mechanism and property of a novel adsorption material PAM/SiO2 towards 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. J. Hazard.Mat., 168, 352–357.
Bao, Q., Zhang, D., & Qi, P. (2011). Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticle and graphene oxide nanosheet composites as a bactericidal agent for water disinfection. J. Colloid & Interface Sci., 360, 463–470.
Bernasconi, C. F. (1971). Kinetic and spectral study of some reactions of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene in basic solution. I. Deprotonation and Janovsky complex formation. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 36, 1671–1679.
Chung, T. V., Trung, L. Q., Minh, D. B., & Luong, N. V. (2010). Voltammetry study of the 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene conversion into the amine compounds using zero-valent iron. Analele Universităţii din Bucureşti–Chimie (serie nouă), 19, 53–59.
Chusova, O., Nõlvak, H., Odlare, M., Truu, J., Truu, M., Oopkaup, K., & Nehrenheim, E. (2015). Biotransformation of pink water TNT on the surface of a low-cost adsorbent pine bark. Biodegradation, 26, 375–386.
Crane, R. A., Dickinson, M., Popescu, I. C., & Scott, T. B. (2011). Magnetite and zero-valent iron nanoparticles for the remediation of uranium contaminated environmental water. Water Research, 45, 2931–2942.
Feidor, J. N., Bostick, W. D., Jarabek, R. J., & Farrell, J. (1998). Understanding the mechanism of uranium removal from groundwater by zero-valent iron using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Environmental Science & Technology, 32, 1466–1473.
Fu, D., Zhang, Y., Lv, F., Chu, P. K., & Shang, J. (2012). Removal of organic materials from TNT red water by bamboo charcoal adsorption. Chemical Engineering Journal, 193–194, 39–49.
Geng, B., Jin, Z., Li, T., & Qi, X. (2009). Preparation of chitosan-stabilized Fe(0) nanoparticles for removal of hexavalent chromium in water. Sci. Tot. Environ., 407, 4994–5000.
Guo, J., Wang, R., Tiju, W. W., Pan, J., & Liu, T. (2012). Synthesis of Fe nanoparticles@graphene composites for environmental applications. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 225–226, 63–73.
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (1998). Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chemical Engineering Journal, 70, 115–124.
Hu, P., Zhang, Y., Tong, K., Wei, F., An, Q., Wang, X., Chu, P. K., & Lv, F. (2015). Removal of organic pollutants from red water by magnetic-activated coke. Desalination and Water Treatment, 54, 2710–2722.
Hummers, S., & Offeman, R. E. (1958). Preparation of graphitic oxide. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 80, 1339.
Hundal, L. S., Singh, J., Bier, E. L., Shea, P. J., Comfort, S. D., & Powers, W. L. (1997). Removal of TNT and RDX from water and soil using iron metal. Environmental Pollution, 97, 55–64.
Jabeen, H., Chandra, V., Jung, S., Lee, J. W., Kim, K. S., & Bin Kim, S. (2011). Enhanced Cr(VI) removal using iron nanoparticles decorated graphene. Nanoscale, 3, 3583–3585.
Jiang, Z. M., Lu, L., Zhang, W., Du, Q., Pan, B., & Yang, L. (2011). Nitrate reduction using nanosized zero-valent iron supported by polystyrene resins: Role of surface functional groups. Water Research, 45, 2191–2198.
Joo, S. H., Feitz, A. J., & Waite, T. D. (2004). Oxidative degradation of the carbothioate herbicide, molinate, using nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environmental Science & Technology, 38, 2242–2247.
Kim, H., Hong, H. J., Jung, J., Kim, S. H., & Yang, J. W. (2010). Degradation of trichloroethylene (TCE) by nanoscalezero-valent iron (nZVI) immobilized in alginate bead. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 176, 1038–1043.
Kostogrud, I. A., Trusov, K. V., & Smovzh, D. V. (2016). Influence of gas mixture and temperature on AP-CVD synthesis of graphene on copper foil. Adv. Mat. Interfaces, 3, 1500823.
Lagergren, S. (1898). About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. K. Sven. Vetenskapsakad. Handl., 24, 1–39.
Laine, D. F., & Chang, I. F. (2007). The destruction of organic pollutants under mild reaction conditions: A review. Microchemical Journal, 85, 183–193.
Lee, J.-W., Yang, T.-H., Shim, W.-G., Kwon, T.-O., & Moon, I.-S. (2007). Equilibria and dynamics of liquid-phase trinitrotoluene adsorption on granular activated carbon: Effect of temperature and pH. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 141, 185–192.
Lee, K. B., Gu, M. B., & Moon, S. H. (2003). Degradation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene by immobilized horseradish peroxidase and electrogenerated peroxide. Water Research, 37, 983–992.
Leofanti, G., Padovan, M., Tozzola, G., & Venturelli, B. (1998). Surface area and pore texture of catalysts. Catalysis Today, 41, 207–219.
Li, B. J., Cao, H. Q., Shao, J., Qu, M. Z., & Warner, J. H. (2011). Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanocrystals@graphene composites for energy storage devices. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 21, 5069–5075.
Li, Y., Gao, W., Ci, L., Wang, C., & Ajayan, P. M. (2010). Catalytic performance of Pt nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide for methanol electro oxidation. Carbon, 48, 1124–1130.
Liou, M. C., Lu, M. C., & Chen, J. N. (2004). Oxidation of TNT by photo-Fenton process. Chemosphere, 57, 1107–1114.
Mangal, H., Saxena, A., Shukla, N., Rai, P. K., Rawat, A. S., Kumar, V., Gupta, V., & Datta, M. (2017). Zero valent metal loaded silica nanoparticles for the removal of TNT from water. Water Science & Technology, 75, 716–726.
Marcio, B. R., Silva, F. T., & Paiva, T. C. (2009). Combined zero-valent iron and Fenton processes for the treatment of Brazilian TNT industry wastewater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 165, 1224–1228.
Mills, P., & Sullivan, J. L. (1983). A study of the core level electrons in iron and its three oxides by means of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 16, 723–732.
Oladipo, A. A., & Gazi, M. (2014). Enhanced removal of crystal violet by low cost alginate/acid activated bentonite composite beads: Optimization and modelling using non-linear regression technique. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2, 43–52.
Oladipo, A. A., Gazi, M., & Yilmaz, E. (2015). Single and binary adsorption of azo and anthraquinone dyes by chitosan-based hydrogel: Selectivity factor and Box-Behnken process design. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 104, 264–279.
Panturu, R. L., Jinescu, G., Panturu, E., Filcenco-Olteanu, A., & Radulescu, R. (2010). Synthesis and characterization of zero valent iron intended to be used for decontamination of radioactive water. U.P.B.Sci Bull., 72, 1454–2331.
Park, C., Kim, T.-H., Kim, S., Kim, S.-W., Lee, J., & Kim, S.-H. (2003). Optimization for biodegradation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) by Pseudomonas putida. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 95, 567–571.
Peng, F., Luo, T., Qiu, L., & Yuan, Y. (2013). An easy method to synthesize graphene oxide–FeOOH composites and their potential application in water purification. Material Res Bull., 48, 2180–2185.
Pouretedal, H. R., Damiri, S., Alikhasti, M., & Mahmoodi, H. (2015). Treatment of TNT red water by chemical-modified carbon adsorbent prepared from cheap raw materials of pine tree wood. Desalination and Water: Treatment.
Rajagopal, C., & Kapoor, J. C. (2001). Development of adsorptive removal process for treatment of explosives contaminated wastewater using activated carbon. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 87, 73–98.
Ramesha, G. K., Vijaya Kumara, A., Muralidhara, H. B., & Sampath, S. (2011). Graphene and graphene oxide as effective adsorbents toward anionic and cationic dyes. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 361, 270–277.
Sarkar, S. K., Raul, K. K., Pradhan, S. S., Basu, S., & Nayak, A. (2014). Magnetic properties of graphite oxide and reduced graphene oxide. Physica E, 64, 78–82.
Stankovich, S., Dikin, D. A., Piner, R. D., Kohlhaas, K. A., Kleinhammes, A., Jia, Y., Wu, Y., Nguyen, S. T., & Ruoff, R. S. (2007). Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon, 45, 1558–1565.
Uenosono, S., Sonobe, A., & Sugihara, H. (2005). Method for producing sponge iron, and reduced iron powder and method for production thereof. US Patent US6918945 B2.
Wang, Q., Qian, H. J., Yang, Y. P., Zhang, Z., Naman, C., & Xu, X. H. (2010). Reduction of hexavalent chromium by carboxymethyl cellulose-stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 114, 35–42.
Weber Jr., W. J., & Morris, J. C. (1963). Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. Am. Soc Civil Engineering, 89.
Wei, F. F., Zhang, Y. H., Lv, F. Z., Chu, P. K., & Ye, Z. F. (2011). Extraction of organic materials from red water by metal-impregnated lignite activated carbon. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 197, 352–360.
Wu, F.-C., Tseng, R.-L., & Juang, R.-S. (2009). Initial behavior of intraparticle diffusion model used in the description of adsorption kinetics. Chemical Engineering Journal, 153, 1–8.
Xu, Z., Wen, Y., Tian, L., & Li, G. (2017). Efficient and selective adsorption of nitroaromatic explosives by Zr-MOF. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 77, 11–13.
Zhang, J., Lin, X., Luo, X., Zhang, C., & Zhu, H. (2011a). A modified lignin adsorbent for the removal of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. Chemical Engineering Journal, 168, 1055–1063.
Zhang, K., Dwivedi, V., Chi, C. Y., & Wu, J. S. (2010). Graphene oxide/ferric hydroxide composites for efficient arsenate removal from drinking water. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 182, 162–168.
Zhang, M. H., Zhao, Q. L., & Ye, Z. F. (2011b). Organic pollutants removal from 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) red water using low cost activated coke. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 23, 1962–1969.
Zhang, X., Lin, Y.-M., & Chen, Z.-L. (2009). 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene reduction kinetics in aqueous solution using nanoscale zero-valent iron. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 165, 923–927.
Zhang, Y., Su, Y., Zhou, X., Dai, C., & Keller, A. A. (2013). A new insight on the core-shell structure of zerovalent iron nanoparticles and its application for Pb(II) sequestration. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 263, 685–693.
Zhang, Y., Wei, F., Xing, J., Lv, F., Meng, X., & Chu, P. K. (2012). Adsorption behaviour and removal of organic materials from TNT red water by lignite activated carbon. J. Residuals Sci. & Technol., 9, 121–129.
Zheng, J. L., LI, J. W., & Chao, F. H. (2001). Study progress on aniline, nitrobenzene and TNT biodegradation. Microbiologica, 28, 85–88.
Zhu, H. J., Jia, Y. F., Wu, X., & Wang, H. (2009). Removal of arsenic from water by supported nano zero-valent iron on activated carbon. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172, 1591–1596.
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to the director of CFEES for his constant encouragement and support. We also express our gratitude to the director of SSPL for allowing us to use the XRD and Raman spectrometer and AIRF-JNU, Delhi, for the TEM analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 750 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bharti, Khurana, I., Shaw, A.K. et al. Removal of Trinitrotoluene with Nano Zerovalent Iron Impregnated Graphene Oxide. Water Air Soil Pollut 229, 17 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3664-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3664-2