Abstract
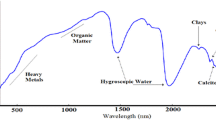
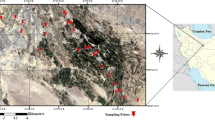
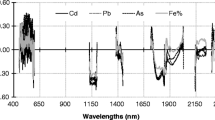
This study aimed to investigate the potency of soil reflectance spectroscopy in the visible and near infrared (Vis-NIR) spectral regions in estimating soil heavy metal pollution in the western coastal front of Thessaloniki (N. Greece) and how the protocol used for chemical analyses can affect the models’ performance. For this purpose, 49 topsoil samples were collected and the concentrations of Cd, Cr, Cu, and Pb were determined by two different analytical methods, i.e., ISO 11466 based on the technique of atomic absorbance spectrometry (AAS) and ISO 14869-1 using the technique of inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES). The spectral signatures were applied for modeling the metal concentrations by using the partial least squares regression (PLSR) method. To eliminate the “noise” of data and enhance the models’ accuracy, four spectral pre-treatment methods were used. The overall results showed that there is heavy metal pollution in the soils of specific areas in the studied region and that the use of different chemical analytical methods can affect the performance of examined prediction models. Better prediction models were created for the cases of Pb, Cu, and Cr concentrations, which were estimated by the application of ISO 14869-1, while for the case of Cd better prediction models were obtained, by the application of ISO 11466. These results may indicate that soil reflectance spectroscopy can measure the total heavy metal content in soil samples.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alloway, B. (1995). Heavy metals in soils: trace metals and metalloids in soils and their bioavailability. In Environmental Pollution (Third ed.). Dordrecht: Springer.
Ben Dor, E., Ong, C., & Lau, I. C. (2015). Reflectance measurements of soils in the laboratory: standards and protocols. Geoderma, 245–246, 112–124, ISSN 0016-7061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.01.002.
Bowers, S. A., & Hanks, R. J. (1965). Reflectance of radiant energy from soils. Soil Science, 100(2), 130–139.
Caporale, A. G., & Violante, A. (2016). Chemical processes affecting the mobility of heavy metals and metalloids in soil environments. Current Pollution Reports, 2(1), 15–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-015-0024-y.
Chandrasekaran, A., & Ravisankar, R. (2015). Spatial distribution of physico-chemical properties and function of heavy metals in soils of Yelagiri hills, Tamilnadu by energy dispersive X-ray florescence spectroscopy (EDXRF) with statistical approach. Spectrochimica Acta. Part A Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 150, 586–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2015.05.083.
Chen, T., Chang, Q., Clevers, J. G. P. W., & Kooistra, L. (2015). Rapid identification of soil cadmium pollution risk at regional scale based on visible and near-infrared spectroscopy. Environmental Pollution, 206, 217–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.07.009.
Christophoridis, C., Dedepsidis, D., & Fytianos, K. (2009). Occurrence and distribution of selected heavy metals in the surface sediments of Thermaikos Gulf, N. Greece. Assessment using pollution indicators. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168(2), 1082–1091.
Cozzolino, D. (2016). Near infrared spectroscopy as a tool to monitor contaminants in soil, sediments and water—state of the art, advantages and pitfalls. Trends in Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 9, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.teac.2015.10.001.
Dupuy, N., & Douay, F. (2001). Infrared and chemometrics study of the interaction between heavy metals and organic matter in soils. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 57(5), 1037–1047. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1386-1425(00)00420-0.
Duruibe, J. O., Ogwuegbu, M. O. C., & Egwurugwu, J. N. (2007). Heavy metal pollution and human biotoxic effects. International Journal of Physical Sciences, 2(5), 112–118 Retrieved from http://www.academicjournals.org/IJPS.
Ferrier, G., Hudson-Edwards, K. A., & Pope, R. J. (2009). Characterisation of the environmental impact of the Rodalquilar mine, Spain by ground-based reflectance spectroscopy. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 100(1), 11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2008.03.001.
Fuller, W.H. (1977). Movement of selected metals, asbestos, and cyanide in soil: applications to waste disposal problems. United States. National Technical Information Service. PB;(USA).
Gholizadeh, A., Borùvka, L., Saberioon, M. M., Kozák, J., Vašát, R., & Nemecek, K. (2015a). Comparing different data preprocessing methods for monitoring soil heavy metals based on soil spectral features. Soil and Water Research, 10(4), 218–227. 10.17221/113/2015-SWR.
Gholizadeh, A., Borùvka, L., Vašát, R., Saberioon, M., Klement, A., Kratina, J., & Drábek, O. (2015b). Estimation of potentially toxic elements contamination in anthropogenic soils on a brown coal mining dumpsite by reflectance spectroscopy: a case study. PLoS One, 10(2), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0117457.
Gore, R. D., Nimbhore, S. S., & Gawali, B. W. (2015). Understanding soil spectral signature through RS and GIS techniques. International Journal of Engineering Research and General Science, 3(6), 866–872.
Huang, W., Peng, P., Yu, Z., & Fu, J. (2003). Effects of organic matter heterogeneity on sorption and desorption of organic contaminants by soils and sediments. Applied Geochemistry, 18(7), 955–972. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00205-6.
ISO, Soil quality, extraction of trace elements soluble in aqua regia, ISO 11466, Geneva, 1995.
ISO, Soil quality, dissolution for the determination of total element content, part 1: dissolution with hydrofluoric and perchloric acids, ISO 14869-1, Geneva, 2001.
Jarvis, R. M., & Goodacre, R. (2005). Genetic algorithm optimization for pre-processing and variable selection of spectroscopic data. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England), 21(7), 860–868. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti102.
Jie, C., Jing-zhang, C., Man-zhi, T., & Zi-tong, G. (2002). Soil degradation: a global problem endangering sustainable development. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 12, 243–252. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02837480.
Kabata-Pendias, A., & Pendias, H. (2001). Trace elements in soils and plants. Boca Raton: CRC Press Inc.
Kooistra, L., Wehrens, R., Leuven, R. S. E., & Buydens, L. M. (2001). Possibilities of visible–near-infrared spectroscopy for the assessment of soil contamination in river floodplains. Analytica Chimica Acta, 446(1), 97–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(01)01265-X.
Lal, R., & Miller, F. P. (1989). Degradation: I. Basic processes. Land Degradation & Rehabilitation, 1(January), 51–69. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3400010106.
Lee, K. S., Sudduth, K. A., Drummond, S. T., Lee, D. H., Kitchen, N. R., & Chung, S. O. (2010). Calibration methods for soil property estimation using reflectance spectoscopy. American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, 53(3), 675–684.
Martens, H., & Martens, M. (2000). Modified Jack-knife estimation of parameter uncertainty in bilinear modelling by partial least squares regression (PLSR). Food Quality and Preference, 11(1–2), 5–16.
TemaNord 2009:549. (2009). Materials for construction of top cover in landfills, experience in the Nordic countries. Copenhagen: Nordic countries of Ministers.
McBratney, A. B., Minasny, B., & Viscarra Rossel, R. (2006). Spectral soil analysis and inference systems: a powerful combination for solving the soil data crisis. Geoderma, 136(1), 272–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2006.03.051.
National Gazette (Greece) 641/7.8.1991.
O’Rourke, S. M., & Holden, N. M. (2011). Optical sensing and chemometric analysis of soil organic carbon—a cost effective alternative to conventional laboratory methods? Soil Use and Management, 27(2), 143–155. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-2743.2011.00337.x.
Okrent, D. (1999). On intergenerational equity and its clash with intragenerational equity and on the need for policies to guide the regulation of disposal of wastes and other activities posing very long-term risks. Risk Analysis, 19(5), 877–901.
Pandit, C. M., Filippelli, G. M., & Li, L. (2010). Estimation of heavy-metal contamination in soil using reflectance spectroscopy and partial least-squares regression. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 31(15), 4111–4123. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160903229200.
Saeys, W., Mouazen, A. M., & Ramon, H. (2005). AE—automation and emerging technologies potential for onsite and online analysis of pig manure using visible and near infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Biosystems Engineering, 91(4), 393–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2005.05.001.
Schwartz, G., Eshel, G., & Ben-Dor, E. (2011). Reflectance spectroscopy as a tool for monitoring contaminated soils. In Soil Contamination, 67–90.
Shi, Z., Wang, Q., Peng, J., Ji, W., Liu, H., Li, X., & Rossel, R. A. V. (2014). Development of a national VNIR soil-spectral library for soil classification and prediction of organic matter concentrations. Science China. Earth Sciences, 57(7), 1671.
Soriano-Disla, J. M., Janik, L. J., Viscarra Rossel, R., Macdonald, L. M., & McLaughlin, M. J. (2014). The performance of visible, near and mid-infrared reflectance spectroscopy for prediction of soil physical, chemical, and biological properties. Applied Spectroscopy Reviews, 49(2), 139–186. https://doi.org/10.1080/05704928.2013.811081.
Stevenson, F. J. (1994). Humus chemistry: genesis, composition, reactions. Hoboken: Wiley.
Todorova, M., Mouazen, A. M., Lange, H., & Atanassova, S. (2014). Potential of near-infrared spectroscopy for measurement of heavy metals in soil as affected by calibration set size. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 225(8), 2036. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2036-4.
VROM. (2000). Circular on target values and intervention values for soil remediation. Netherlands Gov Gaz, 2000, 1–12.
Westad, F., & Martens, H. (2000). Variable selection in near infrared spectroscopy based on significance testing in partial least squares regression. Near Infrared Spectroscopy, 8, 117–124. https://doi.org/10.1255/jnirs.271.
Williams, P. (2004). Near-infrared technology: getting the best out of light: a short course in the practical implementation of near-infrared spectroscopy for the user. PDK Projects, Incorporated, UK.
Wold, S., Sjöström, M., & Eriksson, L. (2001). PLS-regression: a basic tool of chemometrics. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 58(2), 109–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-7439(01)00155-1.
Wu, Y., Chen, J., Wu, X., Tian, Q., Ji, J., & Qin, Z. (2005). Possibilities of reflectance spectroscopy for the assessment of contaminant elements in suburban soils. Applied Geochemistry, 20(6), 1051–1059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2005.01.009.
Wu, Y., Chen, J., Ji, J., Gong, P., Liao, Q., Tian, Q., & Ma, H. (2007). A mechanism study of reflectance spectroscopy for investigating heavy metals in soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 71(3), 918–926. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2006.0285.
Wu, J., Zhang, J., & Xiao, C. (2016). Focus on factors affecting pH, flow of Cr and transformation between Cr(VI) and Cr(III) in the soil with different electrolytes. Electrochimica Acta, 211, 652–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.06.048.
Yin, Y., Impellitteri, C. A., You, S. J., & Allen, H. E. (2002). The importance of organic matter distribution and extract soil:solution ratio on the desorption of heavy metals from soils. The Science of the Total Environment, 287(1–2), 107–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(01)01000-2.
Acknowledgements
This research was co-funded by the “Greece-The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia IPA Cross-Border Program” 2007–2013, under the frame of the project “Soil degradation assessment and rehabilitation strategies for sustainable land use planning” with the acronym TERRA-MED.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Angelopoulou, T., Dimitrakos, A., Terzopoulou, E. et al. Reflectance Spectroscopy (Vis-NIR) for Assessing Soil Heavy Metals Concentrations Determined by two Different Analytical Protocols, Based on ISO 11466 and ISO 14869-1. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 436 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3609-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3609-9