Abstract
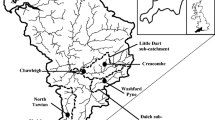
Vanadium has the potential to be released as a by-product of the combustion of fossil fuels such as oil and coal in the aquatic system. Presence of tailing ponds and other mining operations may pose the largest threat to downstream users and to the long-term aquatic health of the Mackenzie River Basin (MRB, Canada). The need for developing a solid baseline for the MRB aquatic ecosystem against which future changes can be measured is urgent. In this study, 36 sets of triplicate diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) samplers were deployed in MRB during the 2012–2014 ice-free seasons to investigate temporal and spatial changes in the concentration of DGT-labile vanadium (V) as part of a Northwest Territories community-based project. Average DGT-labile V concentration (5.9 ± 0.9 nmol L−1) was comparable with non-contaminated aquatic systems, suggesting no significant impact of human activities on V speciation in MRB in 2012–2014. The V concentrations reported in this study constitutes a baseline that can be used to enhance ongoing monitoring efforts. Although the DGT samplers were deployed in collaboration with northern communities, the absence of temporal changes in DGT-labile V indicated that in situ DGT passive samplers constitute a reliable and robust alternative for community-based monitoring programs. Excitation emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence combined with parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC) validated three humic-like (C1–C3) and one protein-like (C4) fluorescent component. However, no significant relationships were apparent between DGT-labile V and dissolved organic carbon (DOC), the PARAFAC loadings, and composition (p > 0.05). Hierarchical cluster analysis revealed that DGT-labile V concentration was negatively correlated with aromatic and humified DOM (r = − 0.70 to − 0.84, p < 0.05).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
AANDC (Aboriginal Affairs and Northern Development Canada). (2013). The Hay River—water monitoring activities in the Hay River region. Canada: The Minister of Aboriginal Affairs and Northern Development Canada ISBN: 978-1-100-233343-7.
AANDC (Aboriginal Affairs and Northern Development Canada) (2015). Mineral tenure map viewer. Retrieved on Sep 24, 2014 from https://www.aadnc-aandc.gc.ca/eng/1100100023768/1100100023772.
Balch, J. P., & Guéguen, C. (2015). Effects of molecular weight on the diffusion coefficient of aquatic dissolved organic matter and humic substances. Chemosphere, 119, 498–503.
Bhatnagar, A., Minocha, A. K., Pudasainee, D., Chung, H., Kim, S., Lee, G., Min, B., & Jeon, B. (2008). Vanadium removal from water by waste metal sludge and cement immobilization. Chemical Engineering Journal, 144, 197–204.
Birdwell, J. E., & Engel, A. S. (2010). Characterization of dissolved organic matter in cave and spring waters using UV–Vis absorbance and fluorescence spectroscopy. Organic Geochemistry, 41(3), 270–280.
Bone, R. M., & Mahnic, R. J. (1984). Norman wells: the oil center of the northwest territories. Arctic, 37(1), 53–60.
CEPA (2016). A Canadian environmental protection act, 1999. Federal environmental quality guidelines, vanadium. Environment and Climate Change Canada. http://www.ec.gc.ca/ese-ees/default.asp?lang=En&n=48D3A655-. Accessed 17 Oct 2017.
Chin, Y. P., Aiken, G., & O’Loughlin, E. (1994). Molecular weight, polydispersity, and spectroscopic properties of aquatic humic substances. Environmental Science & Technology, 28, 1853–1858.
Coble, P. G. (1996). Characterization of marine and terrestrial DOM in seawater using excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy. Marine Chemistry 51, 325–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4203(95)00062-3.
Coble, P. G. (2007). Marine optical biogeochemistry: the chemistry of ocean color. Chemical Reviews, 107, 402–418.
Cuss, C., & Guéguen, C. (2015). Relationships between molecular weight and fluorescence properties for size-fractionated dissolved organic matter from fresh and aged sources. Water Research, 68, 487–497.
Davison, W., & Zhang, H. (1994). In situ speciation measurements of trace components in natural waters using thin-film gels. Nature, 367, 546–548.
Debenest, T., Turcotte, P., Gagné, F., Gagnon, C., & Blaise, C. (2012). Ecotoxicological impacts of effluents generated by oil sands bitumen extraction and oil sands lixiviation on Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Aquatic Toxicology, 112-113, 83–89.
Degryse, F., & Smolders, E. (2016). DGT and bioavailability. In W. Davison (Ed.), Diffusive gradients in thin films for environmental measurements (pp. 216–263). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Dong, Q., Li, P., Huang, Q., Abdelhafez, A. A., & Chen, L. (2014). Occurrence, polarity and bioavailability of dissolved organic matter in the Huangpu River, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 26, 1843–1850.
Evans, H. T., & Landergran, S. (1975). Vanadium. In K. H. Wedepohl (Ed.), Handbook of geochemistry, chap. 23. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
García, E. M., Cruz-Motta, J. J., Farina, O., & Bastidas, C. (2008). Anthropogenic influences on heavy metals across marine habitats in the western coast of Venezuela. Continental Shelf Research, 28, 2757–2766.
Gu, Q., & Kenny, J. E. (2009). Improvement of inner filter effect correction based on determination of effective geometric parameters using a conventional fluorimeter. Analytical Chemistry, 81, 420–426.
Guéguen, C., & Cuss, C. (2011). Characterization of aquatic dissolved organic matter by asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation coupled to UV–Visible diode array and excitation emission matrix fluorescence. Journal of Chromatography. A, 1218, 4188–4198.
Guéguen, C., Guo, L., Wang, D., Tanaka, N., & Hung, C. C. (2005a). Chemical characteristics and origin of dissolved organic matter in the Yukon River. Biogeochem., 77, 139–155.
Guéguen, C., Guo, L., & Tanaka, N. (2005b). Distributions and characteristics of colored dissolved organic matter in the western Arctic Ocean. Continental Shelf Research, 25, 1195–1207.
Guo, L., Cai, Y., Belzile, C., & Macdonald, R. W. (2012). Sources and export fluxes of inorganic and organic carbon and nutrient species from the seasonally ice-covered Yukon River. Biogeochemistry, 107, 187–206.
Hadlari, T. (2015). Oil migration driven by exhumation of the Canol formation oil shale: A new conceptual model for the Norman wells oil field, northwestern Canada. Marine and Petroleum Geology , 65, 172–177.
Helms, J. R., Stubbins, A., Ritchie, J. D., Minor, E. C., Kieber, D. J., & Mopper, K. (2008). Absorption spectral slopes and slope ratios as indicators of molecular weight, source, and photobleaching of chromophoric dissolved organic matter. Limnology and Oceanography, 53, 955–969.
Hong, H., Yang, L., Guo, W., Wang, F., & Yu, X. (2012). Characterization of dissolved organic matter under contrasting hydrologic regimes in a subtropical watershed using PARAFAC model. Biogeochemistry, 109, 163–174.
Hope, B. K. (1997). An assessment of the global impact of anthropogenic vanadium. Biogeochemistry, 37, 1–13.
Huguet, A., Vacher, L., Relexans, S., Saubusse, S., Froidefond, J. M., & Parlanti, E. (2009). Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde estuary. Organic Geochemistry, 40, 706–719.
Johannesson, K. H., Lyons, W. B., Graham, E. Y., & Welch, K. A. (2000). Oxyanion concentrations in eastern Sierra Nevada rivers—3. Boron, molybdenum, vanadium, and tungsten. Aquatic Geochemistry, 6, 19–46.
Kelly, E. N., Schindler, D. W., Hodson, P. V., Short, J. W., Radmanovich, R., & Nielsen, C. C. (2010). Oil sands development contributes elements toxic at low concentrations to the Athabasca River and its tributaries. PNAS, 107, 16178–16183.
Khalaf, F., Literathy, V., & Anderlini, V. (1982). Vanadium as a tracer of oil pollution in the sediments of Kuwait. Hydrobiologia, 91 - 92, 147–154.
Kirk, J. L., Muir, D. C. G., Gleason, A., Wang, X., Lawson, G., Frank, R. A., Lehnherr, I., & Wrona, F. (2014). Atmospheric deposition of mercury and methylmercury to landscapes and waterbodies of the Athabasca oil sands region. Environmental Science & Technology, 48, 7374–7383.
Kothawala, D. N., Stedmon, C. A., Muller, R. A., Weyhenmeyer, G. A., Kohler, S. J., & Tranvik, L. J. (2013). Controls of dissolved organic matter quality: evidence from a large-scale boreal lake survey. Global Change Biology, 20, 1101–1114.
Lacelle, D., Bjornson, J., & Lauriol, B. (2010). Climatic and geomorphic factors affecting contemporary (1950 - 2004) activity of retrogressive thaw slumpson the Aklavik plateau, Richardson Mountains, NWT, Canada. Permafrost and Periglacial Processes, 21, 1–15.
Lacelle, D., Brooker, A., Fraser, R. H., & Kokelj, S. V. (2015). Distribution and growth of thaw slumps in the Richardson Mountains—Peel Plateau region, northwestern Canada. Geomorphology, 235, 40–51.
Lawaetz, A. J., & Stedmon, C. A. (2009). Fluorescence intensity calibration using the Raman scatter peak of water. Applied Spectroscopy, 63, 936–940.
Legendre, P. 2014. lmodel2: model II regression. R package version 1.7–2. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=lmodel2.
Luo, J., Zhang, H., Santner, J., & Davison, W. (2010). Performance characteristics of diffusive gradients in thin films equipped with a binding gel layer containing precipitated Ferrihydrite for measuring arsenic(V), selenium(VI), vanadium(V), and antimony(V). Analytical Chemistry, 82, 8903–8909.
Mangal, V., Zhu, Y., Shi, Y. X., & Guéguen, C. (2016). Assessing cadmium and vanadium accumulation using diffusive gradient in thin-films (DGT) and phytoplankton in the Churchill River estuary, Manitoba. Chemosphere, 163, 90–98.
McBride, M. B., & Cherney, J. (2004). Molybdenum, sulfur, and other trace elements in farm soils and forages after sewage sludge application. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 35, 517–535.
Moskalyk, R. R., & Alfanti, A. M. (2003). Processing of vanadium: a review. Minerals Engineering, 16, 793–805.
Mostofa, K. M. G., Wu, F., Liu, C., Fang, W. L., Yuan, J., Ying, W. L., Wen, L., & Yi, M. (2010). Characterization of Nanming River (southwestern China) sewerage-impacted pollution using an excitation-emission matrix and PARAFAC. Limnology, 11, 217–231.
Murphy, K. R., Stedmon, C. A., Wenig, P., & Bro, R. (2014). OpenFluor—an online spectral library of auto-fluorescence by organic compounds in the environment. Analytical Methods, 6, 658–661.
Naeem, A., Westerhoff, P., & Mustafa, S. (2007). Vanadium removal by metal (hydr)oxide adsorbents. Water Research, 41, 1596–1602.
Nguyen, H. V., Hur, J., & Shin, H. (2010). Changes in spectroscopic and molecular weight characteristics of dissolved organic matter in a river during a storm event. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 212, 395–406.
Nimick, D. A., Gammons, C. H., Cleasby, T. E., Madison, J. P., Skaar, D., & Brick, C. M. (2003). Diel cycles in dissolved metal concentrations in streams: occurrence and possible causes. Water Resources Research, 39, 1247–1283.
Ohno, T., Chorover, J., Omoike, A., & Hunt, J. (2007). Molecular weight and humification index as predictors of adsorption for plant- and manure-derived dissolved organic matter to goethite. European Journal of Soil Science, 58, 125–132.
Österlund, H., Chlot, S., Faarinen, M., Widerlund, A., Rodushkin, I., Ingri, J., & Baxter, D. C. (2010). Simultaneous measurements of As, Mo, Sb, V and W using a ferrihydrite diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) device. Analytica Chimica Acta, 682, 59–65.
Pinedo-Gonzalez, P., West, A. J., Rivera-Duarte, I., & Sanudo-Wilhelmy, S. A. (2014). Diel changes in trace metal concentration and distribution in coastal waters: Catalina Island as a study case. Environmental Science & Technology, 48, 7730–7737.
Pourret, O., Dia, A., Gruau, G., Davranche, M., & Coz, M. B. (2012). Assessment of vanadium distribution in shallow groundwaters. Chemical Geology, 294-295, 89–102.
Price, H. L., Teasdale, P. R., & Jolley, D. F. (2013). An evaluation of ferrihydrite- and Metsorb- DGT techniques for measuring oxyanion species (As, Se, V, P): effective capacity, competition and diffusion coefficients. Analytica Chimica Acta, 803, 56–65.
Rühling, A., & Tyler, G. (2001). Changes in atmospheric deposition rates of heavy metals in Sweden. A summary of Nationwide Swedish surveys in 1968/70-1995. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, Focus 1, 311–323.
Scally, S., Davison, W., & Zhang, H. (2003). In situ measurements of dissociation kinetics and labilities of metal complexes in solution using DGT. Environmental Science & Technology, 37, 1379–1384.
Shi, Y. X., Mangal, V., & Guéguen, C. (2016). Influence of dissolved organic matter on dissolved vanadium speciation in the Churchill River estuary (Manitoba, Canada). Chemosphere, 154(367–509), 374.
Shiller, A. M., & Boyle, E. A. (1987). Dissolved vanadium in rivers and estuaries. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 86, 214–224.
Shiller, A. M., & Mao, L. (1999). Dissolved vanadium on the Louisiana shelf: effect of oxygen depletion. Continental Shelf Research, 19, 1007–1020.
Shiller, A. M., & Mao, L. (2000). Dissolved vanadium in rivers: effects of silicate weathering. Chemical Geology, 165, 13–22.
Shotyk, W., Bicalho, B., Cuss, C. W., Donner, M. W., Grant-Weaver, I., Haas-Neill, S., Javed, M. B., Krachler, M., Noernberg, T., Pelletier, R., & Zaccone, C. (2009). Trace metals in the dissolved fraction (<0.45 μm) of the lower Athabasca river: analytical challenges and environmental implications. The Science of the Total Environment, 580, 660–669.
Shutova, Y., Baker, A., Bridgeman, J., & Henderson, R. K. (2014). Spectroscopic characterisation of dissolved organic matter changes in drinking water treatment: from PARAFAC analysis to online monitoring wavelengths. Water Research, 54, 159–169.
Spencer, R. G. M., Aiken, G. R., Butler, K. D., Dornblaser, M. M., Striegl, R. G., & Hernes, P. J. (2009). Utilizing chromophoric dissolved organic matter measurements to derive export and reactivity of dissolved organic carbon exported to the Arctic Ocean: a case study of the Yukon River, Alaska. Geophysical Research Letters, 36, L06401. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GL036831.
Stedmon, C. A., & Bro, R. (2008). Characterizing dissolved organic matter fluorescence with parallel factor analysis: a tutorial. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods, 6, 572–579.
Stedmon, C. A., Amon, R. M. W., Rinehart, A. J., & Walker, S. A. (2011). The supply and characterisctics of colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in the Arctic Ocean: pan Arctic trends and differences. Marine Chemistry, 124, 108–118.
Stern, A., Yin, X. F., Tsang, S. S., Davison, A., & Moon, J. (1993). Vanadium as a modulator of cellular regulatory cascades and oncogene expression. Biochemistry and Cell Biology, 71, 103.
Suter, G.W. II, Tsao, C.L. (1996). Toxicological benchmarks for screening potential contaminants of concern for effects on aquatic biota: 1996 revision. ES/ER/TM-96/R2. https://rais.ornl.gov/documents/tm96r2.pdf
Tercier-Waeber, M., Hezard, T., Masson, M., & Schäfer, J. (2009). In situ monitoring of the diurnal cycling of dynamic metal species in a stream under contrasting photobenthic biofilm activity and hydrological conditions. Environmental Science & Technology, 43, 7237–7244.
Uribe, R., Mongrin, S., Puy, J., Cecilia, J., Galceran, J., Zhang, H., & Davison, W. (2011). Contribution of partially labile complexes to the DGT metal flux. Environmental Science & Technology, 45, 5317–5322.
Wällstedt, T., Björkvald, L., & Gustafsson, J. P. (2010). Increasing concentrations of arsenic and vanadium in (southern) Swedish streams. Applied Geochemistry, 25, 1162–1175.
Zhang, H., & Davison, W. (1995). Performance characteristics of the technique of diffusion gradients in thin-films (DGT) for the measurement of trace metals in aqueous solution. Analytical Chemistry, 67, 3391–3400.
Zhang, H., & Davison, W. (1999). Diffusional characteristics of hydrogels used in DGT and DET techniques. Analytica Chimica Acta, 398, 329–340.
Zhang, Y., Gao, G., Shi, K., Niu, C., Zhou, Y., Qin, B., & Liu, X. (2014). Absorption and fluorescence characteristics of rainwater CDOM and contribution to Lake Taihu, China. Atmospheric Environment , 98, 483–491.
Zhu, Y., & Guéguen, C. (2016). Evaluation of free/labile concentrations of trace metals in Athabasca oil sands region streams (Alberta, Canada) using diffusive gradient in thin films and a thermodynamic equilibrium model. Environmental Pollution , 219, 1140–1147.
Acknowledgements
The study would not have been possible without the Department of Environment and Natural Resources, Government of the Northwest Territories Community-based Water Quality Monitoring Program staff and community water monitors. We particularly thank Yu Zhu and Antoine Perroud for the DGT preparation and analyses. We would like to thank the anonymous reviewer for the helpful comments on this manuscript.
Funding
Financial support for this study was awarded from NSERC and Canada Research Chair program and from Northwest Territories Cumulative Impact Monitoring Program (CIMP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y.X., Guéguen, C. In Situ Monitoring of Labile Vanadium in the Mackenzie River Basin (Canada) Using Diffusive Gradients in Thin Films. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 420 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3573-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3573-4