Abstract
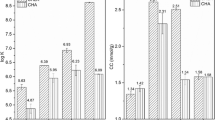
The increase in demand for food due to the rapid population growth in recent years has raised the use of fertilizers, particularly phosphate salts. This fact has contributed to the excess amount of phosphorus species in aquatic systems. This is due to the leaching of these species present in the fertilizers applied to the soil to aquatic environments and may lead to eutrophication in these environments. Substances capable of interacting with the phosphate in the aquatic environment are promising for the reduction on the environmental impact. The humin, an insoluble fraction of humic material, has potential for phosphate retention, behaving like a chelating resin. Thus, the purpose of this research was to study the interaction between humin and phosphate. The equilibrium time between humin and phosphate was 15 min, where hydrogenionic potential (pH) 4.0 was the most effective in the interaction process. In this pH, the humin retained 33% of phosphate added. The complexing capacity of the humin-phosphate system was 11.53 mg g−1. The adsorption studies indicated that the system follows a kinetic pseudo-second-order model. The Freundlich model was the most suitable to describe the phosphate adsorption process in humin. To evaluate the humin application in real systems, humin was added to the domestic wastewater. Sixteen percent of the total phosphate was adsorbed by the humin. Based on these results, humin has the potential to phosphate retention in domestic wastewater and could be used as a chelating resin minimizing environmental impact.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azizian, S. (2004). Kinetic models of sorption: a theoretical analysis. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 276(1), 45–52.
Bagda, E., Ersan, M., & Bagda, E. (2013). Investigation of adsorptive removal of tetracycline with sponge like, Rosa canina gall extract modified, polyacrylamide cryogels. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 1(4), 1079–1084.
Batista, A. P. S., Romão, L. P. C., & Arguelho, M. L. P. M. (2009). Biosorption of Cr(III) using in natura and chemically treated tropical peats. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163(2), 517–523.
Borggaard, O. K., Raben-Lange, B., Gimsing, A. L., & Strobel, B. W. (2005). Influence of humic substances on phosphate adsorption by aluminium and iron oxides. Geoderma, 127(3–4), 270–279.
Botero, W. G., Oliveira, L. C., Rocha, J. C., Rosa, A. H., & Santos, A. (2010). Peat humic substances enriched with nutrients for agricultural applications: competition between nutrients and non-essential metals present in tropical soils. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 177(1–3), 307–311.
Botero, W. G., Oliveira, L. C., Cavagis, A. D. M., Rosa, A. H., Rocha, J. C., & Santos, A. (2013). Influence of the extractant on the complexing capacity of humic substances from peat for macro and micronutrients using continuous flow: agricultural application and environmental impacts. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 24(12), 2015–2020.
Brasil (2011). Resolution CONAMA 430/2011. http://www.mma.gov.br/port/conama. Accessed 10.11.16.
Buffle, J., & Staub, C. (1984). Measurement of complexation properties of metal-ions in natural conditions by ultrafiltration—measurement of equilibrium-constants for complexation of zinc by synthetic and natural ligands. Analytical Chemistry, 56(14), 2837–2842.
Burba, P., Van Den Bergh, J., & Klockow, D. (2001). On-site characterization of humic-rich hydrocolloids and their metal loads by means of mobile size-fractionation and exchange techniques. Fresenius Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 371(5), 660–669.
Cerqueira, S. C. A., Romao, L. P. C., Lucas, S. C. O., Fraga, L. E., Simoes, M. L., Hammer, P., Lead, J. R., Mangoni, A. P., & Mangrich, A. S. (2012). Spectroscopic characterization of the reduction and removal of chromium (VI) by tropical peat and humin. Fuel, 91(1), 141–146.
Contreras, C., De La Rosa, G., Peralta-Videa, J. R., & Gardea-Torresdey, J. L. (2006). Lead adsorption by silica-immobilized humin under flow and batch conditions: assessment of flow rate and calcium and magnesium interference. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 133(1–3), 79–84.
Cunha, G. C., Goveia, D., Romao, L. P. C., & Oliveira, L. C. (2015). Effect of the competition of Cu(II) and Ni(II) on the kinetic and thermodynamic stabilities of Cr(III)-organic ligand complexes using competitive ligand exchange (EDTA). Journal of Environmental Management, 154, 259–265.
De La Rosa, G., Peralta-Videa, J. R., & Gardea-Torresdey, J. L. (2003). Utilization of ICP/determination of volatile organic compounds in drinking water. Chemosphere, 45(3), 275–284.
Freundlich, H. M. F. (1906). Over the adsorption in solution. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 57, 385–470.
Goveia, D., Melo, C. D. A., Oliveira, L. K. D., Fraceto, L. F., Rocha, J. C., Dias Filho, N. L., & Rosa, A. H. (2013). Adsorption and release of micronutrients by humin extracted from peat samples. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 24(5), 721–730.
Guedes, R. S., Melo, L. C. A., Vergutz, L., Rodriguez-Vila, A., Covelo, E. F., & Fernandes, A. R. (2016). Adsorption and desorption kinetics and phosphorus hysteresis in highly weathered soil by stirred flow chamber experiments. Soil and Tillage Research, 162, 46–54.
Gustafsson, J.P. (2016). Visual MINTEQ, ver. 3.1. Stockholm: Royal Institute of Technology, Div. of Land and Water Resources Engineering. Available at: https://vminteq.lwr.kth.se/visual-minteq-ver-3-1/.
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (1999). The sorption of lead(II) ions on peat. Water Research, 33(2), 578–584.
Ho, Y. S., Ng, J. C. Y., & McKay, G. (2000). Kinetics of pollutant sorption by biosorbents: review. Separation and Purification Methods, 29(2), 189–232.
Jacundino, J. S., Santos, O. S., Santos, J. C. C., Botero, W. G., Goveia, D., Carmo, J. B., & Oliveira, L. C. (2015). Interactions between humin and potentially toxic metals: Prospects for its utilization as an environmental repair agent. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 3(2), 708–715.
Lai, L., Xie, Q., Chi, L., Gu, W., & Wu, D. (2016). Adsorption of phosphate from water by easily separable Fe3O4@SiO2 core/shell magnetic nanoparticles functionalized with hydrous lanthanum oxide. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 465, 76–82.
Langmuir, I. (1916). The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I. Solids. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 38, 2221–2295.
Manahan, S., & Manahan, S. E. (2009). Environmental chemistry. New York: Press Taylor & Francis.
Mezenner, N. Y., & Bensmaili, A. (2009). Kinetics and thermodynamic study of phosphate adsorption on iron hydroxide-eggshell waste. Chemical Engineering Journal, 147(2–3), 87–96.
Millier, H. K. G. R., & Hooda, P. S. (2011). Phosphorus species and fractionation e why sewage derived phosphorus is a problem. Journal of Environmental Management, 92(4), 1210–1214.
Ninfant’eva, T. I., Shkinev, V. M., Spivakov, B. Y., & Burba, P. (1999). Membrane filtration studies of aquatic humic substances and their metal species: a concise overview. Part 2. Evaluation of conditional stability constants by using ultrafiltration. Talanta, 48(2), 257–267.
Nkhili, E., Guyot, G., Vassal, N., & Richard, C. (2012). Extractability of water-soluble soil organic matter as monitored by spectroscopic and chromatographic analyses. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 19(6), 2400–2407.
Paula Filho, F. J., Marins, R. V. (2004). Distribuição e partição geoquímica de fósforo em sedimentos estaurinos do rio Jaguaribe/CE – Fortaleza-CE. http://www.repositorio.ufc.br/handle/riufc/1311. Accessed 20 June 2016.
Raij, B. V., Quaggio, J. A., Cantarella, H., Ferreira, M. E., Lopes, A. S., Bataglia, O. C. (1987). Análise química do solo para fins de fertilidade. Campinas: Fundação Cargill.
Rice, J. (2001). Humin. Soil Science, 166(11), 848–857.
Rocha, J. C., Rosa, A. H., & Cardoso, A. A. (2009). Introduction to environmental chemistry. Porto Alegre: Bookman.
Rodrigues, L. A., & Silva, M. L. C. P. (2009). Adsorption of phosphate ions on hydrous niobium oxide. Quimica Nova, 32(5), 1206–1211.
Romao, L. P. C., Castro, G. R., Rosa, A. H., Rocha, J. C., Padilha, P. M., & Silva, H. C. (2003). Tangencial flow ultrafiltration: a versatile metodology for determination of complexation parameters in refractory organic matter from brazilian water and soil samples. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 375(8), 1097–1100.
Rosa, A. H., Rocha, J. C., & Furlan, M. (2000). Humic substances of peat: study of the parameters that influence on the process of alkaline e extraction. Quimica Nova, 23(4), 472–476.
Rosa, A. H., Goveia, D., Bellin, I. C., Lessa, S. S., Dias Filho, N. L., & Padilha, P. M. (2006). New analytical procedure based on cellulose bag and ion exchanger with p-aminobenzoic groups for differentiation of labile and inert metals species in aquatic systems. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 386(7–8), 2153–2160.
Sakadevan, K., & Bavor, H. J. (1998). Phosphate adsorption characteristics of soils, slags and zeolite to be used as substrates in constructed wetland systems. Water Research, 32(2), 393–399.
Sargentini Jr., E., Rocha, J. C., Rosa, A. H., Zara, L. F., & Santos, A. (2001). Aquatic humic substances: molecular size fractionation and characterization of inner rearrangements after metal ions complexation. Química Nova, 24(3), 399–344.
Souza, S. O., Oliveira, L. C., Cavagis, A. D. M., & Botero, W. G. (2014). Cyanogenic residues: environmental impacts, complexation with humic substances, and possible application as biofertilizer. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 225, 2223–2233.
Souza, S. O., Silva, M. M., Santos, J. C. C., Oliveira, L. C., Carmo, J. B., & Botero, W. G. (2016). Evaluation of different fractions of the organic matter of peat on tetracycline retention in the environmental conditions: in vitro studies. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 16(6), 1764–1775.
Standard Methods for the Examination of Water & Wastewater (2005). New York: American Public Health Association.
Voudrias, E., Fytianos, K., & Bozani, E. (2002). Sorption desorption isotherms of dyes from aqueous solutions and wastewaters with different sorbent materials. Global NEST Journal, 4(1), 75–83.
Wan Ngah, W. S., Endud, C. S., & Mayanar, R. (2002). Removal of copper (II) ions from solution onto chitosan and cross-linked chitosan beads. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 50(2), 181–190.
Winarso, S., Sulistyanto, D., & Handayanto, E. (2011). Effects of humic compounds and phosphate solubilizing bacteria on phosphorus availability in an acid soil. Journal of Ecology and the Natural Environment, 3(7), 232–240.
Yan, L., Xu, Y., Yu, H., Xin, X., Wei, Q., & Du, B. (2010). Adsorption of phosphate from aqueous solution by hydroxy-aluminum, hydroxy-iron and hydroxy-iron–aluminum pillared bentonites. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 179(1–3), 244–250.
Zamparas, M., Drosos, M., Georgiou, Y., Deligiannakis, Y., & Zacharias, I. (2013). A novel bentonite-humic acid composite material Bephos™ for removal of phosphate and ammonium from eutrophic waters. Chemical Engineering Journal, 225(1), 43–51.
Zhang, J., He, M., & Shi, Y. (2009). Comparative sorption of benzo[α]phrene to different humic acids and humin in sediments. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 166(2–3), 802–809.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq Process 478361/2013-0) for the financial support provided.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Oliveira, D.A.V., Botero, W.G., Santos, J.C.C. et al. Interaction Study Between Humin and Phosphate: Possible Environmental Remediation for Domestic Wastewater. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 265 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3447-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3447-9