Abstract
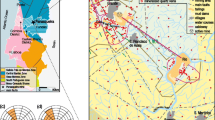
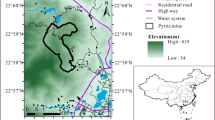
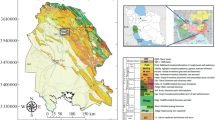
On November 5, 2015, after the collapse of the Fundão tailings dam, a massive amount of iron mine waste was released into the Doce River system in southeast Brazil. The aim of our study was to determine the mass fractions of potentially toxic elements in soil affected by the deposition of material by the waste wave. A preliminary screening was performed with portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (PXRF) and principal component analysis (PCA). The EPA 3050B method was further applied to digest the samples for quantitative determination of As, Ba, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb, V, and Zn by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. PCA was useful to classify the mine waste samples based on the Fe signal from the PXRF spectra, in spite of the heterogeneous nature of the material discharged into the Doce River system. The anomalous levels of As (up to 164 mg kg−1) and Mn (as high as 2410 mg kg−1) found in some mine waste and affected soil samples are within the background ranges typically observed in the soils of the Iron Quadrangle region. The toxicity characteristic leaching procedure shows no evidence of hazards regarding As, but a high natural background level of Mn was found in the mobile fraction. This preliminary environmental assessment highlights the importance of evaluation of long-term effects on soil directly impacted, as well as on the aquatic biota of the Doce River system and adjacent coastal environment given the large affected area, which includes regions with varying background levels of toxic elements.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azam, S., & Li, Q. (2010). Tailings dam failures: a review of the last one hundred years, Geotechnical News, December, 50–53.
Bird, G., Brewer, P. A., Macklin, M. G., Balteanu, D., Serban, M., Driga, B., & Zaharia, S. (2008). River system recovery following the Novaţ-Roşu tailings dam failure, Maramureş County, Romania. Applied Geochemistry, 23, 3498–3518.
Ciszewski, D., & Grygar, T. M. (2016). A review of flood-related storage and remobilization of heavy metal pollutants in river systems. Water, Air & Soil Pollution, 227, 239–257.
Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente (CONAMA). Resolução n° 357, de 17 de março de (2005). Publicada no DOU n° 053, de 18/03/2005, pag. 58–63.
Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente (CONAMA). Resolução n° 420, de 28 de dezembro de (2009). Publicada no DOU n° 249, de 30/12/2009, pag. 81–84.
CPRM, Companhia de Pesquisa de Recursos Minerais. Monitoramento Especial da Bacia do Rio Doce (2016). Relatório 3: monitoramento simultâneo ao longo de 15 dias. Available at: http://www.cprm.gov.br/publique/media/hidrologia/eventos_criticos/riodoce_relatorio3.pdf.
EPA (1996) 3050B method—acid digestion of sediments, sludges and soils. Available at: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-06/documents/epa-3050b.pdf, Accessed on September 2016.
EPA (1992) Method 1311. Toxicity characteristic leaching procedure. Available at: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-12/documents/1311.pdf, Accessed on October 2016.
Garcia, L. C., Ribeiro, D. B., Roque, F. O., Ochoa-Quintero, J. M., & Laurance, W. F. (2017). Brazil’s worst mining disaster: corporations must be compelled to pay the actual environmental costs. Ecological Applications, 27, 5–9.
Grimalt, J. O., Ferrer, M., & Macpherson, E. (1999). The mine tailing accident in Aznalcollar. Science of the Total Environment, 242, 3–11.
Guerra, M. B. B., Lima Neto, E., Prianti, M. T. A., Pereira-Filho, E. R., & Schaefer, C. E. G. R. (2013). Post-fire study of the Brazilian Scientific Antarctic Station: toxic element contamination and potential mobility on the surrounding environment. Microchemical Journal, 110, 21–27.
Hudson-Edwards, K. A., Macklin, M. G., Jamieson, H. E., Brewer, P. A., Coulthard, T. J., Howard, A. J., & Turner, J. N. (2003). The impact of tailings dam spills and clean-up operations on sediment and water quality in river systems: the Ríos Agrio–Guadiamar, Aznalcóllar, Spain. Applied Geochemistry, 18, 221–239.
IBAMA (2016). Parecer técnico sobre os resultados obtidos nas coletas de amostras de água e sedimento no Rio Doce e na região da Foz, no estado do Espírito Santo. Available at: http://www.ibama.gov.br/phocadownload/barragemdefundao/relatorios/2016-03-relatorio_analise_agua_marco.pdf.
ICOLD. (2001). Tailings dams—risk of dangerous occurrences. Lessons learnt from practical experiences. Paris: Committee on Tailings Dams and Waste Lagoons.
Kossoff, D., Dubbin, W. E., Alfredsson, M., Edwards, S. J., Macklin, M. G., & Hudson-Edwards, K. A. (2014). Mine tailings dams: characteristics, failure, environmental impacts, and remediation. Applied Geochemistry, 51, 229–245.
Kraus, U., & Wiegand, J. (2006). Long-term effects of the Aznalcóllar mine spill—heavy metal content and mobility in soils and sediments of the Guadiamar river valley (SW Spain). Science of the Total Environment, 367, 855–871.
Liu, H., Probst, A., & Liao, B. (2005). Metal contamination of soils and crops affected by the Chenzhou lead/zinc mine spill (Hunan, China). Science of the Total Environment, 339, 153–166.
López-Pamo, E., Barettino, D., Antón-Pacheco, C., Ortiz, G., Arránz, J. C., Gumiel, J. C., Martínez-Pledel, B., Aparicio, M., & Montouto, O. (1999). The extent of the Aznalcóllar pyritic sludge spill and its effects on soils. Science of the Total Environment, 242, 57–88.
Lottermoser, B. G. (2010). Mine wastes—characterization, treatment, and environmental impacts (3rd ed.). Dordrecht: Springer.
Meira, R. M. S. A., Peixoto, A. L., Coelho, M. A. N., Ponzo, A. P. L., Esteves, V. G. L., Silva, M. C., Câmara, P. E. A. S., & Meira-Neto, J. A. A. (2016). Brazil’s mining code under attack: giant mining companies impose unprecedented risk to biodiversity. Biodiversity and Conservation, 25, 407–409.
Miranda, L. S., & Marques, A. C. (2016). Hidden impacts of the Samarco mining waste dam collapse to Brazilian marine fauna—an example from the staurozoans (Cnidaria). Biota Neotropica, 16, 1–4.
Morgenstern, N. R., Vick, S. G., Viotti, C. B., & Watts, B. D.(2016). Fundão tailings dam review panel. Report on the immediate causes of the failure of the Fundão Dam. Available at: http://fundaoinvestigation.com/wp-content/uploads/general/PR/en/FinalReport.pdf.
Ordóñez Fernandez, R., Giráldez Cervera, J. V., Vanderlinden, K., Carbonell Bojollo, R., & González Fernández, P. (2007). Temporal and spatial monitoring of the pH and heavy metals in a soil polluted by mine spill. Post cleaning effects. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 178, 229–243.
Paye, H. S., Mello, J. W. V., Abrahão, W. A. P., Fernandes Filho, E. I., Dias, L. C. P., Castro, M. L. O., Melo, S. B., & França, M. M. (2010). Valores de referência de qualidade para metais pesados em solos no estado do Espírito Santo. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 34, 2041–2051.
Porto, M. F. S. (2016). The tragedy of mining and development in Brazil: public health challenges. Cadernos de Saúde Pública, 32, 1–3.
Rico, M., Benito, G., & Díez-Herrero, A. (2008a). Floods from tailings dam failures. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 154, 79–87.
Rico, M., Benito, G., Salgueiro, A. R., Díez-Herrero, A., & Pereira, H. G. (2008b). Reported tailings dam failures. A review of the European incidents in the worldwide context. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 152, 846–852.
Schaefer, C. E. G. R., Santos, E. E., Fernandes Filho, E. I., & Assis, I. R. (2016). Paisagens de lama: Os tecnossolos para recuperação ambiental de áreas afetadas pelo desastre da Barragem de Fundão, em Mariana, Boletim informativo da SBCS, (Jan-Abr), 18–23.
Segura, F. R., Nunes, E. A., Paniz, F. P., Paulelli, A. C. C., Rodrigues, G. B., Braga, G. U. L., Pedreira Filho, W. R., Barbosa Jr., F., Cerchiaro, G., Silva, F. F., & Batista, B. L. (2016). Potential risks of the residue from Samarco’s mine dam burst (Bento Rodrigues, Brazil). Environmental Pollution, 218, 813–825.
Simón, M., Ortiz, I., García, I., Fernández, E., Fernández, J., Dorronsoro, C., & Aguilar, J. (1999). Pollution of soils by the toxic spill of a pyrite mine (Aznalcollar, Spain). The Science of the Total Environment, 242, 105–115.
Souza, J. J. L. L., Abrahão, W. A. P., Mello, J. W. V., Silva, J., Costa, L. M., & Oliveira, T. S. (2015). Geochemistry and spatial variability of metal(loid) concentrations in soils of the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Science of the Total Environment, 505, 338–349.
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (1994). Technical assistance document for complying with the TC rule and implementing the toxicity characteristic leaching procedure (TCLP). Available at: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-07/documents/tclp-1994_0.pdf.
USDA (1999). United States Department of Agriculture. Soil taxonomy—a basic system of soil classification for making and interpreting soil surveys. Second Edition.
Wadige, C. P. M. M., Taylor, A. M., Krikowa, F., & Maher, W. A. (2016). Sediment metal concentration survey along the mine-affected Molonglo River, NSW, Australia. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 70, 572–582.
WISE, World Information Service on Energy (2017). Chronology of major tailings dam failures. Available at: http://www.wise-uranium.org/mdaf.html. Last webpage update on 3 Apr 2017.
Acknowledgements
The authors express their deepest gratitude to the faculty and students from the Federal University of Viçosa who collected all soil and mine waste samples for this study. Special thanks to Dr. Débora Corrêa for her careful review. The National Science Foundation Major Research Instrumentation grant (MRI-1429544) supported this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guerra, M.B.B., Teaney, B.T., Mount, B.J. et al. Post-catastrophe Analysis of the Fundão Tailings Dam Failure in the Doce River System, Southeast Brazil: Potentially Toxic Elements in Affected Soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 252 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3430-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3430-5