Abstract
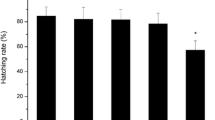
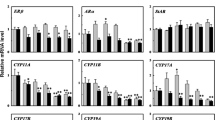
Bisphenol B (BPB) exhibited higher estrogenic activity and anti-androgenic effects than bisphenol A (BPA) in vitro assays. This result indicates that BPB has higher priority for entry into expensive and stressful testing on animals. However, the disrupting mechanisms of BPB on steroid hormone signaling pathway by in vivo assay have not been investigated yet. In this study, the potential disrupting mechanisms of BPB on the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal (HPG) axis and liver were probed by employing the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) 21-day short-term fecundity assay with zebrafish. We found that BPB exposure (1 mg/L) could impair the reproductive function of zebrafish and decline the egg numbers, hatching rate, and survival rate. This finding is related to modifications of the testis and ovary histology of the treated zebrafish. The homogenate T levels in male zebrafish decreased in a concentration-dependent manner, and the E2 level significantly increased when exposed to 0.01, 0.1, and 1 mg/L BPB. Real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed to examine the gene expressions in the HPG axis and liver. Hepatic vitellogenin (vtg) expression was upregulated in all exposure males, suggesting that BPB possesses estrogenic activity. The disturbed hormone balance was contributed by the significant alteration of the genes along the HPG axis. These alterations suggest that BPB can lead to adverse effects on the endocrine system of teleost fish, and these effects were more prominent in males than in females.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson, E., Nijenhuis, W., Male, R., Swanson, P., Bogerd, J., Taranger, G. L., & Schulz, R. W. (2009). Pharmacological characterization, localization and quantification of expression of gonadotropin receptors in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) ovaries. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 163(3), 329–339.
Ankley, G. T., & Johnson, R. D. (2004). Small fish models for identifying and assessing the effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals. ILAR Journal, 45(4), 469–483.
Chen, D., Kannan, K., Tan, H., Zheng, Z. G., Feng, Y. L., & Wu, Y., et al. (2016). Bisphenol analogues other than bpa: environmental occurrence, human exposure, and toxicity—a review. Environmental Science Technology, 50(11), 5438–5453.
Clelland, E., & Peng, C. (2009). Endocrine/paracrine control of zebrafish ovarian development. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 312(1), 42–52.
Cunha, S. C., & Fernandes, J. O. (2010). Quantification of free and total bisphenol a and bisphenol b in human urine by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME) and heart-cutting multidimensional gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (MD-GC/MS). Talanta, 83(1), 117–125.
Cunha, S. C., & Fernandes, J. O. (2013). Assessment of bisphenol a and bisphenol b in canned vegetables and fruits by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry after quechers and dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Food Control, 33(2), 549–555.
Cunha, S. C., Almeida, C., Mendes, E., & Fernandes, J. O. (2011). Simultaneous determination of bisphenol a and bisphenol b in beverages and powdered infant formula by dispersive liquid-liquid micro-extraction and heart-cutting multidimensional gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Food Additives and Contaminants - Part A Chemistry, Analysis, Control, Exposure and Risk Assessment, 28(4), 513–526.
Cunha, S. C., Cunha, C., & Ferreira, A. R. (2012). Determination of bisphenol a and bisphenol b in canned seafood combining quechers extraction with dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction followed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 404(8), 2453–2463.
Daouk, T., Larcher, T., Roupsard, F., Lyphout, L., Rigaud, C., Ledevin, M., Loizeau, V., & Cousin, X. (2011). Long-term food-exposure of zebrafish to PCB mixtures mimicking some environmental situations induces ovary pathology and impairs reproduction ability. Aquatic Toxicology, 105(3), 270–278.
European Commission (2011). Bisphenol A: EU ban on baby bottles to enter into force tomorrow.
FDA (2008). Draft assessment of Bisphenol A for use in food contact applications, U.S. Food and Drug Administration.http://www.fda.gov/downloads/AdvisoryCommittees/CommitteesMeetingMaterials/ScienceBoardtotheFoodandDrugAdministrationUCM179157.pdf. Accessed 25 October 2016
Filby, A. L., van Aerle, R., Duitman, J., & Tyler, C. R. (2008). The kisspeptin/gonadotropin-releasing hormone pathway and molecular signaling of puberty in fish. Biology of Reproduction, 78(2), 278–289.
Glausiusz, J. (2014). Toxicology: the plastics puzzle. Nature, 508(7496), 306.
Harries, J. E., Sheahan, D. A., Jobling, S., Matthiessen, P., Neall, M., Sumpter, J. P., Taylor, T., & Zaman, N. (1997). Estrogenic activity in five United Kingdom rivers detected by measurement of vitellogenesis in caged male trout. Environmental Toxicology Chemistry, 16, 534–542.
Health Canada (2009). Survey of bisphenol A in canned drink products.
Hecker, M., Wan, J. K., Park, J. W., Murphy, M. B., Villeneuve, D., Coady, K. K., et al. (2005). Plasma concentrations of estradiol and testosterone, gonadal aromatase activity and ultrastructure of the testis in xenopus laevis, exposed to estradiol or atrazine. Aquatic Toxicology, 72(4), 383–396.
Ji, K., Hong, S., Kho, Y., & Choi, K. (2013). Effects of bisphenol S exposure on endocrine functions and reproduction of zebrafish. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(15), 8793–8800.
Keiter, S., Baumann, L., Färber, H., Holbech, H., Skutlarek, D., Engwall, M., et al. (2012). Long-term effects of a binary mixture of perfluorooctane sulfonate (pfos) and bisphenol a (bpa) in zebrafish (danio rerio). Aquatic Toxicology, 118–119(2), 116–129.
Kusakabe, M., Nakamura, I., Evans, J., Swanson, P., & Young, G. (2006). Changes in mRNAs encoding steroidogenic acute regulatory protein, steroidogenic enzymes and receptors for gonadotropins during spermatogenesis in rainbow trout testes. Journal of Endocrinology, 189(3), 541–554.
Kwok, H. F., So, W. K., Wang, Y., & Ge, W. (2005). Zebrafish gonadotropins and their receptors: I. Cloning and characterization of zebrafish follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone receptors—evidence for their distinct functions in follicle development. Biology of Reproduction, 72(6), 1370–1381.
Liao, C., Liu, F., Guo, Y., Moon, H. B., Nakata, H., Wu, Q., & Kannan, K. (2012a). Occurrence of eight bisphenol analogues in indoor dust from the United States and several Asian countries: implications for human exposure. Environmental Science & Technology, 46(16), 9138–9145.
Liao, C., Liu, F., Moon, H. B., Yamashita, N., Yun, S., & Kannan, K. (2012b). Bisphenol analogues in sediments from industrialized areas in the United States, Japan, and Korea: spatial and temporal distributions. Environmental Science & Technology, 46(21), 11558–11565.
Liu, C., Yu, L., Deng, J., Lam, P. K., Wu, R. S., & Zhou, B. (2009). Waterborne exposure to fluorotelomer alcohol 6: 2 FTOH alters plasma sex hormone and gene transcription in the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal (HPG) axis of zebrafish. Aquatic Toxicology, 93(2), 131–137.
Liu, X., Ji, K., Jo, A., Moon, H. B., & Choi, K. (2013). Effects of TDCPP or TPP on gene transcriptions and hormones of HPG axis, and their consequences on reproduction in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquatic Toxicology, 134, 104–111.
Mandich, A., Bottero, S., Benfenati, E., Cevasco, A., Erratico, C., Maggioni, S., Massari, A., Pedemonte, F., & Vigano, L. (2007). In vivo exposure of carp to graded concentrations of bisphenol A. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 153(1), 15–24.
Nash, J. P., Kime, D. E., Van der Ven, L. T., Wester, P. W., Brion, F., Maack, G., Allner, P. S., & Tyler, C. R. (2004). Long-term exposure to environmental concentrations of the pharmaceutical ethynylestradiol causes reproductive failure in fish. Environmental Health Perspectives, 112, 1725–1733.
Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (2009). Fish short term reproduction assay. OECD guideline 229. Paris, France.
Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development. 2009(b). 21-day Fish Assay. OECD guideline 230. Paris, France. Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development. Fish short term reproduction assay; OECD guideline 229; Paris, France, 2009.
Rochester, J. R. (2013). Bisphenol A and human health: a review of the literature. Reproductive Toxicology, 42, 132–155.
Shang, E. H. H., Yu, R. M. K., & Wu, R. S. S. (2006). Hypoxia affects sex differentiation and development, leading to a male-dominated population in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environmental Science & Technology, 40, 3118–3122.
Shi, J., Jiao, Z., Zheng, S., Li, M., Zhang, J., Feng, Y., Yin, J., & Shao, B. (2015). Long-term effects of bisphenol AF (BPAF) on hormonal balance and genes of hypothalamus–pituitary–gonad axis and liver of zebrafish (Danio rerio), and the impact on offspring. Chemosphere, 128, 252–257.
Sohoni, P. C. R. T., Tyler, C. R., Hurd, K., Caunter, J., Hetheridge, M., Williams, T., Woods, C., & Sumpter, J. P. (2001). Reproductive effects of long-term exposure to bisphenol A in the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Environmental Science & Technology, 35(14), 2917–2925.
Song, M., Liang, D., Liang, Y., Chen, M., Wang, F., Wang, H., & Jiang, G. (2014). Assessing developmental toxicity and estrogenic activity of halogenated bisphenol A on zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere, 112, 275–281.
Thompson, E. D., Mayer, G. D., Walsh, P. J., & Hogstrand, C. (2002). Sexual maturation and reproductive zinc physiology in the female squirrelfish. Journal of Experimental Biology, 205, 3367–3376.
Trabucco, E. (2009). Measurement of bisphenol A and bisphenol B levels in human blood sera from healthy and endometriotic women. Biomedical Chromatography, 23(11), 1186–1190.
Uren Webster, T. M., Laing, L. V., Florance, H., & Santos, E. M. (2014). Effects of glyphosate and its formulation, roundup, on reproduction in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environmental Science & Technology, 48(2), 1271–1279.
Van den Belt, K., Verheyen, R., & Witters, H. (2001). Reproductive effects of ethynylestradiol and 4t-octylphenol on the zebrafish (Danio rerio). Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 41(4), 458–467.
Wang, Q., Lam, J. C., Han, J., Wang, X., Guo, Y., Lam, P. K., & Zhou, B. (2015). Developmental exposure to the organophosphorus flame retardant tris (1, 3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate: estrogenic activity, endocrine disruption and reproductive effects on zebrafish. Aquatic Toxicology, 160, 163–171.
Yang, X., Liu, Y., Li, J., Chen, M., Peng, D., Liang, Y., Zhang, J., & Jiang, G. (2014). Exposure to bisphenol AF disrupts sex hormone levels and vitellogenin expression in zebrafish. Environmental Toxicology, 31(3), 285–294.
Yön, N. D., & Akbulut, C. (2014). Histological changes in zebrafish (Danio rerio) ovaries following administration of bisphenol A. Pakistan Journal of Zoology, 46(4), 1153–1159.
Yu, X., Xue, J., Hong, Y., Qian, W., Venkatesan, A. K., Halden, R. U., et al. (2015). Occurrence and estrogenic potency of eight bisphenol analogs in sewage sludge from the U.S. EPA targeted national sewage sludge survey. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 299, 733–739.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (General Program) (No. BK20151100), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21507038), and Graduate Research and Innovation Projects of Jiangsu Province (No. KYLX15_0813).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Q., Yang, X., Liu, J. et al. Exposure to Bisphenol B Disrupts Steroid Hormone Homeostasis and Gene Expression in the Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Gonadal Axis of Zebrafish. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 112 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3282-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3282-z