Abstract
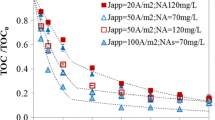
The electrochemical elimination of the herbicide diquat dibromide (DQ) in an undivided electrochemical cell (Condiacell®-type cell) and an H-type cell (a divided electrochemical cell) using boron-doped diamond (BDD) electrodes is reported for the first time. The degradation of essentially 100% of the DQ present was achieved in the undivided electrochemical cell and ca. 92% in the H-type cell. Nearly 80% of the total organic carbon (TOC) and of the chemical oxygen demand (COD) were removed after 5 h of treatment at different current densities (i.e., 0.5, 1.0, and 1.5 mA/cm2 for the undivided cell, and 2.5, 5.0, and 7.5 mA/cm2 for the H-type cell) with a maximum specific energy consumption of approximately 150 kWh kg−1 of COD degraded in the undivided cell, and 300 kWh kg−1 of COD in the H-type cell. Energy consumption of about 0.30 kWh g−1 of TOC occurred in the undivided electrochemical cell and 2.0 in the H-type cell. In spite of obtaining similar percentages of DQ degradation and of COD and TOC removal, a smaller energy usage was required in the undivided cell since smaller current densities were employed. Best results were obtained with the undivided cell, since it required a smaller current density to obtain virtually the same percentage of DQ degradation and removal of COD and TOC. The results obtained herein show that the use of electrochemical advanced oxidation processes may be a good alternative for DQ degradation in polluted water.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Ghalwa, N., Abu-Shawish, H. M., Hamada, M., Hartani, K., & Hakem-Basheer, A. A. (2012). Studies on degradation of diquat pesticide in aqueous solutions using electrochemical method. American Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 3, 99–105.
APHA, AWWA, WPCF, in: A.D. Eaton, A.E. Clesceri, E.W. Rice, A.E. Greenberg (Eds.) (1999) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20st ed., American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and Water Environment Federation, Washington, D.C.
Bard, A. J., & Faulkner, L. R. (2001). Electrochemical methods fundamentals and applications (Second editionth ed., p. 339). New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Blanco, J., & Malato, S. S. (2003). Solar detoxification. France: UNESCO Publishing.
Bouétard, A., Besnard, A. L., Vassaux, D., Lagadic, L., & Coutellec, M. A. (2013). Impact of the redox-cycling herbicide diquat on transcript expression and antioxidant enzymatic activities of the freshwater snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Aquatic Toxicology, 126, 256–265.
Brillas, E. (2014). Electro-Fenton, UVA photoelectro-Fenton and solar photoelectro-Fenton treatments of organics in waters using a boron-doped diamond anode: a review. Journal of the Mexican Chemical Society, 58, 239–255.
Brillas, E., & Martínez-Huitle, C. A. (2014). Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods. An updated review, Applied Catalysis B, 166–167, 603–643.
Brillas, E., Sirés, I., & Oturan, M. A. (2009). Electro-Fenton process and related electrochemical technologies based on Fenton’s reaction chemistry. Chemical Reviews, 109, 6570–6631.
Campos-Gonzalez, E., Frontana-Uribe, B. A., Vasquez-Medrano, R., Macias-Bravo, S., & Ibanez, J. G. (2014). Advanced electrochemical oxidation of methyl parathion at boron doped diamond electrodes. Journal of the Mexican Chemical Society, 58, 315–321.
Carbajal-Palacios, P., Balderas-Hernández, P., Ibanez, J. G., & Roa-Morales, G. (2012). Replacing dichromate with hydrogen peroxide in the chemical oxygen demand (COD) test. Water Science & Technology, 66, 1069–1073.
Cartaxo, M. A. M., Borges, C. M., Pereira, M. I. S., & Mendonca, M. H. (2015). Electrochemical oxidation of paraquat in neutral medium. Electrochimica Acta, 176, 1010–1018.
Cocenza, D. S., de Moraes, M. A., Beppu, M. M., & Fraceto, L. F. (2012). Use of biopolymeric membranes for adsorption of paraquat herbicide from water. Water Air Soil Pollution, 223, 3093–3104.
Compton, R. G., Laborda, E., & Ward, K. R. (2014). Understanding voltammetry: simulation of electrode processes (p. 30). London: Imperial College Press.
Cork, D. J., & Krueger, J. P. (1991). Microbial transformations of herbicides and pesticides. Advances in Applied Microbiology, 36, 1–66.
Cussler, E. L. (2007). Diffusion mass transfer in fluid systems (3rd ed., pp. 284–297). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Davis, J., Baygents, C., & Farrell, J. (2014). Understanding persulfate production at boron doped diamond film anodes. Electrochimica Acta, 150, 68–74.
de Moraes, A. M., Sgarbi-Cocenza, D., Vasconcellos, F., Fernandes-Fraceto, L., & Masumi-Beppu, M. (2013). Chitosan and alginate biopolymer membranes for remediation of contaminated water with herbicides. Journal of Environmental Management, 131, 222–227.
Delgado, J. (2007). Molecular diffusion coefficients of organic compounds in water at different temperatures. Journal of Phase Equilibria and Diffusion, 28, 427–432.
Devipriya, S., & Yesodharan, S. (2005). Photocatalytic degradation of pesticide contaminants in water. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 86, 309–348.
EFEDO, Risks of diquat dibromide use to the federally threatened delta smelt (Hypomesus transpacificus), Environmental Fate and Effects Division Officer of Pesticide Programs. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi = 10.1.1.185.1235&rep = rep1&type = pdf, 2010 (accessed Jul. 4, 2016).
El-Ghenymy, A., Garrido, J. A., Rodríguez, R. M., Cabotm, P. L., Centellas, F., Arias, C., & Brillas, E. (2013). Degradation of sulfanilamide in acidic medium by anodic oxidation with a boron-doped diamond anode. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 689, 149–157.
El-Ghenymy, A., Centellas, F., Garrido, J. A., Rodríguez, R. M., Sirés, I., Cabot, P. L., & Brillas, E. (2014). Decolorization and mineralization of Orange G azo dye solutions by anodic oxidation with a boron-doped diamond anode in divided and undivided tank reactors. Electrochimica Acta, 130, 568–576.
Espinoza-Montero, P. J., Vasquez-Medrano, R., Ibanez, J. G., & Frontana-Uribe, B. A. (2013). Efficient anodic degradation of phenol paired to improve cathodic production of H2O2 at BDD electrodes. Journal of Electrochemical Society, 160, G3171–G3177.
Florencio, M. H., Pires, E., Castro, A. L., Nunes, M. R., Borges, C., & Costa, F. M. (2004). Photodegradation of diquat and paraquat in aqueous solutions by titanium dioxide: evolution of degradation reactions and characterisation of intermediates. Chemosphere, 55, 345–355.
Fortenberry, G. Z., Beckman, J., Schwartz, A., Prado, J. B., Graham, L. S., Higgins, S., Lackovic, M., Mulay, P., Bojes, H., Waltz, J., Mitchell, Y., Leinenkugel, K., Oriel, M. S., Evans, E., & Calvert, G. M. (2016). Magnitude and characteristics of acute paraquat- and diquat-related illnesses in the US: 1998–2013. Environmental Research, 146, 191–199.
Friedman, C. L., Templey, A. T., & Hay, A. (2006). Degradation of chloroacetanilide herbicides by anodic Fenton treatment. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 54, 2640–2651.
Gao, L., Liu, G., Zhu, J., Wang, C., & Liu, J. (2015). Solid phase microextraction combined with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry for the determination of diquat residues in water. Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 70, 552–557.
Garcia Bessegato, G., Tasso-Guaraldo, T., Ferreira de Brito, J., Brugnera, M. F., & Boldrin-Zanoni, M. V. (2015). Achievements and trends in photoelectrocatalysis: from environmental to energy applications. Electrocatalysis, 6, 415–441.
García, O., Isarain, E., El-Ghenymy, A., Brillas, E., & Peralta, J. M. (2014). Degradation of 2,4-D herbicide in a recirculation flow plant with a Pt/air-diffusion and a BDD/BDD cell by electrochemical oxidation and electro-Fenton process. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 728, 1–9.
Guo, X., Li, D., Wan, J., & Yu, X. (2015). Preparation and electrochemical property of TiO2/nano-graphite composite anode for electro-catalytic degradation of ceftriaxone sodium. Electrochimica Acta, 180, 957–964.
Gupta, P.K. Herbicides and fungicides, in P.K. Gupta (Ed.) (2014). Biomarkers in toxicology, (pp. 409–431). Academic Press.
Ikehata, K., & El-Din, G. M. (2006). Aqueous pesticide degradation by hydrogen peroxide/ultraviolet irradiation and Fenton-type advanced oxidation processes: a review. Journal of Environmental Engineering and Science, 5, 81–135.
Kapalka, A., Fóti, G., & Comninellis, C. (2010). Basic principles of the electrochemical mineralization of organic pollutants for wastewater treatment. In C. Comninellis & G. Chen (Eds.), Electrochemistry for the environment (pp. 1–23). New York: Springer.
Karuppagounder, S. S., Ahuja, M., Buabeid, M., Parameshwaran, K., Abdel-Rehman, E., Suppiramaniam, V., & Dhanasekaran, M. (2012). Investigate the chronic neurotoxic effects of diquat. Neurochemical Research, 37, 1102–1111.
Khorram, M. S., Zhang, Q., Lin, D., Zheng, Y., Fang, H., & Yu, Y. (2016). Biochar: a review of its impact on pesticide behavior in soil 3 environments and its potential applications. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 44, 269–279.
Maharana, D., Xu, D., Niu, J., & Rao, N. N. (2015). Electrochemical oxidation of 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid by metal-oxide-coated Ti electrodes. Chemosphere, 136, 145–152.
Martínez-Huitle, C. A., & Ferro, S. (2006). Electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants for the wastewater treatment: direct and indirect processes. Chemical Society Reviews, 35, 1324–1340.
Martínez-Huitle, C. A., Rodrigo, M. A., Sirés, I., & Scialdone, O. (2015). Single and coupled electrochemical processes and reactors for the abatement of organic water pollutants: a critical review. Chemical Reviews, 115, 13362–13407.
Michaud, P. A., Mahé, E., Haenni, W., Perret, A., & Comninellis, C. (2000). Preparation of peroxodisulfuric acid using boron-doped diamond thin film electrode. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 3(2), 77–79.
Montes, I. J. S., Silva, B. F., & Aquino, J. M. (2017). On the performance of a hybrid process to mineralize the herbicide tebuthiuron using a DSA® anode and UVC light: a mechanistic study. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 200, 237–245.
Moreira, F. C., Boaventura, R. A. R., Brillas, E., & Vilar, V. J. P. (2017). Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: a review on their application to synthetic and real wastewaters. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 202, 217–261.
NCFAP, Pesticide use in U.S. crop production: 1997, National Center for Food and Agricultural Policy. http://www.ncfap.org/documents/nationalsummary1997.pdf, 2000 (accessed Jul. 4, 2016).
Núñez, O., Kima, J. B., Moyano, E., Galceran, M. T., & Terabe, S. (2002). Analysis of the herbicides paraquat, diquat and difenzoquat in drinking water by micellar electrokinetic chromatography using sweeping and cation selective exhaustive injection. Journal of Chromatography A, 961, 65–75.
Panizza, M., & Cerisola, G. (2009). Direct and mediated anodic oxidation of organic pollutants. Chemical Reviews, 109, 6541–6569.
Panizza, M., Michaud, P. A., Cerisola, G., & Comninellis, C. (2001). Electrochemical treatment of wastewaters containing organic pollutants on boron-doped diamond electrodes: prediction of specific energy consumption and required electrode area. Electrochemistry Communications, 3, 336–339.
Pateiro-Moure, M., Martínez-Carballo, E., Arias-Estévez, M., & Simal-Gándara, J. (2008). Determination of quaternary ammonium herbicides in soils: comparison of digestion, shaking and microwave-assisted extractions. Journal of Chromatography A, 1196–1197, 110–116.
Pateiro-Moure, M., Arias-Estévez, M., & Simal-Gándara, J. (2013). Critical review on the environmental fate of quaternary ammonium herbicides in soils devoted to vineyards. Environmental Science & Technology, 47, 4984–4998.
Pereira, G. F., Rocha, R. C., Bocchi, N., & Biaggio, S. R. (2015). Electrochemical degradation of the herbicide picloram using a filter-press flow reactor with a boron-doped diamond or β-PbO2 anode. Electrochimica Acta, 179, 588–598.
Pipi, A. R. F., de Andrade, A. R., Brillas, E., & Sirés, I. (2014). Total removal of alachlor from water by electrochemical processes. Separation and Purification Technology, 132, 674–683.
Prosser, R. S., Anderson, J. C., Hanson, M. L., Solomon, K. R., & Sibley, P. K. (2016). Indirect effects of herbicides on biota in terrestrial edge-of-field habitats: a critical review of the literature. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 232, 59–72.
Rajeshwar, K., & Ibanez, J. G. (1997). Environmental electrochemistry: fundamentals and applications in pollution abatement (p. 364). New York: Academic.
Ribeiro, A. R., Nunes, O. C., Pereira, M. F. R., & Silva, A. M. T. (2015). An overview on the advanced oxidation processes applied for the treatment of water pollutants defined in the recently launched Directive 2013/39/EU. Environment International, 75, 33–51.
Saidi, I., Soutrel, I., Fourcade, F., Amrane, A., Bellakhal, N., & Geneste, F. (2016). Electrocatalytic reduction of metronidazole using titanocene/Nafion 1-modified graphite felt electrode. Electrochimica Acta, 191, 821–831.
Santos, T. E. S., Solva, R. S., Eguiluz, K. I. B., & Salazar, G. R. (2015). Development of Ti/(RuO2)0.8(MO2)0.2(M = Ce, Sn or Ir) anodes for atrazine electro-oxidation. Influence of the synthesis method. Materials Letters, 146, 4–8.
Särkkä, H., Bhatnagar, A., & Sillanpää, M. (2015). Recent developments of electro-oxidation in water treatment—a review. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 754, 46–56.
Serrano, K., Michaud, P. A., Comninellis, C., & Savall, A. (2002). Electrochemical preparation of peroxodisulfuric acid using boron doped diamond thin film electrodes. Electrochimica Acta, 48, 431–436.
Shibin, O. M., Yesodharan, S., & Yesodharan, E. P. (2015). Sunlight induced photocatalytic degradation of herbicide diquat in water in presence of ZnO. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 3, 1107–1116.
Souza, F., Quijorna, S., Lanza, M. R. V., Saez, C., Cañizares, P., & Rodrigo, M. A. (2017). Applicability of electrochemical oxidation using diamond anodes to the treatment of a sulfonylurea herbicide. Catalysis Today, 280, 192–198.
Subba-Rao, A. N., & Venkatarangaiah, V. T. (2014). Metal oxide-coated anodes in wastewater treatment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 3197–3217.
Tröster, I., Fryda, M., Herrmann, D., Schäfer, L., Hänni, W., Perret, A., Blaschke, M., Kraft, A., & Stadelmann, M. (2002). Electrochemical advanced oxidation process for water treatment using DiaChem® electrodes. Diamond and Related Materials, 11, 640–645.
Vymazal, J., & Brezinova, T. (2015). The use of constructed wetlands for removal of pesticides from agricultural runoff and drainage: a review. Environment International, 75, 11–20.
Weber, J. B., & Coble, H. D. (1968). Microbial decomposition of diquat adsorbed on montmorillonite and kaolinite clays. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 16, 475–478.
Wu, W., Huang, Z. H., & Lim, T. T. (2014). Recent development of mixed metal oxide anodes for electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants in water. Applied Catalysis A: General, 480, 58–78.
Yu, Y., Zhou, S., Bu, L., Shi, Z., Zhu, S. (2016). Degradation of diuron by electrochemically activated persulfate. Water Air Soil Pollution, 227–279.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the financial support from the research office of the Universidad Iberoamericana Project No. 54. “Electrochemical and photochemical reactions for more efficient energy use, 2nd. Phase,” and the experimental assistance by Samuel Macias-Bravo.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valenzuela, A.L., Vasquez-Medrano, R., Ibanez, J.G. et al. Remediation of Diquat-Contaminated Water by Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation Processes Using Boron-Doped Diamond (BDD) Anodes. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 67 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3244-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3244-5