Abstract
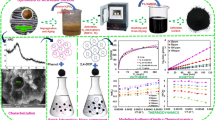
The aim of this study is to evaluate the fluoride removal from contaminated water using a new adsorbent material of high efficiency to obtain drinking water. The ZrCl4-graphene supported on vegetal activated carbon composite (G-ZrCl4/VAC) was synthesized and characterized using transmission and scanning electron microscopy, N2 physisorption, energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry, Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and Raman spectroscopy. Furthermore, the point of zero charge was determined. The G-ZrCl4/VAC was evaluated for fluoride adsorptive removal from water under several operating conditions in batch system. The results indicated that fluoride adsorption by G-ZrCl4/VAC is favored at low pH values with the maximum adsorption at pH 2, corresponding to 97.22% removal. Among the conditions of temperature and agitation evaluated, the best results were achieved at 30 °C and 130 rpm, with removal percentages equal to 47.78 and 48.48%, respectively. The equilibrium of the system was achieved in 5 h of operation. The pseudo-first order kinetic model was the one that best described the kinetic data, while the equilibrium data were best described by the Langmuir isotherm with maximum adsorption capacity equal to 3.89 mg g−1. Therefore, the results obtained show that the material synthesized has a great capacity for adsorption and demonstrate the viability of use of G-ZrCl4/VAC in the removal of fluoride to obtain drinking water.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal, R., Margandan, K., Acharya, R., Sharma, S., & Qanungo, K. (2014). Fabrication and testing of activated alumina based defluoridation filters with yarn cartridges. International Journal of ChemTech Research, 6(1), 845–859.
Ahmad, A. F., Moin, F. H. A., Mohd, H. M. K., Rahman, I. A., Mohamed, F., Hua, C. C., Ramli, S., & Radiman, S. (2013). Graphene colloidal dispersion in various organic solvents. Malaysian Journal of Analytical Sciences, 17(3), 475–480.
Alagumuthu, G., & Rajan, M. (2010). Kinetic and equilibrium studies on fluoride removal by zirconium (iv)-impregnated groundnut shell carbon. Hemijska Industrija. doi:10.2298/hemind100307017a.
Alagumuthu, G., Veeraputhiran, V., & Venkataraman, R. (2011). Fluoride sorption using cynodon dactylon-based activated carbon. Hemijska Industrija. doi:10.2298/hemind100712052a.
Ali, S., Thakur, S. K., Sarkar, A., & Shekhar, S. (2016). Worldwide contamination of water by fluoride. Environmental Chemistry Letters. doi:10.1007/s10311-016-0563-5.
APHA/AWWA/WEF - American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation. (2012). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (22nd Ed.). Washington: American Public Health Association.
Barrett, E. P., Joyner, L. G., & Halenda, P. P. (1951). The determination of pore volume and area distributions in porous substances. I. Computations from nitrogen. Isotherms. Journal of the American Chemical Society. doi:10.1021/ja01145a126.
Bhaumik, R., & Mondal, N. K. (2016). Optimizing adsorption of fluoride from water by modified banana peel dust using response surface modelling approach. Applied Water Science. doi:10.1007/s13201-014-0211-9.
Blackwell, J. A., & Carr, P. W. (1991). Study of the fluoride adsorption characteristics of porous microparticulate zirconium oxide. Journal of Chromatography A. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(00)91417-1.
Brasil. (2011). Ministério da Saúde. Portaria n° 2.914, de 12 de dezembro de 2011. Biblioteca Virtual em Saúde. http://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/saudelegis/gm/2011/prt2914_12_12_2011.html. Accessed 15 may 2013.
Brunauer, S., Emmett, P. H., & Teller, E. (1938). Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. Journal of the American Chemical Society. doi:10.1021/ja01269a023.
Brunauer, S., Deming, L. S., Deming, W. E., & Teller, E. (1940). On a theory of Van der Waals adsorption of gases. Journal of the American Chemical Society. doi:10.1021/ja01864a025.
CDC - Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2006). Fluoride in drinking water: a scientific review of EPA’s standards. Washington: The National Academies Press.
Chanda, D., Hnát, J., Dobrota, A. S., Pašti, I. A., Paidar, M., & Bouzek, B. (2015). The effect of surface modification by reduced graphene oxide on the electrocatalytic activity of nickel towards the hydrogen evolution reaction. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. doi:10.1039/c5cp04238k.
Chandra, V., Park, J., Chun, Y., Lee, J. W., Hwang, I.-C., & Kim, K. S. (2010). Water-dispersible magnetite-reduced graphene oxide composites for arsenic removal. ACS Nano. doi:10.1021/nn1008897.
Chen, N., Zhang, Z., Feng, C., Sugiura, N., Li, M., & Chen, R. (2010). Fluoride removal from water by granular ceramic adsorption. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2010.04.048.
D’Alessandro, W., Bellomo, S., & Parello, F. (2012). Fluorine adsorption by volcanic soils at Mt. Etna, Italy. Applied Geochemistry. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2012.02.028.
Davila-Rodriguez, J. L., Escobar-Barrios, V. A., Shirai, K., & Rangel-Mendez, J. R. (2009). Synthesis of a chitin-based biocomposite for water treatment: optimization for fluoride removal. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry. doi:10.1016/j.jfluchem.2009.05.012.
Djomgoue, P., & Njopwouo, D. (2013). FT-IR spectroscopy applied for surface clays characterization. Journal of Surface Engineered Materials and Advanced Technology. doi:10.4236/jsemat.2013.34037.
Ferrari, A. C. (2007). Raman spectroscopy of graphene and graphite: disorder, electron–phonon coupling, doping and nonadiabatic effects. Solid State Communications. doi:10.1016/j.ssc.2007.03.052.
Ferrari, A. C., & Robertson, J. (2000). Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. Physical Review B. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.61.14095.
Finar, I. L. (1985). Organic chemistry: the fundamental principles (6ªth ed.). England: ELBS/Longman.
Ganguly, A., Sharma, S., Papakonstantinou, P., & Hamilton, J. (2011). Probing the thermal deoxygenation of graphene oxide using high-resolution in situ x-ray-based spectroscopies. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C. doi:10.1021/jp203741y.
Ganvir, V., & Das, K. (2011). Removal of fluoride from drinking water using aluminum hydroxide coated ricehusk ash. Journal of Hazardous Materials. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.10.044.
Geankoplis, C. J. (1993). Transport processes and unit operations (3ªth ed.). Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall International.
Gogoi, P. K., & Baruah, R. (2008). Fluoride removal from water by adsorption on acid activated kaolinite clay. Indian Journal of Chemical Technology, 15(5), 500–503.
Goldstein, J. I., Newbury, D. E., Echlin, P., Joy, D. C., Lyman, C. E., Romig, A. D., Fiori, C. E., & Lifshin, E. (1992). Scanning electron microscopy and x-ray microanalysis (3ªth ed.). New York: Plenum.
Gu, W., Zhang, W., Li, X., Zhu, H., Wei, J., Li, Z., Shu, Q., Wang, C., Wang, K., Shen, W., Kang, F., & Wu, D. (2009). Graphene sheets from worm-like exfoliated graphite. Journal of Materials Chemistry. doi:10.1039/b904093p.
Guerra, D. L., Airoldi, C., Lemos, V. P., Angélica, R. S., & Viana, R. R. (2007). Aplication of al-pilc in the adsorption of Cu2+, Ni2+e CO2+ using adsorption physico-chemical models. Ecletica Quimica. doi:10.1590/S0100-46702007000300008.
Guo, B., Hong, L., & Jiang, H. X. (2003). Macroporous poly(calcium acrylate-divinylbenzene) bead—a selective orthophosphate sorbent. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. doi:10.1021/ie030156i.
Health Canada. (2016). Guidelines for Canadian drinking water quality. Guideline technical document—fluoride. http://healthycanadians.gc.ca/publications/healthy-living-vie-saine/water-fluoride-fluorure-eau/index-eng.php?page=2#part1. Accessed 03 march 2016.
Ho, Y. S., & Mckay, G. (1998). A comparison of chemisorption kinetic models applied to pollutant removal on various sorbents. Process Safety and Environmental Protection. doi:10.1205/095758298529696.
IUPAC. (1976). Manual of symbols and terminology for physicochemical quantities and units—appendix II. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 46(1), 71–90.
Jana, S., & Biswas, P. K. (1997). Chemical behaviour of zirconium oxychloride octahydrate and acetic acid in precursor solution for zirconia film formation on glass. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology. doi:10.1007/bf02437186.
Karthikeyan, M., & Elango, K. P. (2009). Removal of fluoride from water using aluminium containing compounds. Journal of Environmental Sciences. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62448-1.
King, P., Rakesh, N., Beenalahari, S., Kumar, Y. P., & Prasad, V. S. R. K. (2007). Prasad removal of lead from aqueous solution using syzygium cumini L.: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Journal of Hazardous Materials. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.08.027.
Kumar, A. S. K., Jiang, S.-J., & Tseng, W.-L. (2016). Facile synthesis and characterization of thiol-functionalized graphene oxide as effective adsorbent for Hg(II). Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2016.03.034.
Lagergren, S. (1898). About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens Handlingar, 24(4), 1–39.
Langmuir, I. (1918). The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. Journal of the American Chemical Society. doi:10.1021/ja02242a004.
Li, Y., Zhang, P., Du, Q., Peng, X., Liu, T., Wang, Z., Xia, Y., Zhang, W., Wang, K., Zhu, H., & Wu, D. (2011). Adsorption of fluoride from aqueous solution by graphene. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2011.07.032.
Li, M., Wang, J., Jiao, C., Wang, C., Wu, Q., & Wang, Z. (2016). Graphene oxide framework: an adsorbent for solid phase extraction of phenylurea herbicides from water and celery samples. Journal of Chromatography A. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2016.09.056.
Lu, A.-H., Salabas, E. L., & Schüth, F. (2007). Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. doi:10.1002/anie.200602866.
Malakootian, M., Fatehizadeh, A., Yousefi, N., Ahmadian, M., & Moosazadeh, M. (2011). Fluoride removal using regenerated spent bleaching earth (RSBE) from groundwater: case study on Kuhbonan water. Desalination. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2011.04.033.
Mariappan, R., Vairamuthu, R., & Ganapathy, A. (2015). Use of chemically activated cotton nut shell carbon for the removal of fluoride contaminated drinking water: kinetics evaluation. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering. doi:10.1016/j.cjche.2014.05.019.
Meenakshi, S., & Viswanathan, N. (2007). Identification of selective ion-exchange resin for fluoride sorption. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2006.12.032.
Mondal, N. K., Bhaumik, R., & Datta, J. K. (2015). Removal of fluoride by aluminum impregnated coconut fiber from synthetic fluoride solution and natural water. Alexandria Engineering Journal. doi:10.1016/j.aej.2015.08.006.
Nagatani, T., Saito, S., Sato, M., & Yamada, M. (1987). Development of an ultra-high resolution scanning electron microscope by means of a field emission source and in-lens system. Scanning Microscopy, 11(3), 901–909.
Ni, Z., Wang, Y., Yu, T., & Shen, Z. (2008). Raman spectroscopy and imaging of graphene. Nano Research. doi:10.1007/s12274-008-8036-1.
Nine, M. J., Cole, M. A., Tran, D. N. H., & Losic, D. (2015). Graphene: a multipurpose material for protective coatings. Journal of Materials Chemistry A. doi:10.1039/c5ta01010a.
Noh, J. S., & Schwarz, J. A. (1989). Estimation of the point of zero charge of simple oxides by mass titration. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science. doi:10.1016/0021-9797(89)90086-6.
Nur, T., Loganathan, P., Nguyen, T. C., Vigneswaran, S., Singh, G., & Kandasamy, J. (2014). Batch and column adsorption and desorption of fluoride using hydrous ferric oxide: solution chemistry and modeling. Chemical Engineering Journal. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2014.03.009.
Paudyal, H., Pangeni, B., Inoue, K., Kawakita, H., Ohto, K., Harada, H., & Alam, S. (2011). Adsorptive removal of fluoride from aqueous solution using orange waste loaded with multi-valent metal íons. Journal of Hazardous Materials. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.05.070.
Paudyal, H., Pangeni, B., Ghimire, K. N., Inoue, K., Ohto, K., Kawakita, H., & Alam, S. (2012a). Adsorption behavior of orange waste gel for some rare earth ions and its application to the removal of fluoride from water. Chemical Engineering Journal. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2012.04.061.
Paudyal, H., Pangeni, B., Inoue, K., Kawakita, H., Ohto, K., & Alam, S. (2012b). Removal of fluoride from aqueous solution by using porous resins containing hydrated oxide of cerium(IV) and zirconium(IV). Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan. doi:10.1252/jcej.11we181.
Poursaberi, T., Hassanisadi, M., Torkestani, K., & Zare, M. (2012). Development of zirconium (IV)-metalloporphyrin grafted Fe3O4 nanoparticles for efficient fluoride removal. Chemical Engineering Journal. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2012.02.039.
Rafique, A., Awan, M. A., Wasti, A., Qazi, I. A., & Arshad, M. (2013). Removal of fluoride from drinking water using modified immobilized activated alumina. Journal of Chemistry. doi:10.1155/2013/386476.
Saito, R., Furukawa, M., Dresselhaus, G., & Dresselhaus, M. S. (2010). Raman spectra of graphene ribbons. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/22/33/334203.
Sepehr, M. N., Sivasankar, V., Zarrabi, M., & Kumar, M. S. (2013). Surface modification of pumice enhancing its fluoride adsorption capacity: an insight into kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chemical Engineering Journal. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2013.04.089.
Shalaby, A., Nihtianova, D., Markov, P., Staneva, A. D., Iordanova, R. S., & Dimitriev, Y. B. (2015). Structural analysis of reduced graphene oxide by transmission electron microscopy. Bulgarian Chemical Communications, 47(1), 291–295.
Sheng, Y., Tang, X., Peng, E., & Xue, J. (2013). Graphene oxide based fluorescent nanocomposites for cellular imaging. Journal of Materials Chemistry B. doi:10.1039/c2tb00123c.
Shimanouchi, T. (1977). Tables of molecular vibrational frequencies. Consolidated volume II. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data. doi:10.1063/1.555560.
Srinivas, G., Zhu, Y., Piner, R., Skipper, N., Ellerby, M., & Ruoff, R. (2010). Synthesis of graphene-like nanosheets and their hydrogen adsorption capacity. Carbon. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2009.10.003.
Swain, S. K., Mishra, S., Patnaik, T., Patel, R. K., Jha, U., & Dey, R. K. (2012). Fluoride removal performance of a new hybrid sorbent of Zr(IV)–ethylenediamine. Chemical Engineering Journal. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2011.12.091.
Tomar, V., Prasad, S., & Kumar, D. (2014). Adsorptive removal of fluoride from aqueous media using Citrus limonum (lemon) leaf. Microchemical Journal. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2013.09.010.
Tovar-Gómez, R., Moreno-Virgen, M. R., Dena-Aguilar, J. A., Hernández-Montoya, V., Bonilla-Petriciolet, A., & Montes-Morán, M. A. (2013). Modeling of fixed-bed adsorption of fluoride on bone char using a hybrid neural network approach. Chemical Engineering Journal. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2013.05.080.
Weber, W. J., & Morris, J. C. (1963). Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. Journal of the Sanitary Engineering Division, 89(2), 31–60.
World Health Organization. (2011). Guidelines for drinking-water quality (4th Ed.). Geneva: World Health Organization.
Xiong, P., Hu, C., Fan, Y., Zhang, W., Zhu, J., & Wang, X. (2014). Ternary manganese ferrite/graphene/polyaniline nanostructure with enhanced electrochemical capacitance performance. Journal of Power Sources. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.05.048.
Yadav, A. K., Abbassi, R., Gupta, A., & Dadashzadeh, M. (2013). Removal of fluoride from aqueous solution and groundwater by wheat straw, sawdust and activated bagasse carbon of sugarcane. Ecological Engineering. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2012.12.069.
Yamaguchi, N. U., Bergamasco, R., & Hamoudi, S. (2016). Magnetic MnFe2O4-graphene hybrid composite for efficient removal of glyphosate from water. Chemical Engineering Journal. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2016.03.051.
Yang, D., Velamakanni, A., Bozoklu, G., Park, S., Stoller, M., Piner, R. D., Stankovich, S., Jung, I., Field, D. A., Ventrice, C. A., Jr., & Ruoff, R. S. (2009). Chemical analysis of graphene oxide films after heat and chemical treatments by X-ray photoelectron and micro-Raman spectroscopy. Carbon. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2008.09.045.
Zhang, L. Y., Zhang, W., Zhou, Z., & Li, C. M. (2016). γ-Fe2O3 nanocrystals-anchored macro/meso-porous graphene as a highly efficient adsorbent toward removal of methylene blue. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2016.05.025.
Zhou, M., Tian, T., Li, X., Sun, X., Zhang, J., Cui, P., Tang, J., & Qin, L. C. (2014). Production of graphene by liquid-phase exfoliation of intercalated graphite. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 9(2), 810–820.
Zhu, J., Wei, S., Gu, H., Rapole, S. B., Wang, Q., Luo, Z., Haldolaarachchige, N., Young, D. P., & Guo, Z. (2012). One-pot synthesis of magnetic graphene nanocomposites decorated with core@double-shell nanoparticles for fast chromium removal. Environmental Science & Technology. doi:10.1021/es2014133.
Zhu, J., Lin, X., Wu, P., Zhou, Q., & Luo, X. (2015). Fluoride removal from aqueous solution by Al(III)–Zr(IV) binary oxide adsorbent. Applied Surface Science. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.09.012.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq - Brazil), the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), and Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI) for financial support. They also are grateful to Richard Janvier for TEM characterization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marin, P., Módenes, A.N., Bergamasco, R. et al. Synthesis, Characterization and Application of ZrCl4-Graphene Composite Supported on Activated Carbon for Efficient Removal of Fluoride to Obtain Drinking Water. Water Air Soil Pollut 227, 479 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3188-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3188-1