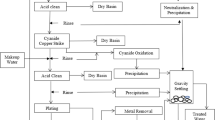
Abstract
This study is concerned with the removal performance of the antibiotic ciprofloxacin (CIP) from synthetic solutions by electrocoagulation (EC), as well as the toxic effects of treated CIP solutions. A response surface analysis (RSA) was applied to search optimal operational parameter values of the pH of solution, electrical current density (ECD), and electrolysis time (ET). The EC efficiency was evaluated by determining the total organic carbon (TOC) and CIP concentration performed by high-performance liquid chromatography. Although the best EC efficiency was attained at pH = 8, ECD = 22.2 A m−2, and ET = 75 min, toxicity and antibacterial tests were performed using Artemia salina cysts and Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli microorganisms in a wide ET range and other pH and ECD values. Increasing optimal pH value (9), along with reducing optimal ECD value (18 A m−2) and regarding low ET values, similar results for the removal of CIP (98%) and TOC (87%) were also attained. Toxicity variation was observed during EC process in synthetic solutions with the lowest antibacterial effects due to CIP and recalcitrant compound residues after 40 min of ET. These results clearly showed that the EC process presents a promising alternative method for the treatment of wastewaters containing high CIP concentrations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA - American Public Health Association. (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (21st ed.). Washington: APHA.
Arsand, D. R., Kummerer, K., & Martins, A. F. (2013). Removal of dexamethasone from aqueous solution and hospital waste by electrocoagulation. Science of the Total Environment, 443, 351–357.
Benotti, M. J., Trenholm, R. A., Vanderford, B. J., Holady, J. C., Stanford, B. D., & Snyder, S. A. (2009). Pharmaceuticals and endocrine disrupting compounds in U.S. drinking water. Environmental Science and Technology, 43, 597–603.
Bruker, S2 PICOFOX TXRF (2011). Spectrometer for element analysis. User manual. Berlin.
Carlucci, G. (1998). Analysis of fluoroquinolones in biological fluids by high-performance liquid chromatography. Journal of Chromatography A, 812, 343–367.
Chen, G. (2004). Electrochemical technologies in wastewater treatment. Separation and Purification Technology, 38, 11–41.
De Bel, E., Dewulf, J., De Witte, B., Langenhove, H. V., & Janssen, C. (2009). Influence of pH on the sonolysis of ciprofloxacin: biodegradability, ecotoxicity and antibiotic activity of its degradation products. Chemosphere, 77, 291–295.
De Witte, B., Langenhove, H. V., Demeestere, K., Saerens, K., Wispelaere, P., & Dewulf, J. (2010). Ciprofloxacin ozonation in hospital wastewater treatment plant effluent: effect of pH and H2O2. Chemosphere, 78, 1142–1147.
Drogui, P., Asselin, M., Brar, S. K., Benmoussa, H., & Blais, J. F. (2008). Electrochemical removal of pollutants from agro-industry wastewaters. Separation and Purification Technology, 61, 301–310.
Espinoza-Quiñones, F. R., Fornari, M. M. T., Módenes, A. N., Palácio, S. M., Silva, F. G., Szymanski, N., Kroumov, A. D., & Trigueros, D. E. G. (2009). Pollutant removal from tannery effluent by electrocoagulation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 151, 59–65.
Espinoza-Quiñones, F.R., Módenes, A.N., Pauli, A.R., & Palácio, S.M. (2015). Analysis of trace elements in groundwater using ICP-OES and TXRF techniques and its compliance with Brazilian protection standards. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 226, article 32.
Gad-Allah, T. A., Ali, M. E. M., & Badawy, M. I. (2011). Photocatalytic oxidation of ciprofloxacin under simulated sunlight. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 186, 751–755.
González-Pleiter, M., Gonzalo, S., Rodea-Palomares, I., Leganés, F., Rosal, R., Marco, E., & Fernández-Piñas, F. (2013). Toxicity of five antibiotics and their mixtures towards photosynthetic aquatic organisms: implications for environmental risk assessment. Water Research, 47, 2050–2064.
Hamilton, M. A., Russo, R. C., & Thurston, R. V. (1977). Trimmed Spearman Karber statistical method for estimating median lethal concentration in toxicity bioassays. Environmental Science & Technology, 11, 714–719.
Herrera, A. V., Hernandez-Borges, J., Borges-Miquel, T. M., & Rodriguez-Delgado, M. A. (2010). Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with nonaqueous capillary electrophoresis for the determination of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in waters. Electrophoresis, 31, 3457–3465.
Holt, P. K., Barton, G. W., & Mitchell, C. A. (2005). The future for electrocoagulation as a localized water treatment technology. Chemosphere, 59, 355–367.
Ilhan, F., Kurt, U., Apaydin, O., & Gonullu, M. T. (2008). Treatment of leachate by electrocoagulation using aluminum and iron electrodes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 154, 381–389.
Jalil, M. E. R., Baschini, M., & Sapag, K. (2015). Influence of pH and antibiotic solubility on the removal of ciprofloxacin from aqueous media using montmorillonite. Applied Clay Science, 114, 69–76.
Jiang, L., Hu, X., Zhang, H., Sheng, D., & Yin, D. (2013). Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes and their relationship with antibiotics on the Huangpu River and the drinking water sources, Shanghai, China. The Science of the Total Environment, 458–460, 267–272.
Kamaraj, R., & Vasudevan, S. (2015). Evaluation of electrocoagulation process for the removal of strontium and cesium from aqueous solution. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 93, 522–530.
Kamaraj, R., & Vasudevan, S. (2016a). Facile one-pot synthesis of nano-zinc hydroxide by electro-dissolution of zinc as a sacrificial anode and the application for adsorption of Th4+, U4+, and Ce4+ from aqueous solution. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 42, 4077–4095.
Kamaraj, R., & Vasudevan, S. (2016b). Facile one-pot electrosynthesis of Al(OH)3—kinetics and equilibrium modeling for adsorption of 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid from aqueous solution. New Journal of Chemistry, 40, 2249–2258.
Kamaraj, R., Davidson, D. J., Sozhan, G., & Vasudevan, S. (2014). Adsorption of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) from water by in situ generated metal hydroxides using sacrificial anodes. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 45, 2943–2949.
Kamaraj, R., Davidson, D. J., Sozhan, G., & Vasudevan, S. (2015). Adsorption of herbicide 2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy) propanoic acid by electrochemically generated aluminum hydroxides: an alternative to chemical dosing. RSC Advances, 5, 39799–39809.
Kamaraj, R., Pandiarajan, A., Jayakiruba, S., Naushad, M., & Vasudevan, S. (2016). Kinetics, thermodynamics and isotherm modeling for removal of nitrate from liquids by facile one-pot electrosynthesized nano zinc hydroxide. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 215, 204–211.
Khandegar, V., & Saroha, A. K. (2013). Electrocoagulation for the treatment of textile industry effluent—a review. Journal of Environmental Management, 128, 949–963.
Kummerer, K. (2009). Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—a review—part I. Chemosphere, 75, 417–434.
Lupo, A., Coyne, S., & Berendonk, T. U. (2012). Origin and evolution of antibiotic resistance: the common mechanisms of emergence and spread in the water bodies. Frontiers in Microbiology, 3, 1–13.
Manenti, D. R., Módenes, A. N., Soares, P. A., Espinoza-Quiñones, F. R., Boaventura, R. A. R., Bergamasco, R., & Vilar, V. J. P. (2014). Assessment of a multistage system based on electrocoagulation, solar photo-Fenton and biological oxidation processes for real textile wastewater treatment. Chemical Engineering Journal, 252, 120–130.
Martinez, J. L. (2009). Environmental pollution by antibiotics and by antibiotic resistance determinants. Environmental Pollution, 157, 2893–2902.
Marx, C., Gunther, N., Schubert, S., Oertel, R., Ahnert, M., Krebs, P., & Kuehn, V. (2015). Mass flow of antibiotics in a wastewater treatment plant focusing on removal variation due to operational parameters. The Science of the Total Environment, 538, 779–788.
Meyer, B. N., Ferrigni, N. R., Putnam, J. E., Jacobsen, L. B., Nichols, D. E., & Mclaughlin, J. L. (1982). Brine shrimp: a convenient general bioassay for active plant constituents. Journal of Medicinal Plant Research, 45, 35–36.
Michael, I., Rizzo, L., Mcardell, C. S., Manaia, C. M., Merlin, C., Schwartz, T., Dagot, C., & Fatta-Kassinos, D. (2013). Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for the release of antibiotics in the environment: a review. Water Research, 47, 957–995.
Mollah, M. Y. A., Morkovsky, P., Gomes, J. A. G., Kesmez, M., Pargad, J., & Cocke, D. L. (2004). Fundamentals, present and future perspectives of electrocoagulation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 114(1–3), 199–210.
Montgomery, D. C. (2008). Design and analysis of experiments (7th ed.). New York: Wiley. 656 pp.
NCCLS (2003). Performance standards for antimicrobial disk susceptibility tests; approved standard—eighth edition. NCCLS document M2-A8 (ISBN 1-56238-485-6). NCCLS, Wayne, Pennsylvania, USA.
Ouaissa, Y. A., Chabani, M., Amrane, A., & Bensmaili, A. (2014). Removal of tetracycline by electrocoagulation: kinetic and isotherm modeling through adsorption. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2, 177–184.
Padhye, L. P., Yao, H., Kung’u, F. T., & Huang, C.-H. (2014). Year-long evaluation on the occurrence and fate of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and endocrine disrupting chemicals in an urban drinking water treatment plant. Water Research, 51, 266–276.
Perini, J. A. L., Moya, M. P., & Nogueira, R. F. P. (2013). Photo-Fenton degradation kinetics of low ciprofloxacin concentration using different iron sources and pH. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 259, 53–58.
Rodriguez, J., Stopié, S., Krause, G., & Friedrich, B. (2007). Feasibility assessment of electrocoagulation towards a new sustainable wastewater treatment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 14(7), 477–482.
Rodriguez-Mozaz, S., Chamorro, S., Marti, E., Huerta, B., Gros, M., Sanchez-Melsio, A., Borrego, C. M., Barcelo, D., & Balcazar, J. L. (2015). Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in the hospital and urban wastewaters and their impact on the receiving river. Water Research, 69, 234–242.
Sturini, M., Speltini, A., Maraschi, F., Pretali, L., Profumo, A., Fasani, E., Albini, A., Migliavacca, R., & Nucleo, E. (2012). Photodegradation of fluoroquinolones in surface water and antimicrobial activity of the photoproducts. Water Research, 46, 5575–5582.
Vadja, A. M., Barber, L. B., Gray, J. L., Lopez, E. M., Bolden, A. M., Schoenfuss, H. L., & Norris, D. O. (2011). Demasculinization of male fish by wastewater treatment plant effluent. Aquatic Toxicology, 103, 213–221.
Vasconcelos, T. G., Kummeres, K., Henriques, D. M., & Martins, A. F. (2009). Ciprofloxacin in hospital effluent: degradation by ozone and photoprocesses. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 169, 1154–1158.
Vasudevan, S., & Lakshmi, J. (2012). Electrochemical removal of boron from water: adsorption and thermodynamic studies. Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 90, 1017–1026.
Vasudevan, S., & Oturan, M. A. (2014). Electrochemistry: as cause and cure in water pollution—an overview. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 12, 97–108.
Vasudevan, S., Sozhan, G., Ravichandran, S., Jayaraj, J., Lakshmi, J., & Sheela, S. M. (2008). Studies on the removal of phosphate from drinking water by electrocoagulation process. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 47, 2018–2023.
Vasudevan, S., Jayaraj, J., Lakshmi, J., & Sozhan, G. (2009a). Removal of iron from drinking water by electrocoagulation: adsorption and kinetics studies. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 26, 1058–1064.
Vasudevan, S., Lakshmi, J., & Sozhan, G. (2009b). Optimization of the process parameters for the removal of phosphate from drinking water by electrocoagulation. Desalination and Water Treatment, 12, 407–414.
Vasudevan, S., Lakshmi, J., & Sozhan, G. (2011). Studies on the Al–Zn–In-alloy as anode material for the removal of chromium from drinking water in electrocoagulation process. Desalination, 275, 260–268.
Vasudevan, S., Lakshmi, J., & Sozhan, G. (2013). Electrochemically assisted coagulation for the removal of boron from water using zinc anode. Desalination, 310, 122–129.
Woodling, J. D., Lopez, E. M., Maldonado, T. A., Norris, D. O., & Vadja, A. M. (2006). Intersex and other reproductive disruption of fish in wastewater effluent dominated Colorado streams. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, 144, 10–15.
Xu, X., Liu, L., Jia, Z., & Shu, Y. (2015). Determination of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in foods of animal origin by capillary electrophoresis with field amplified sample stacking-sweeping technique. Food Chemistry, 176, 219–225.
Zhang, X., Dong, L. L., Cai, K., & Li, R. P. (2013). A routine method for simultaneous determination of three classes of antibiotics in aquaculture water by SPE-RPLC-UV. Advanced in Material Research, 726, 1253–1259.
Zhang, X., Li, R., Jia, M., Wang, S., Huang, Y., & Chen, C. (2015). Degradation of ciprofloxacin in aqueous bismuth oxybromide (BiOBr) suspensions under visible light irradiation: a direct hole oxidation pathway. Chemical Engineering Journal, 274, 290–297.
Zhuo, J. J., Ying, G. G., Liu, S., Zhao, J. L., Chen, F., Zhang, R. Q., Peng, F. Q., & Zhang, Q. Q. (2012). Simultaneous determination of human and veterinary antibiotics in various environmental matrices by rapid resolution liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1244, 123–138.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES), National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), and Araucaria Foundation for the financial support of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Espinoza-Quiñones, F.R., de Souza, A.R.C., Módenes, A.N. et al. Removal Performance, Antibacterial Effects, and Toxicity Assessment of Ciprofloxacin Treated by the Electrocoagulation Process. Water Air Soil Pollut 227, 460 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3165-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3165-8