Abstract
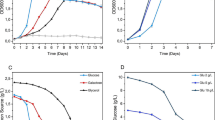
As major endocrine disruptors, natural estrogens such as 17β-estradiol (E2) have been found with adverse effects on animals and humans. How to control E2 pollution as well as that of other estrogens in the environment is a worldwide concern. A novel E2-degrading bacterium (strain JX-2) was isolated from the activated sludge of a sewage treatment plant and was identified as Rhodococcus sp. Strain JX-2 grew well and metabolized up to 94 % of the substrate E2 added (30 mg L−1) within 7 days at 30 °C. The optimal environmental conditions for E2 degradation by JX-2 were pH 7.0 and 30 °C. Strain JX-2 was immobilized in sodium alginate. The optimal conditions for strain JX-2 immobilization were 4 % sodium alginate, 1:1 bacteria/sodium alginate ratio, 5 % CaCl2⋅2H2O, and 6 h crosslinking time. The degradation performance of immobilized strain JX-2 was apparently superior to that of the free strain, particularly under pH <6.0 or >8.0 either below 20 or above 35 °C. Immobilized strain JX-2 removed E2 in natural sewage and cow dung with removal efficiency of more than 64 and 81 %, respectively. This is the first report of utilizing immobilized bacteria to remove estrogens in sewage and livestock manure. The results suggest that strain JX-2 could be used to remove E2 from the environment efficiently.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, S. A., Shamaan, N. A., Arif, N. M., Koon, G. B., Shukor, M. Y. A., & Syed, M. A. (2012). Enhanced phenol degradation by immobilized Acinetobacter sp. strain AQ5NOL 1. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 28, 347–352.
Andaluri, G., Suri, R. P. S., & Kumar, K. (2012). Occurrence of estrogen hormones in biosolids, animal manure and mushroom compost. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 1197–1205.
Baronti, C., Curini, R., D’Ascenzo, G., Di Corcia, A., Gentili, A., & Samperi, R. (2000). Monitoring natural and synthetic estrogens at activated sludge sewage treatment plants and in a receiving river water. Environmental Science & Technology, 34, 5059–5066.
Belfroid, A. C., Van der Horst, A., Vethaak, A. D., Schafer, A. J., Rijs, G., Wegener, J., & Cofino, W. P. (1999). Analysis and occurrence of estrogenic hormones and their glucuronides in surface water and waste water in the Netherlands. Science of the Total Environment, 225, 101–108.
Byers, H. K., Stackebrandt, E., Hayward, C., & Blackall, L. L. (1998). Molecular investigation of a microbial mat associated with the Great Artesian basin. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 25, 391–403.
Chang, J. S., Chou, C., & Chen, S. Y. (2001). Decolorization of azo dyes with immobilized Pseudomonas luteola. Process Biochemistry, 36, 757–763.
Chung, T. P., Tseng, H. Y., & Juang, R. S. (2003). Mass transfer effect and intermediate detection for phenol degradation in immobilized Pseudomonas putida systems. Process Biochemistry, 38, 1497–1507.
Covarrubias, S. A., De-Bashan, L. E., Moreno, M., & Bashan, Y. (2012). Alginate beads provide a beneficial physical barrier against native microorganisms in wastewater treated with immobilized bacteria and microalgae. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 93, 2669–2680.
Crisp, T. M., Clegg, E. D., Cooper, R. L., Anderson, D. G., Baetcke, K. P., Hoffmann, J. L., Morrow, M. S., Rodier, D. J., Schaeffer, J. E., & Touart, L. W. (1997). Special report on environmental endocrine disruption: an effects assessment and analysis. Washington: Environmental Protection Agency.
Desbrow, C., Routledge, E. J., Brighty, G. C., Sumpter, J. P., & Waldock, M. (1998). Identification of estrogenic chemicals in STW effluent. 1. Chemical fractionation and in vitro biological screening. Environmental Science & Technology, 32, 1549–1558.
Duan, H. M. (2012). Biodegradation characteristics of chlorpyrifos by immobilized bacteria. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 20, 1636–1642.
Folmar, L. C., Denslow, N. D., Rao, V., Chow, M., Crain, D. A., Enblom, J., Marcino, J., & Guillette, L. J. (1996). Vitellogenin induction and reduced serum testosterone concentrations in feral male carp (Cyprinus carpio) captured near a major metropolitan sewage treatment plant. Environmental Health Perspectives, 104, 1096–1101.
Fujii, K., Kikuchi, S., Satomi, M., Ushio-Sata, N., & Morita, N. (2002). Degradation of 17 beta-estradiol by a gram-negative bacterium isolated from activated sludge in a sewage treatment plant in Tokyo. Japan Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 2057–2060.
Garrity, G. M., Bell, J. A., & Lilburn, T. G. (2004). Taxonomic outline of the prokaryotes. Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology. New York: Springer.
Gentili, A. R., Cubitto, M. A., Ferrero, M., & Rodriguez, M. S. (2006). Bioremediation of crude oil polluted seawater by a hydrocarbon-degrading bacterial strain immobilized on chitin and chitosan flakes. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradration, 57, 222–228.
Idris, A., & Suzana, W. (2006). Effect of sodium alginate concentration, bead diameter, initial pH and temperature on lactic acid production from pineapple waste using immobilized Lactobacillus delbrueckii. Process Biochemistry, 41, 1117–1123.
Järvenpää, P., Kosunen, T., Fotsis, T., & Adlercreutz, H. (1980). In vitro metabolism of estrogens by isolated intestinal micro-organisms and by human faecal microflora. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry, 13, 345–349.
Jiang, L., Yang, J., & Chen, J. (2010). Isolation and characteristics of 17 beta-estradiol-degrading Bacillus spp. strains from activated sludge. Biodegradation, 21, 729–736.
Jobling, S., Beresford, N., Nolan, M., Rodgers-Gray, T., Brighty, G. C., Sumpter, J. P., & Tyler, C. R. (2002). Altered sexual maturation and gamete production in wild roach (Rutilus rutilus) living in rivers that receive treated sewage effluents. Biology of Reproduction, 66, 272–281.
Johnson, A. C., & Williams, R. J. (2004). A model to estimate influent and effluent concentrations of estradiol, estrone, and ethinylestradiol at sewage treatment works. Environmental Science & Technology, 38, 3649–3658.
Kavlock, R. J., Daston, G. P., DeRosa, C., FennerCrisp, P., Gray, L. E., Kaattari, S., Lucier, G., Luster, M., Mac, M. J., Maczka, C., Miller, R., Moore, J., Rolland, R., Scott, G., Sheehan, D. M., Sinks, T., & Tilson, H. A. (1996). Research needs for the risk assessment of health and environmental effects of endocrine disruptors: a report of the US EPA-sponsored workshop. Environmental Health Perspectives, 1044, 715–740.
Kornman, K. S., & Loesche, W. J. (1982). Effects of estradiol and progesterone on Bacteroides melaninogenicus and Bacteroides gingivalis. Infection and Immunity, 35, 256–263.
Kuch, H. M., & Ballschmiter, K. (2001). Determination of endocrine-disrupting phenolic compounds and estrogens in surface and drinking water by HRGC-(NCI)-MS in the picogram per liter range. Environmental Science & Technology, 35, 3201–3206.
Lau, P. S., Tam, N., & Wong, Y. S. (1997). Wastewater nutrients (N and P) removal by carrageenan and alginate immobilized Chlorella vulgaris. Environmental Technology, 18, 945–951.
Le, T. A. H., Clemens, J., & Nguyen, T. H. (2013). Performance of different composting techniques in reducing oestrogens content in manure from livestock in a Vietnamese setting. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185, 415–423.
Lee, S. T., Rhee, S. K., & Lee, G. M. (1994). Biodegradation of pyridine by freely suspended and immobilized Pimelobacter sp. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 41, 652–657.
Li, H., Zhang, Y., Irina, K., Xu, H., & Mang, C. (2007). Dynamic changes in microbial activity and community structure during biodegradation of petroleum compounds: a laboratory experiment. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 19, 1003–1013.
Li, X., Ling, W. T., Liu, J. X., Sun, M. X., Gao, Y. Z., & Liu, J. (2015). Immobilization of estrogen-degrading bacteria to remove the 17β-estradiol and diethylstilbestrol from polluted water and cow dung. Environmental Sciences, 36, 2581–2590 (in Chinese).
Nasu, M., Goto, M., Kato, H., Oshima, Y., & Tanaka, H. (2001). Study on endocrine disrupting chemicals in wastewater treatment plants. Water Science and Technology, 43, 101–108.
Ojanotko-Harri, A., Laine, M., & Tenovuo, J. (1991). Metabolism of 17β-estradiol by oral Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus sanguis, Bacillus cereus and Candida albicans. Oral Microbiology and Immunology, 6, 126–128.
Pauwels, B., Wille, K., Noppe, H., De Brabander, H., van de Wiele, T., Verstraete, W., & Boon, N. (2008). 17 Alpha-ethinylestradiol cometabolism by bacteria degrading estrone, 17 beta-estradiol and estriol. Biodegradation, 19, 683–693.
Purdom, C. E., Hardiman, P. A., Bye, V. V. J., Eno, N. C., Tyler, C. R., & Sumpter, J. P. (1994). Estrogenic effects of effluents from sewage treatment works. Chemistry and Ecology, 8, 275–285.
Quan, X. C., Shi, H. C., Zhang, Y. M., Wang, H. L., & Qian, Y. (2004). Biodegradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol and phenol in an airlift inner-loop bioreactor immobilized with Achromobacter sp. Separation and Purification Technology, 34, 97–103.
Rahman, R. N. Z. A., Ghazali, F. M., Salleh, A. B., & Basri, M. (2006). Biodegradation of hydrocarbon contamination by immobilized bacterial cells. Journal of Microbiology, 44, 354–359.
Selimoglu, S. M., & Elibol, M. (2010). Alginate as an immobilization material for MAb production via encapsulated hybridoma cells. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 30, 145–159.
Shi, J. H., Suzuki, Y., Lee, B. D., Nakai, S., & Hosomi, M. (2002). Isolation and characterization of the ethynylestradiol-biodegrading microorganism Fusarium proliferatum strain HNS-1. Water Science and Technology, 45, 175–179.
Silva, C. P., Otero, M., & Esteves, V. (2012). Processes for the elimination of estrogenic steroid hormones from water: a review. Environmental Pollution, 165, 38–58.
Snyder, S. A., Keith, T. L., Verbrugge, D. A., Snyder, E. M., Gross, T. S., Kannan, K., & Giesy, J. P. (1999). Analytical methods for detection of selected estrogenic compounds in aqueous mixtures. Environmental Science & Technology, 33, 2814–2820.
Solé, M., de Alda, M., Castillo, M., Porte, C., Ladegaard-Pedersen, K., & Barceló, D. (2000). Estrogenicity determination in sewage treatment plants and surface waters from the Catalonian area (NE Spain). Environmental Science & Technology, 34, 5076–5083.
Sun, K., Liu, J., Jin, L., & Gao, Y. (2014). Utilizing pyrene-degrading endophytic bacteria to reduce the risk of plant pyrene contamination. Plant and Soil, 374, 251–262.
Tabata, A., Kashiwada, S., Ohnishi, Y., Ishikawa, H., Miyamoto, N., Itoh, M., & Magara, Y. (2001). Estrogenic influences of estradiol-17 beta, p-nonylphenol and bisphenol-A on Japanese Medaka (Oryzias latipes) at detected environmental concentrations. Water Science and Technology, 43, 109–116.
Ternes, T. A., Stumpf, M., Mueller, J., Haberer, K., Wilken, R. D., & Servos, M. (1999). Behavior and occurrence of estrogens in municipal sewage treatment plants—I. Investigations in Germany, Canada and Brazil. Science of the Total Environment, 225, 81–90.
Tyler, C. R., Jobling, S., & Sumpter, J. P. (1998). Endocrine disruption in wildlife: a critical review of the evidence. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 28, 319–361.
Vanotti, M. B., & Hunt, P. G. (2000). Nitrification treatment of swine wastewater with acclimated nitrifying sludge immobilized in polymer pellets. Transactions of ASAE, 43, 405–413.
Vos, J. G., Dybing, E., Greim, H. A., Ladefoged, O., Lambre, C., Tarazona, J. V., Brandt, I., & Vethaak, A. D. (2000). Health effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals on wildlife, with special reference to the European situation. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 30, 71–133.
Wang, C. C., Lee, C. M., & Kuan, C. H. (2000). Removal of 2, 4-dichlorophenol by suspended and immobilized Bacillus insolitus. Chemosphere, 41, 447–452.
Weber, S., Leuschner, P., Kampfer, P., Dott, W., & Hollender, J. (2005). Degradation of estradiol and ethinyl estradiol by activated sludge and by a defined mixed culture. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 67, 106–112.
Xu, R. F., Sun, M. X., Liu, J., Wang, H., Li, X., Zhu, X. Z., & Ling, W. T. (2014). Isolation, characteristics, and performance of a diethylstilbestrol-degrading bacteria strain Serratia sp. Environmental Sciences, 35, 328–333 (in Chinese).
Yang, S., Jin, H., Wei, Z., He, R., Ji, Y., Li, X., & Yu, S. (2009). Bioremediation of oil spills in cold environments: a review. Pedosphere, 19, 371–381.
Yoshimoto, T., Nagai, F., Fujimoto, J., Watanabe, K., Mizukoshi, H., Makino, T., Kimura, K., Saino, H., Sawada, H., & Omura, H. (2004). Degradation of estrogens by Rhodococcus zopfii and Rhodococcus equi isolates from activated sludge in wastewater treatment plants. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 5283–5289.
Yu, C., Roh, H., & Chu, K. (2007). 17 Beta-estradiol-degrading bacteria isolated from activated sludge. Environmental Science & Technology, 41, 486–492.
Zeng, Q., Li, Y., & Yang, S. (2013). Sludge retention time as a suitable operational parameter to remove both estrogen and nutrients in an anaerobic-anoxic-aerobic activated sludge system. Environmental Engineering Science, 30, 161–169 (in Chinese).
Zheng, W., Yates, S. R., & Bradford, S. A. (2007). Analysis of steroid hormones in a typical dairy waste disposal system. Environmental Science & Technology, 42, 530–535.
Zhou, Y., Zha, J., Xu, Y., Lei, B., & Wang, Z. (2012). Occurrences of six steroid estrogens from different effluents in Beijing. China Environmental Monitoring Assessment, 184, 1719–1729.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51278252, 21477056), Research Project of Environmental Protection in Jiangsu Province, China (2015023), and Jiangsu Provincial Key Research and Development Plan, China (BE2015682).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Jingxian Liu and Juan Liu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Liu, J., Xu, D. et al. Isolation, Immobilization, and Degradation Performance of the 17β-Estradiol-Degrading Bacterium Rhodococcus sp. JX-2. Water Air Soil Pollut 227, 422 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3122-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3122-6