Abstract
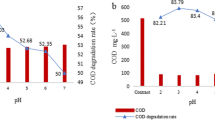
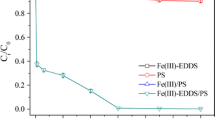
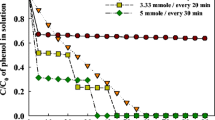
An electrochemically activated persulfate (EC/PS) system was proposed for the degradation of herbicide diuron in this study. In the EC/PS system, the ferrous ions (Fe2+) produced from iron electrode can activate persulfate to generate sulfate radical (SO4 ·-) as well as hydroxyl radical (OH•). The results showed that the degradation of diuron was significantly enhanced in the EC/PS system, compared to electrocoagulation, persulfate, and Fe2+/PS process. Both of SO4 ·- and OH· contributed to the degradation of diuron in the EC/PS system according to the radical scavenging studies. The pseudo first-order rate constants of diuron increased with increasing the applied currents and dosages of persulfate. pH affected the degradation of diuron indirectly through the speciation of iron and resulted in higher removal efficiency in acidic condition than in alkaline condition. Chloride, carbonate, and bicarbonate in real water inhibited the degradation of diuron dramatically through consuming SO4 ·- and OH· and abided by the order of CO3 2−>HCO3 −>Cl−. This study demonstrates that the EC/PS system is a novel, efficient, promising, and environmental-friendly method to treat diuron contamination.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anipsitakis, G. P., & Dionysiou, D. D. (2004). Radical generation by the interaction of transition metals with common oxidants. Environmental Science & Technology, 38, 3705–3712.
Antonin, V. S., Santos, M. C., Garcia-Segura, S., & Brillas, E. (2015). Electrochemical incineration of the antibiotic ciprofloxacin in sulfate medium and synthetic urine matrix. Water Research, 83, 31–41.
Bu, L., Zhou, S., Shi, Z., Deng, L., Li, G., Yi, Q., & Gao, N. (2016). Degradation of oxcarbazepine by UV-activated persulfate oxidation: kinetics, mechanisms, and pathways. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(3), 2848–2855.
Buxton, G. V., Greenstock, C. L., Helman, W. P., & Ross, A. B. (1988). Critical-review of rate constants for reactions of hydrated electrons, hydrogen-atoms and hydroxyl radicals (•OH/•O−) in aqueous solution. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 17, 513–886.
Cao, J., Zhang, W.-X., Brown, D. G., & Sethi, D. (2008). Oxidation of lindane with Fe (II)-activated sodium persulfate. Environmental Engineering Science, 25, 221–228.
Carrier, M., Besson, M., Guillard, C., & Gonze, E. (2009). Removal of herbicide diuron and thermal degradation products under Catalytic Wet Air Oxidation conditions. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 91, 275–283.
Chen, W.-S., & Huang, C.-P. (2015). Mineralization of aniline in aqueous solution by electrochemical activation of persulfate. Chemosphere, 125, 175–181.
Chiron, S., Fernandez-Alba, A., Rodriguez, A., & Garcia-Calvo, E. (2000). Pesticide chemical oxidation: state-of-the-art. Water Research, 34, 366–377.
Chu, W., Li, D., Gao, N., Templeton, M. R., Tan, C., & Gao, Y. (2015). The control of emerging haloacetamide DBP precursors with UV/persulfate treatment. Water Research, 72, 340–348.
Furman, O. S., Teel, A. L., & Watts, R. J. (2010). Mechanism of base activation of persulfate. Environmental Science & Technology, 44, 6423–6428.
Gao, N., Chu, W., Zhao, D., & Dong, B. (2009). Removal of the herbicide diuron from drinking water by nanofiltration membrane. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 18, 1723–1729.
Govindan, K., Raja, M., Noel, M., & James, E. (2014). Degradation of pentachlorophenol by hydroxyl radicals and sulfate radicals using electrochemical activation of peroxomonosulfate, peroxodisulfate and hydrogen peroxide. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 272, 42–51.
Guardiola, F. A., Cuesta, A., Meseguer, J., & Esteban, M. A. (2012). Risks of using antifouling biocides in aquaculture. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13, 1541–1560.
Huovinen, M., Loikkanen, J., Naarala, J., & Vähäkangas, K. (2015). Toxicity of diuron in human cancer cells. Toxicology in Vitro, 29, 1577–1586.
Lakshmanan, D., Clifford, D. A., & Samanta, G. (2009). Ferrous and ferric Ion generation during iron electrocoagulation. Environmental Science & Technology, 43, 3853–3859.
Lin, H., Wu, J., & Zhang, H. (2013). Degradation of bisphenol A in aqueous solution by a novel electro/Fe3+/peroxydisulfate process. Separation and Purification Technology, 117, 18–23.
Luo, C., Ma, J., Jiang, J., Liu, Y., Song, Y., Yang, Y., Guan, Y., & Wu, D. (2015). Simulation and comparative study on the oxidation kinetics of atrazine by UV/H2O2. Water Research, 80, 99–108.
Messeguer, A. (2011). Potential implication of aniline derivatives in the Toxic Oil Syndrome (TOS). Chemico-Biological Interactions, 192, 136–141.
Neta, P., Huie, R. E., & Ross, A. B. (1988). Rate constants for reactions of inorganic radicals in aqueous solution. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 17, 1027–1284.
Rastogi, A., Al-Abed, S. R., & Dionysiou, D. D. (2009). Sulfate radical-based ferrous–peroxymonosulfate oxidative system for PCBs degradation in aqueous and sediment systems. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 85, 171–179.
Romero, A., Santos, A., Vicente, F., & González, C. (2010). Diuron abatement using activated persulphate: effect of pH, Fe (II) and oxidant dosage. Chemical Engineering Journal, 162, 257–265.
Sheng, H. L., Lin, C. M., & Leu, H. G. (1999). Operating characteristics and kinetic studies of surfactant wastewater treatment by fenton oxidation. Water Research, 33, 1735–1741.
Tan, C., Gao, N., Chu, W., Li, C., & Templeton, M. R. (2012a). Degradation of diuron by persulfate activated with ferrous ion. Separation and Purification Technology, 95, 44–48.
Tan, C., Gao, N., Deng, Y., An, N., & Deng, J. (2012b). Heat-activated persulfate oxidation of diuron in water. Chemical Engineering Journal, 203, 294–300.
Tan, C., Gao, N., Deng, Y., Zhang, Y., Sui, M., Deng, J., & Zhou, S. (2013). Degradation of antipyrine by UV, UV/H2O2 and UV/PS. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 260, 1008–1016.
Usman, M., Tascone, O., Faure, P., & Hanna, K. (2014). Chemical oxidation of hexachlorocyclohexanes (HCHs) in contaminated soils. Science of the Total Environment, 476, 434–439.
Vicente, F., Santos, A., Romero, A., & Rodriguez, S. (2011). Kinetic study of diuron oxidation and mineralization by persulphate: effects of temperature, oxidant concentration and iron dosage method. Chemical Engineering Journal, 170, 127–135.
Wacławek, S., Antoš, V., Hrabák, P., Černík, M., & Elliott, D. (2016). Remediation of hexachlorocyclohexanes by electrochemically activated persulfates. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(1), 1–9.
Wu, J., Zhang, H., & Qiu, J. (2012). Degradation of Acid Orange 7 in aqueous solution by a novel electro/Fe2+/peroxydisulfate process. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 215, 138–145.
Xie, P., Ma, J., Liu, W., Zou, J., Yue, S., Li, X., Wiesner, M. R., & Fang, J. (2015). Removal of 2-MIB and geosmin using UV/persulfate: contributions of hydroxyl and sulfate radicals. Water Research, 69, 223–233.
Xu, X.-R., & Li, X.-Z. (2010). Degradation of azo dye Orange G in aqueous solutions by persulfate with ferrous ion. Separation and Purification Technology, 72, 105–111.
Yu, X.-Y., Bao, Z.-C., & Barker, J. R. (2004). Free radical reactions involving Cl, Cl2-, and SO4-in the 248 nm photolysis of aqueous solutions containing S2O82-and Cl. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. A, 108, 295–308.
Yuan, S., Liao, P., & Alshawabkeh, A. N. (2013). Electrolytic manipulation of persulfate reactivity by iron electrodes for trichloroethylene degradation in groundwater. Environmental Science & Technology, 48, 656–663.
Zhao, X., Zhang, B., Liu, H., Chen, F., Li, A., & Qu, J. (2012). Transformation characteristics of refractory pollutants in plugboard wastewater by an optimal electrocoagulation and electro-Fenton process. Chemosphere, 87, 631–636.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (51508174) and the Central University Basic Scientific Research Business Special Fund Projects (531107040812).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Y., Zhou, S., Bu, L. et al. Degradation of Diuron by Electrochemically Activated Persulfate. Water Air Soil Pollut 227, 279 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2978-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2978-9