Abstract
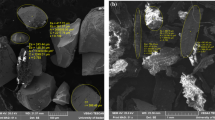
Presented are the synthesis and characterization of Fe(III)-modified 13X molecular sieves and their application as a novel adsorbent for removing arsenic from aqueous solutions. Batch experimental results showed that Fe(III) adsorption by 13X molecular sieves matched well with the Langmuir adsorption isotherm. The adsorption kinetics of arsenic on the Fe(III)-modified molecular sieves fit well with a pseudo-second-order model. The Langmuir adsorption isotherms of arsenic adsorption indicated the highest adsorption capacities of 1167.79 for As(V) at pH 4 and 731.56 mg/kg for As(III) at pH 9. The Fe(III)-modified 13X molecular sieves removed much more As(V) than As(III) at equivalent arsenic concentrations, regardless of the pH conditions. After As(V) removal, the Fe(III)-modified 13X molecular sieves were characterized by PXRD, SEM-EDX, and ATR-FTIR to analyze the morphology and arsenic speciation. The results of PXRD and SEM-EDX spectroscopy indicated that the material was physically stable after As(V) adsorption. ATR-FTIR spectroscopy showed that the formation of inner-sphere surface complexations between Fe hydroxide on the surface of the molecular sieves and As(V) could be a plausible mechanism for the uptake of arsenic by the Fe(III)-modified 13X molecular sieves. Therefore, the relatively low cost and remarkable arsenic-adsorption performance make the title material a promising absorbent for the treatment of arsenic in wastewater.

Arsenic removal by Fe(III)-modified 13X molecular sieves







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baskan, M. B., & Pala, A. (2013). Batch and fixed-bed column studies of arsenic adsorption on the natural and modified clinoptilolite. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 225, 1798.
Catalano, J. G., Park, C., Fenter, P., & Zhang, Z. (2008). Simultaneous inner- and outer-sphere arsenate adsorption on corundum and hematite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 72, 1986–2004.
Dixit, S., & Hering, J. G. (2003). Comparison of arsenic(V) and arsenic(III) sorption onto iron oxide minerals: Implications for arsenic mobility. Environmental Science and Technology, 37, 4182–4189.
Elizalde-Gonzalez, M. P., Mattusch, J., Einicke, W. D., & Wennrich, R. (2001a). Sorption on natural solids for arsenic removal. Chemical Engineering Journal, 81, 187–195.
Elizalde-Gonzalez, M. P., Mattusch, J., Wennrich, R., & Morgenstern, P. (2001b). Uptake of arsenite and arsenate by clinoptilolite-rich tuffs. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 46, 277–286.
Elizalde-Gonzalez, M. P., Mattusch, J., & Wennrich, R. (2001c). Application of natural zeolites for preconcentration of arsenic species in water samples. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 3, 22–26.
Gao, X., Root, R. A., Farrell, J., Ela, W., & Chorover, J. (2013). Effect of silicic acid on arsenate and arsenite retention mechanisms on 6-L ferrihydrite: a spectroscopic and batch adsorption approach. Applied Geochemistry, 38, 110–120.
Guo, L., Ye, P., Wang, J., Fu, F., & Wu, Z. (2015). Three-dimensional Fe3O4-graphene macroscopic composites for arsenic and arsenate removal. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 298, 28–35.
Jeon, C. S., Baek, K., Park, J. K., Oh, Y. K., & Lee, S. D. (2009). Adsorption characteristics of As(V) on iron-coated zeolite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163, 804–808.
Jia, Y., & Demopoulos, G. P. (2008). Coprecipitation of arsenate with iron(III) in aqueous sulfate media: effect of time, lime as base and co-ions on arsenic retention. Water Research, 42, 661–668.
Jia, Y., Xu, L., Wang, X., & Demopoulos, G. P. (2007). Infrared spectroscopic and X-ray diffraction characterization of the nature of adsorbed arsenate on ferrihydrite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71, 1643–1654.
Li, Z., Beachner, R., McManama, Z., & Hanlie, H. (2007). Sorption of arsenic by surfactant-modified zeolite and kaolinite. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 105, 291–297.
Li, Z., Jean, J. S., Jiang, W. T., Chang, P. H., Chen, C. J., & Liao, L. (2011). Removal of arsenic from water using Fe-exchanged natural zeolite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 187, 318–323.
Lin, S., Wei, W., Wu, X., Zhou, T., Mao, J., & Yun, Y. S. (2015). Selective recovery of Pd(II) from extremely acidic solution using ion-imprinted chitosan fiber: Adsorption performance and mechanisms. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 299, 10–17.
Lv, G., Li, Z., Jiang, W.-T., Ackley, C., Fenske, N., & Demarco, N. (2014). Removal of Cr(VI) from water using Fe(II)-modified natural zeolite. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 92, 384–390.
Melo, C. R., Riella, H. G., Kuhnen, N. C., Angioletto, E., Melo, A. R., Bernardin, A. M., da Rocha, M. R., & da Silva, L. (2012). Synthesis of 4A zeolites from kaolin for obtaining 5A zeolites through ionic exchange for adsorption of arsenic. Materials Science and Engineering B, 177, 345–349.
Mertens, J., Rose, J., Kagi, R., Chaurand, P., Plotze, M., Wehrli, B., & Furrer, G. (2012). Adsorption of arsenic on polyaluminum granulate. Environmental Science and Technology, 46, 7310–7.
Mohan, D., & Pittman, C. U., Jr. (2007). Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—a critical review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 142, 1–53.
Muller, K., Ciminelli, V. S., Dantas, M. S., & Willscher, S. (2010). A comparative study of As(III) and As(V) in aqueous solutions and adsorbed on iron oxy-hydroxides by Raman spectroscopy. Water Research, 44, 5660–72.
Neupane, G., Donahoe, R. J., & Arai, Y. (2014). Kinetics of competitive adsorption/desorption of arsenate and phosphate at the ferrihydrite–water interface. Chemical Geology, 368, 31–38.
O’Reilly, S. E., Strawn, D. G., & Sparks, D. L. (2001). Residence time effects on arsenate adsorption/desorption mechanisms on goethite. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 65, 67–77.
Payne, K., & Abdel-Fattah, T. (2005). Adsorption of arsenate and arsenite by iron-treated activated carbon and zeolites: effects of pH, temperature, and ionic strength. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A, 40, 723–749.
Qiu, W., & Zheng, Y. (2007). Arsenate removal from water by an alumina-modified zeolite recovered from fly ash. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 148, 721–726.
Rodriguez-Lado, L., Sun, G., Berg, M., Zhang, Q., Xue, H., Zheng, Q., & Johnson, C. A. (2013). Groundwater arsenic contamination throughout China. Science, 341, 866–868.
Ruggieri, F., Marin, V., Gimeno, D., Fernandez-Turiel, J. L., Garcia-Valles, M., & Gutierrez, L. (2008). Application of zeolitic volcanic rocks for arsenic removal from water. Engineering Geology, 101, 245–250.
Shevade, S., & Ford, R. G. (2004). Use of synthetic zeolites for arsenate removal from pollutant water. Water Research, 38, 3197–3204.
Simsek, E. B., Ozdemir, E., & Beker, U. (2013a). Process Optimization for Arsenic Adsorption onto Natural Zeolite Incorporating Metal Oxides by Response Surface Methodology. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 224.
Simsek, E. B., Özdemir, E., & Beker, U. (2013b). Zeolite supported mono- and bimetallic oxides: promising adsorbents for removal of As(V) in aqueous solutions. Chemical Engineering Journal, 220, 402–411.
Smedley, P. L., & Kinniburgh, D. G. (2002). A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 517–568.
Stanić, T., Daković, A., Živanović, A., Tomašević-Čanović, M., Dondur, V., & Milićević, S. (2008). Adsorption of arsenic (V) by iron (III)-modified natural zeolitic tuff. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 7, 161–166.
Swedlund, P. J., Holtkamp, H., Song, Y., & Daughney, C. J. (2014). Arsenate-ferrihydrite systems from minutes to months: a macroscopic and ir spectroscopic study of an elusive equilibrium. Environmental Science and Technology, 48, 2759–2765.
Tuna, A. Ö. A., Özdemir, E., Şimşek, E. B., & Beker, U. (2013). Removal of As(V) from aqueous solution by activated carbon-based hybrid adsorbents: Impact of experimental conditions. Chemical Engineering Journal, 223, 116–128.
Vadahanambi, S., Lee, S. H., Kim, W. J., & Oh, I. K. (2013). Arsenic removal from contaminated water using three-dimensional graphene-carbon nanotube-iron oxide nanostructures. Environmental Science and Technology, 47, 10510–10517.
Waychunas, G. A., Fuller, C. C., Rea, B. A., & Davis, J. A. (1996). Wide angle X-ray scattering (WAXS) study of “'two-line”' ferrihydrite structure: effect of arsenate sorption and counterion variation and comparison with EXAFS results. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60, 1765–1781.
Zhang, G., Qu, J., Liu, H., Liu, R., & Wu, R. (2007). Preparation and evaluation of a novel Fe-Mn binary oxide adsorbent for effective arsenite removal. Water Research, 41, 1921–1928.
Zhao, Z., Jia, Y., Xu, L., & Zhao, S. (2011). Adsorption and heterogeneous oxidation of As(III) on ferrihydrite. Water Research, 45, 6496–504.
Zhu, H., Jia, Y., Wu, X., & Wang, H. (2009). Removal of arsenic from water by supported nano zero-valent iron on activated carbon. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172, 1591–6.
Zhu, J., Lou, Z., Liu, Y., Fu, R., Baig, S. A., & Xu, X. (2015). Adsorption behavior and removal mechanism of arsenic on graphene modified by iron–manganese binary oxide (FeMnOx/RGO) from aqueous solutions. RSC Advances, 5, 67951–67961.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Fundation of China (Nos. 41530643, 41273133) and the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. XDB14020203).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 452 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Wang, S., Wang, X. et al. Adsorption Behavior and Removal Mechanism of Arsenic from Water by Fe(III)-Modified 13X Molecular Sieves. Water Air Soil Pollut 227, 257 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2955-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2955-3