Abstract
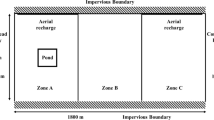
In the present paper we suggest a novel calibration method of the model for hydrodynamic and contaminant transport using the example of a sewage disposal site set up uninsulated in a sandy environment. With the hydrodynamic model we applied time-dependent model calculations in order to fit the individual hydrodynamic parameters. For the calibration of the transport model, sodium was chosen, which has a negligible retardation factor. We demonstrated that this approach is suitable for creating a model that provides calculated results comparable to the actually measured, experimental ones. The created model proved to be appropriate for use in the estimation of the maximal spatial extension of the contamination, which—in the case of the investigated sewage disposal site—was found to be 0.1 km2 in the near-surface (1–3 m deep) layers, whereas it was three times higher at a depth of 40–60 m.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Khashman, O. A. (2008). Assessment of the spring water quality in The Shoubak area, Jordan. Environmentalist, 28, 203–215.
Campbell, C. S. (1985). Soil Physics with Basic. New York: Elsevier.
Chakraborty, R., & Ghosh, A. (2009). Finite difference method for computation of sodium and chloride migration in porous media, Proceedings of the Indian Geotechnical Conference, pp. 268–271.
Chawla, A., & Singh, S. K. (2014). Modelling of contaminant transport from landfills. International Journal of Engineering Science and Innovative Technology, 3(5), 222–227.
Cho, J.-C., Cho, H. B., & Kim, S.-J. (2000). Heavy contamination of a subsurface aquifer and a stream by livestock wastewater in a stock farming area, Wonju, Korea. Environmental Pollution, 109, 137–146.
Datta, B., Chakrabarty, D., & Dhar, A. (2011). Identification of unknown groundwater pollution sources using classical optimization with linked simulation. Journal of Hydro-Environment Research, 5, 25–36.
Delkash, M., Al-Faraj, F. A. M., & Scholz, M. (2014). Comparing the export coefficient approach with the soil and water assessment tool to predict phosphorous pollution: the Kan watershed case study. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 225, 2122.
Dövényi, Z. (Ed.). (2010). Magyarország kistájainak katasztere (Inventory of natural micro-regions of Hungary). Budapest: MTA FKI.
Fejes, I., Farsang, A., & Puskás, I. (2012). Potential effects of the contaminated groundwater on human health in Szeged, SE Hungary. Carpathian Journal of Earth and Environmental Sciences, 7(3), 119–126.
Green Side, K. (2008). Mikepércs külterület 080 hrsz. alatti települési folyékony hulladék leürítőhely rekultivációja. (The recultivation of the sewage disposal site at 080 Hrsz. in the outskirts of Mikepércs. Plan documentation.). Miskolc: Tervdokumentáció.
Greenwood, N. N., & Earnshaw, A. (1999). Az elemek kémiája I. (Chemistry of elements I.). Budapest: Nemzeti Tankönyvkiadó.
Harbaugh, A. W. (2005). MODFLOW-2005, the U.S. Geological Survey modular ground-water model—the ground-water flow process: U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods 6-A16.
Kerényi, A. (2003). Európa Természet- és Környezetvédelme (Nature- and environmental protection of Europe). Budapest: Nemzeti Tankönyv Kiadó Rt.
Marton, L. (2009). Energiaszint változások az ÉK-Alföld fő vízadó rétegeiben. (Energy level changes in the main water-supplying ground layers in the north-eastern region of the Great Hungarian Plain.) (pp. 1–2). Debrecen: Debreceni műszaki közlemények.
Müller, H. W., Dohrmann, R., Klosa, D., Rehder, S., & Eckelmann, W. W. (2009). Comparison of two procedures for particle‐size analysis: Köhn pipette and X‐ray granulometry. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 172(2), 172–179.
Nakaya, S., Natsume, H., Masuda, H., Mitamura, M., Biswas, D. K., & Seddique, A. A. (2011). Effect of groundwater flow on forming arsenic contaminated groundwater in Sonargaon, Bangladesh. Journal of Hydrology, 409, 724–736.
Panno, S. V., Hackley, K. C., Hwang, H. H., Greenberg, S., Krapac, I. G., Landsberger, S., & O’Kelly, D. J. (2002). Source identification of sodium and chloride contamination in natural waters: preliminary results. In 12th Annual Research Conference of the Illinois Groundwater Consortium. Research on Agrichemicals in Illinois. Carbondale, Illinois: Groundwater Status and Future Direction XII.
Panno, S. V., Hackley, K. C., Hwang, H. H., Greenberg, S. E., Krapac, I. G., Landsberger, S., & O’Kelly, D. J. (2006). Characterization and identification of Na‐Cl sources in ground water. Groundwater, 44(2), 176–187.
Phan, K., Phan, S., Heng, S., Huoy, L., & Kim, K.-W. (2014). Assessing arsenic intake from groundwater and rice by residents in Prey Veng province, Cambodia. Environmental Pollution, 185, 84–89.
Phan, K., Phan, S., Huoy, L., Suy, B., Wong, M. H., Hashim, J. H., Yasin, M. S. M., Aljunid, S. M., Sthiannopkao, S., & Kim, K.-W. (2013). Assessing mixed trace elements in groundwater and their health risk of residents living in the Mekong River basin of Cambodia. Environmental Pollution, 182, 111–119.
Regadío, M., Ruiz, A. I., de Soto, I. S., Rastrero, M. R., Sánchez, N., Gismera, M. J., Sevilla, M. T., da Silva, P., Procopio, R. J., & Cuevas, J. (2012). Pollution profiles and physicochemical parameters in old uncontrolled landfills. Waste Management, 32, 482–497.
Rowe, R. K., Quigely, R. M., Brachman, R. W. I., & Booker, J. R. (2004). Barrier system for waste disposal facilities. London: Taylor and Francis.
Sayyed, A. J., & Bhosle, B. A. (2011). Analysis of chloride, sodium and potassium in groundwater samples of Nanded City in Mahabharata, India. European Journal of Experimental Biology, 1(1), 74–82.
Shahid, S., Nath, S. K., & Roy, J. (2000). Groundwater potential modelling in a soft rock area using a GIS. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 21(9), 1919–1924.
Sipos, P., Kovács Kis, V., Márton, E., Németh, T., May, Z., & Szalai, Z. (2012). Lead and zinc in the suspended particulate matter and settled dust in Budapest, Hungary. European Chemical Bulletin, 1(11), 449–454.
Slack, R. J., Gronow, J. R., Hall, D. H., & Voulvoulis, N. (2007). Household hazardous waste disposal to landfill: using LandSim to model leachate migration. Environmental Pollution, 146, 501–509.
Slack, R. J., Gronow, J. R., & Voulvoulis, N. (2005). Household hazardous waste in municipal landfills: contaminants in leachate. Science of the Total Environment, 337, 119–137.
Somlyódi, L. (2002). A hazai vízgazdálkodás és stratégiai pillérei. In L. Somlyódi (Ed.), A hazai vízgazdálkodás stratégiai kérdései. (Strategic issues of national water management.) (pp. 23–74). Budapest: MTA.
Sonneveld, M. P. W., Brus, D. J., & Roelsma, J. (2010). Validation of regression models for nitrate concentrations in the upper groundwater in sandy soils. Environmental Pollution, 158, 92–97.
Szabó, Gy., & Bessenyei, É. (2013). Studying groundwater pollution in the surroundings of a recultivated sewage disposal site in eastern Hungary. Journal of Selçuk University Natural and Applied Science, Special Issue (I) 1–12.
Szabó, Sz., & Szabó, Gy. (2005). Mikepércs községi folyékony hulladék leürítőhely részleges környezetvédelmi felülvizsgálata. Debrecen: (Partial environmental review of the municipal sewage disposal site of Mikepércs town.) manuscript.
Szabó, Gy., Szabó, Sz., Szabó, A., & Szemán, B. (2007a). Spatial and time variations of the groundwater quality of two different landscapes. In M. Boltižiar (Ed.), Implementation of landscape ecology in new and changing conditions (pp. 421–427). Bratislava: ILE Slovak Academy of Sciences.
Szabó, Sz., Papp, L., & Szabó, Gy. (2007b). Investigation of a communal sewage disposal site from the aspect of landscape protection. In M. Boltižiar (Ed.), Implementation of landscape ecology in new and changing conditions (pp. 415–420). Bratislava: ILE Slovak Academy of Sciences.
Szabó, Sz., Szabó, Gy., Fodor, Cs., & Papp, L. (2007c). Sewage disposal and its effects on groundwater and soil quality. In E. Kallabova, B. Frantal, & P. Klusacek (Eds.), Regions, localities and landscapes in new Europe. Brno, Czech Republic: 7th International Geographical Conference CONGEO’07, Enhanced Abstracts and Full Texts.
Zhan, T. L. T., Guan, C., Xie, H. J., & Chena, Y. M. (2013). Vertical migration of leachate pollutants in clayey soils beneath an uncontrolled landfill at Huainan, China: a field and theoretical investigation. Science of the Total Environment, 470–471, 290–298.
Zhang, H., Xu, W. L., & Hiscock, K. M. (2013). Application of MT3DMS and geographic information system to evaluation of groundwater contamination in the Sherwood Sandstone Aquifer, UK. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 224, 1438.
Zheng, C., & Wang, P. P. (1999). MT3DMS: a modular three-dimensional multispecies transport model for simulation of advection, dispersion and chemical reactions of contaminants in groundwater systems; documentation and user’s guide, Contract Report SERDP-99-1. Vicksburg, MS: U.S. Army Engineer Research and Development Center.
Acknowledgments
This research was realized in the framework of TÁMOP 4.2.4. A/2-11-1-2012-0001 “National Excellence Program—Designing and Operating a Personal Support System Convergence Program for Hungarian Students and Researchers,” and it was supported by TÁMOP-4.2.2/B-10/1-2010-0024 as well. The project was cofinanced by the European Union and European Social Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szabó, G., Bessenyei, É., Hajnal, A. et al. The Use of Sodium to Calibrate the Transport Modeling of Water Pollution in Sandy Formations Around an Uninsulated Sewage Disposal Site. Water Air Soil Pollut 227, 45 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2742-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2742-6