Abstract
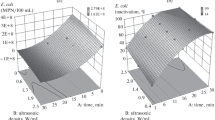
The effects of ultrasonic wave irradiation on bacterial inactivation were investigated as functions of the ionic strength (IS), humic acid, and temperature. Escherichia coli (E. coli) D21g was selected as a model bacterium to better catch the effect of three parameters on the cell inactivation behavior. The Suwannee River humic acid (SRHA) was chosen as a representative humic acid, and the concentration for ultrasonic tests was kept to 10 ppm. The frequency of ultrasonic wave employed was 20 kHz, and the inactivation efficiency at two exposure times (5 and 10 min) was compared. The removal efficiency of E. coli D21g was confirmed to be 100 % at 10 min in all conditions except the 10-min temperature-controlled condition. The removal efficiency with the high IS was greater than that with the low IS, by 26 %, confirming an increase in the bacterial inactivation level with increasing IS. The bacterial removal efficiency with SRHA (96.6 %) was much greater than that without SRHA (69.6 %). The removal efficiency in the temperature-controlled condition (at a relatively low temperature) was significantly lower than that in the uncontrolled condition. Furthermore, the trend obtained using two other types of bacteria with more complex surface structure was consistent with that using the E. coli D21g cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Bsoul, A., Magnin, J. P., Commenges-Bernole, N., Gondrexon, N., Willison, J., & Petrier, C. (2010). Effectiveness of ultrasound for the destruction of Mycobacterium sp strain (6PY1). Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 17(1), 106–110.
Al-Juboori, R. A., & Yusaf, T. (2012). Identifying the Optimum Process Parameters for Ultrasonic Cellular Disruption of E. Coli. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng., 10.
Antoniadis, A., Poulios, I., Nikolakaki, E., & Mantzavinos, D. (2007). Sonochemical disinfection of municipal wastewater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 146(3), 492–495.
Burleson, G. R., Murray, T. M., & Pollard, M. (1975). Inactivation of viruses and bacteria by ozone, with and without sonication. Applied Microbiology, 29(3), 340–344.
Cameron, M., McMaster, L. D., & Britz, T. J. (2008). Electron microscopic analysis of dairy microbes inactivated by ultrasound. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 15(6), 960–964.
Char, C. D., Mitilinaki, E., Guerrero, S. N., & Alzamora, S. M. (2010). Use of high-intensity ultrasound and UV-C light to inactivate some microorganisms in fruit juices. Food Bioprocess Technology, 3(6), 797–803.
Chong, M. N., Jin, B., Chow, C. W. K., & Saint, C. (2010). Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: a review. Water Research, 44(10), 2997–3027.
D'amico, D. J., Silk, T. M., Wu, J. R., & Guo, M. R. (2006). Inactivation of microorganisms in milk and apple cider treated with ultrasound, J. J Food Prot, 69(3), 556–563.
Daughton, C. G. (2001). Emerging pollutants, and communicating the science of environmental chemistry and mass spectrometry: pharmaceuticals in the environment. Journal of American Society for Mass Spectrometry, 12(10), 1067–1076.
Deborde, M., & von Gunten, U. (2008). Reactions of chlorine with inorganic and organic compounds during water treatment - Kinetics and mechanisms: a critical review. Water Research, 42(1–2), 13–51.
Drakopoulou, S., Terzakis, S., Fountoulakis, M. S., Mantzavinos, D., & Manios, T. (2009). Ultrasound-induced inactivation of gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria in secondary treated municipal wastewater. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 16(5), 629–634.
Furuta, M., Yamaguchi, M., Tsukamoto, T., Yim, B., Stavarache, C. E., Hasiba, K., & Maeda, Y. (2004). Inactivation of Escherichia coli by ultrasonic irradiation. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 11(2), 57–60.
Gao, S., Hemar, Y., Ashokkumar, M., Paturel, S., & Lewis, G. D. (2014). Inactivation of bacteria and yeast using high-frequency ultrasound treatment. Water Research, 60, 93–104.
Gogate, P. R. (2007). Application of cavitational reactors for water disinfection: current status and path forward. Journal of Environmental Management, 85(4), 801–815.
Han, Y., Kim, D., Hwang, G., Lee, B., Eom, I., Kim, P. J., Tong, M. P., & Kim, H. (2014). Aggregation and dissolution of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by different methods: Influence of ionic strength and humic acid. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 451, 7–15.
Haznedaroglu, B. Z., Kim, H. N., Bradford, S. A., & Walker, S. L. (2009). Relative transport behavior of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella enterica serovar pullorum in packed bed column systems: influence of solution chemistry and cell concentration. Environmental Science and Technology, 43(6), 1838–1844.
Hua, I., & Thompson, J. E. (2000). Inactivation of Escherichia coli by sonication at discrete ultrasonic frequencies. Water Research, 34(15), 3888–3893.
Jiang, X., Tong, M., & Kim, H. (2012). Influence of natural organic matter on the transport and deposition of zinc oxide nanoparticles in saturated media. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 386, 34–43.
Joyce, E., Phull, S. S., Lorimer, J. P., & Mason, T. J. (2003). The development and evaluation of ultrasound for the treatment of bacterial suspensions. A study of frequency, power and sonication time on cultured Bacillus species. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 10(6), 315–318.
Joyce, E., Al-Hashimi, A., & Mason, T. J. (2011). Assessing the effect of different ultrasonic frequencies on bacterial viability using flow cytometry. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 110(4), 862–870.
Jyoti, K. K., & Pandit, A. B. (2001). Water disinfection by acoustic and hydrodynamic cavitation. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 7(3), 201–212.
Kim, H. N., & Walker, S. L. (2009). Escherichia coli transport in porous media: Influence of cell strain, solution chemistry, and temperature. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 71(1), 160–167.
Kim, E. S., Lee, D. H., Yum, B. W., & Chang, H. W. (2005). The effect of ionic strength and hardness of water on the non-ionic surfactant-enhanced remediation of perchloroethylene contamination. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 119(1–3), 195–203.
Kim, H. N., Bradford, S. A., & Walker, S. L. (2009a). Escherichia coli O157:H7 transport in saturated porous media: role of solution chemistry and surface macromolecules. Environmental Science and Technology, 43(12), 4340–4347.
Kim, H. N., Hong, Y., Lee, I., Bradford, S. A., & Walker, S. L. (2009b). Surface characteristics and adhesion behavior of Escherichia coli O157: H7: role of extracellular macromolecules. Biomacromolecules, 10(9), 2556–2564.
Koda, S., Miyamoto, M., Toma, M., Matsuoka, T., & Maebayashi, M. (2009). Inactivation of Escherichia coli and Streptococcus mutans by ultrasound at 500 kHz. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 16(5), 655–659.
Labatiuk, C. W., Belosevic, M., & Finch, G. R. (1992). Factors influencing the infectivity of Giardia-Muris cysts following ozone inactivation in laboratory and natural-waters. Water Research, 26(6), 733–743.
Lee, H. I., Zhou, B., Liang, W., Feng, H., & Martin, S. E. (2009). Inactivation of Escherichia coli cells with sonication, manosonication, thermosonication, and manothermosonication: microbial responses and kinetics modeling. Journal of Food Engineering, 93(3), 354–364.
Manas, P., & Pagan, R. (2005). Microbial inactivation by new technologies of food preservation. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 98(6), 1387–1399.
Marchesini, G., Fasolato, L., Novelli, E., Balzan, S., Contiero, B., Montemurro, F., Andrighetto, I., & Segato, S. (2015). Ultrasonic inactivation of microorganisms: a compromise between lethal capacity and sensory quality of milk. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 29, 215–221.
Mazmanci, M. A., & Unyayar, A. (2005). Decolourisation of Reactive Black 5 by Funalia trogii immobilised on Luffa cylindrica sponge. Process Biochemistry, 40(1), 337–342.
McCarthy, J. F., McKay, L. D., & Bruner, D. D. (2002). Influence of ionic strength and cation charge on transport of colloidal particles in fractured shale saprolite. Environmental Science and Technology, 36(17), 3735–3743.
Naddeo, V., Belgiorno, V., & Napoli, R. M. A. (2007). Behaviour of natural organic matter during ultrasonic irradiation. Desalination, 210(1–3), 175–182.
Pinto, F., Maillard, J. Y., & Denyer, S. P. (2010). Effect of surfactants, temperature, and sonication on the virucidal activity of polyhexamethylene biguanide against the bacteriophage MS2. American Journal of Infection Control, 38(5), 393–398.
Richardson, S. D. (2003). Disinfection by-products and other emerging contaminants in drinking water. Trac-Trend Analytical Chemistry, 22(10), 666–684.
Richardson, S. D., & Ternes, T. A. (2011). Water analysis: emerging contaminants and current issues. Analytical Chemistry, 83(12), 4614–4648.
Sesal, N. C., & Kekeç, Ö. (2014). Effects of pulsed ultrasound on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 108(6), 348–353.
Stanley, K. D., Golden, D. A., Williams, R. C., & Weiss, J. (2004). Inactivation of Escherichia coli O157: H7 by high-intensity ultrasonication in the presence of salts. Food Bourne Pathogens & Disease, 1(4), 267–280.
Tong, M. P., Zhu, P. T., Jiang, X. J., & Kim, H. (2011). Influence of natural organic matter on the deposition kinetics of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on silica. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 87(1), 151–158.
Ugarte‐Romero, E., Feng, H., Martin, S. E., Cadwallader, K. R., & Robinson, S. J. (2006). Inactivation of Escherichia coli with power ultrasound in apple cider. Journal of Food Science, 71(2), E102–E108.
Vajnhandl, S., Željko, T., Majcen Le Marechal, A., & Valh, J. V. (2014). Feasibility study of ultrasound as water disinfection technology. Desalination and Water Treatment, (ahead-of-print), 1–7.
Van Tran, A. (2008). Removal of COD and color loads in bleached kraft pulp effluents by bottom ashes from boilers. Environmental Technology, 29(7), 775–784.
Walker, S. L., Redman, J. A., & Elimelech, M. (2004). Role of cell surface lipopolysaccharides in Escherichia coli K12 adhesion and transport. Langmuir, 20(18), 7736–7746.
Wu, X. G., Joyce, E. M., & Mason, T. J. (2012). Evaluation of the mechanisms of the effect of ultrasound on Microcystis aeruginosa at different ultrasonic frequencies. Water Research, 46(9), 2851–2858.
Yang, H. Y., Kim, H., & Tong, M. P. (2012). Influence of humic acid on the transport behavior of bacteria in quartz sand. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 91, 122–129.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Programs through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (NRF-2011-0023782).
Compliance with Ethical Standards
ᅟ
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Re-submitted on June 05, 2015
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, G., Han, Y., Choi, S.Q. et al. Bacterial Inactivation by Ultrasonic Waves: Role of Ionic Strength, Humic Acid, and Temperature. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 304 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2573-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2573-5