Abstract
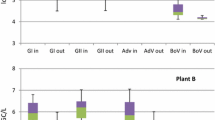
Enteric viruses enter surface waters through discharge of sewage treatment plants. They have a high environmental resistance and persistence and have low infectious doses. The aim of this study was to investigate the efficiency of polishing pond in the removal of viruses and bacteria. The samples were taken approximately once a week at the influent of secondary treatment (n = 39), effluent of secondary treatment (n = 39), and polishing pond (tertiary treatment, n = 29). Human adenoviruses (HAdV) were detected in 82–100 % of wastewater samples, whereas 62–79 % of the samples were positive for human polyomavirus (HPyV). The median concentrations ranged from 6.8 × 103 genome equivalents/l (HAdV) to 6.0 × 103 genome equivalents/l (HPyV). The concentration of HAdV and HPyV did not change significantly during the wastewater treatment. For somatic coliphages and bacteria an overall reduction of 1.84–2.65 log10 has been detected. Based on the data collected, this type of tertiary treatment achieved a significant reduction in bacteria and phages, but not for viruses.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albinana-Gimenez, N., Clemente-Casares, P., Bofill-Mas, S., Hundesa, A., Ribas, F., & Girones, R. (2006). Distribution of human polyomaviruses, adenoviruses, and hepatitis E virus in the environment and in a drinking-water treatment plant. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 7416–7422.
APHA. (1998). American public health association, standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington, D.C.: American Public Health Association.
Bauer, R., Dizer, H., Graeber, I., Rosenwinkel, K. H., & Lopez-Pila, J. M. (2011). Removal of bacterial fecal indicators, coliphages and enteric adenoviruses from waters with high fecal pollution by slow sand filtration. Water Research, 45, 439–452.
Biel, S. S., Held, T. K., Landt, O., Niedrig, M., Gelderblom, H. R., Siegert, W., & Nitsche, A. (2000). Rapid quantification and differentiation of human polyomavirus DNA in undiluted urine from patients after bone marrow transplantation. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 38, 3689–3695.
Bofill-Mas, S., Albinana-Gimenez, N., Clemente-Casares, P., Hundesa, A., Rodriguez-Manzano, J., Allard, A., Calvo, M., & Girones, R. (2006). Quantification and stability of human adenoviruses and polyomavirus JCPyV in wastewater matrices. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72, 7894–7896.
Carducci, A., Morici, P., Pizzi, F., Battistini, R., Rovini, E., & Verani, M. (2008). Study of the viral removal efficiency in an urban wastewater treatment plant. Water Science and Technology, 58, 893–897.
Choi, W. S., Rodriguez, R. A., & Sobsey, M. D. (2014). Persistence of viral genomes after autoclaving. Journal of Virological Methods, 198, 37–40.
de Bruyn, G., & Limaye, A. P. (2004). BK virus-associated nephropathy in kidney transplant recipients. Reviews in Medical Virology, 14, 193–205.
DIN (2000). Wasserbeschaffenheit, Nachweis und Zählung von Intestinalen Enterokokken, Teil 2: Verfahren durch Membranfiltration. In DIN EN ISO 7899–2.
DIN (2001). Wasserbeschaffenheit, Nachweis und Zählung von E. coli und coliformen Bakterien, Teil 1: Membranfiltrationsverfahren In DIN EN ISO 9308–1.
Duran, A. E., Muniesa, M., Mendez, X., Valero, F., Lucena, F., & Jofre, J. (2002). Removal and inactivation of indicator bacteriophages in fresh waters. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 92, 338–347.
Feachem, R.G., Bradley, D.J., Gerelick, H., Mara, D. 1983. Sanitation and Disease, Health Aspects of Excreta and Wastewater Management Wiley-Blackwell.
Fong, T. T., Phanikumar, M. S., Xagoraraki, I., & Rose, J. B. (2010). Quantitative detection of human adenoviruses in wastewater and combined sewer overflows influencing a Michigan river. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76, 715–723.
Hamza, I. A., Jurzik, L., Stang, A., Sure, K., Uberla, K., & Wilhelm, M. (2009a). Detection of human viruses in rivers of a densely populated area in Germany using a virus adsorption elution method optimized for PCR analyses. Water Research, 43, 2657–2668.
Hamza, I. A., Jurzik, L., Wilhelm, M., & Uberla, K. (2009b). Detection and quantification of human bocavirus in river water. Journal of General Virology, 90, 2634–2637.
Hamza, I. A., Jurzik, L., Uberla, K., & Wilhelm, M. (2011a). Evaluation of pepper mild mottle virus, human picobirnavirus and Torque teno virus as indicators of fecal contamination in river water. Water Research, 45, 1358–1368.
Hamza, I. A., Jurzik, L., Uberla, K., & Wilhelm, M. (2011b). Methods to detect infectious human enteric viruses in environmental water samples. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 214, 424–436.
Heim, A., Ebnet, C., Harste, G., & Pring-Akerblom, P. (2003). Rapid and quantitative detection of human adenovirus DNA by real-time PCR. Journal of Medical Virology, 70, 228–239.
Hot, D., Legeay, O., Jacques, J., Gantzer, C., Caudrelier, Y., Guyard, K., Lange, M., & Andreoletti, L. (2003). Detection of somatic phages, infectious enteroviruses and enterovirus genomes as indicators of human enteric viral pollution in surface water. Water Research, 37, 4703–4710.
ISO (2002). International Organization for Standardization. Water quality- Detection and enumeration of bacteriophages, part 2: Enumeration of somatic coliphages. In ISO 10705–2 (Geneva), 1–21.
Jurzik, L., Hamza, I. A., Puchert, W., Uberla, K., & Wilhelm, M. (2010). Chemical and microbiological parameters as possible indicators for human enteric viruses in surface water. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 213, 210–216.
Kuo, D. H., Simmons, F. J., Blair, S., Hart, E., Rose, J. B., & Xagoraraki, I. (2010). Assessment of human adenovirus removal in a full-scale membrane bioreactor treating municipal wastewater. Water Research, 44, 1520–1530.
Lee, C., & Kim, S. J. (2008). Molecular detection of human enteric viruses in urban rivers in Korea. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 18, 1156–1163.
Locas, A., Martinez, V., & Payment, P. (2010). Removal of human enteric viruses and indicator microorganisms from domestic wastewater by aerated lagoons. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 56, 188–194.
Lodder, W. J., & de Roda Husman, A. M. (2005). Presence of noroviruses and other enteric viruses in sewage and surface waters in The Netherlands. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71, 1453–1461.
McQuaig, S. M., Scott, T. M., Lukasik, J. O., Paul, J. H., & Harwood, V. J. (2009). Quantification of human polyomaviruses JC virus and BK virus by TaqMan quantitative PCR and comparison to other water quality indicators in water and fecal samples. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75, 3379–3388.
Myrmel, M., Rimstad, E., & Wasteson, Y. (2000). Immunomagnetic separation of a Norwalk-like virus (geno group I) in artificially contaminated environmental water samples. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 62, 17–26.
Nakajima, M., Uwatoko, K., Kobayashi, K., Pan, I. J., Iwabuchi, N., & Sunairi, M. (2003). Adhesion and releasing of poliovirus to activated sludge of wastewater purifying plants. Water Science and Technology, 47, 117–121.
Nelson, K. L., Cisneros, B. J., Tchobanoglous, G., & Darby, J. L. (2004). Sludge accumulation, characteristics, and pathogen inactivation in four primary waste stabilization ponds in central Mexico. Water Research, 38, 111–127.
Noble, R. T., Lee, I. M., & Schiff, K. C. (2004). Inactivation of indicator micro-organisms from various sources of faecal contamination in seawater and freshwater. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 96, 464–472.
Pusch. (2005). Detection of enteric viruses and bacterial indicators in German environmental waters. Archives of Virology, 150, 929–947.
Pusch, D., Ihle, S., Lebuhn, M., Graeber, I., & Lopez-Pila, J. M. (2005). Quantitative detection of enteroviruses in activated sludge by cell culture and real-time RT-PCR using paramagnetic capturing. Journal of Water and Health, 3, 313–324.
Queiroz, A. P., Santos, F. M., Sassaroli, A., Harsi, C. M., Monezi, T. A., & Mehnert, D. U. (2001). Electropositive filter membrane as an alternative for the elimination of PCR inhibitors from sewage and water samples. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67, 4614–4618.
Quinonez-Diaz, M. J., Karpiscak, M. M., Ellman, E. D., & Gerba, C. P. (2001). Removal of pathogenic and indicator microorganisms by a constructed wetland receiving untreated domestic wastewater. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part A, Toxic/Hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering, 36, 1311–1320.
Rao, V. C., Lakhe, S. B., & Waghmare, S. V. (1981). Virus removal in waste stabilization ponds in India. Water Research, 15, 773–778.
Reinoso, R., Torres, L. A., & Becares, E. (2008). Efficiency of natural systems for removal of bacteria and pathogenic parasites from wastewater. Science of the Total Environment, 395, 80–86.
Sinton, L. W., Hall, C. H., Lynch, P. A., & Davies-Colley, R. J. (2002). Sunlight inactivation of fecal indicator bacteria and bacteriophages from waste stabilization pond effluent in fresh and saline waters. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 1122–1131.
Skraber, S., Gassilloud, B., & Gantzer, C. (2004). Comparison of coliforms and coliphages as tools for assessment of viral contamination in river water. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 3644–3649.
van den Berg, H., Lodder, W., van der Poel, W., Vennema, H., & de Roda Husman, A. M. (2005). Genetic diversity of noroviruses in raw and treated sewage water. Research in Microbiology, 156, 532–540.
WHO, (2011). Guidelines for drinking-water quality. 4th edition.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Mrs. Isabel Bossow (B. Sc.), Mrs. Hanna Flamme (M.Sc.), and Mr. Frederik Santer (B. Sc.) for sampling and analyzing. Additionally, we are thankful to Elke Uhlenbrock, Sabine Wagener, and Gregor Perna for collecting the samples.
Conflict of Interest
All authors have no conflict of interests in relation to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jurzik, L., Hamza, I.A. & Wilhelm, M. Investigating the Reduction of Human Adenovirus (HAdV) and Human Polyomavirus (HPyV) in a Sewage Treatment Plant with a Polishing Pond as a Tertiary Treatment. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 284 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2545-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2545-9