Abstract
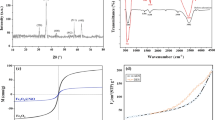
Scallop shell-Fe3O4 nanoparticles were synthesized by co-precipitation and hydrothermal methods. The removal efficiency of RB5 was studied as a function of pH, adsorbent dosage, initial RB5 concentration, ionic strength, and temperature. Coating of Fe3O4 nanoparticles onto Scallop shell was identified by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis. Maximum adsorption was obtained at pH 3. The removal efficiency of RB5 was increased with increasing adsorbent dosage. However, it was decreased with increasing initial RB5 concentration, temperature and in the presence of any anions. Adsorption kinetic study revealed that the pseudo-second order model better described the removal rate than the pseudo-first order model and intra-particle diffusion model. Adsorption isotherm was analyzed by both Langmuir and Freundlich equation. Experimental result was well described by the Langmuir equation. Maximum adsorption capacity was estimated to be 1111.11 mg/g. Thermodynamic studies indicated that the adsorption of RB5 onto Scallop shell-Fe3O4 nanoparticles was an endothermic (∆H = 178.14 KJ mol−1) process. The negative values of free energy (∆G) for the adsorption indicated that adsorption of RB5 was spontaneous reaction. Adsorption activity of RB5 by Scallop shell-Fe3O4 nanoparticles was maintained even after six successive cycles.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguedach, A., Brosillon, S., Morvan, J., & Lhadi, E. K. (2005). Photocatalytic degradation of azo-dyes Reactive Black 5 and reactive yellow 145 in water over a newly deposited titanium dioxide. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 57, 55–62.
Aksu, Z. (2001). Biosorption of reactive dyes by dried activated sludge: equilibrium and kinetic modelling. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 7, 79–84.
Alinsafi, A., Khemis, M., Pons, M., Leclerc, J., Yaacoubi, A., Benhammou, A., & Nejmeddine, A. (2005). Electro-coagulation of reactive textile dyes and textile wastewater. Chemical Engineering and Processing Process Intensification, 44, 461–470.
Araghi, S. H., & Entezari, M. H. (2015). Amino-functionalized silica magnetite nanoparticles for the simultaneous removal of pollutants from aqueous solution. Applied Surface Science, 333, 68–77.
Azizian, S. (2004). Kinetic models of sorption: a theoretical analysis. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 276, 47–52.
Bazrafshan, E., Kord Mostafapour, F., Rahdar, S., & Mahvi, A. H. (2014). Equilibrium and thermodynamics studies for decolorization of Reactive Black 5 (RB5) by adsorption onto MWCNTs. Desalination and Water Treatment, 1–11.
Chang, C.-J., Lin, C.-Y., & Hsu, M.-H. (2014). Enhanced photocatalytic activity of Ce-doped ZnO nanorods under UV and visible light. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 45, 1954–1963.
Chen, A.-H., & Huang, Y.-Y. (2010). Adsorption of Remazol Black 5 from aqueous solution by the templated crosslinked-chitosans. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 177, 668–675.
Choi, H.-D., Shin, M.-C., Kim, D.-H., Jeon, C.-S., & Baek, K. (2008). Removal characteristics of Reactive Black 5 using surfactant-modified activated carbon. Desalination, 223, 290–298.
de Luna, M. D. G., Flores, E. D., Genuino, D. A. D., Futalan, C. M., & Wan, M.-W. (2013). Adsorption of Eriochrome Black T (EBT) dye using activated carbon prepared from waste rice hulls—optimization, isotherm and kinetic studies. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 44, 646–653.
Eren, Z., & Acar, F. N. (2007). Equilibrium and kinetic mechanism for Reactive Black 5 sorption onto high lime Soma fly ash. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 143, 226–232.
Farrokhi, M., Hosseini, S.-C., Yang, J.-K., & Shirzad-Siboni, M. (2014). Application of ZnO–Fe3O4 nanocomposite on the removal of azo dye from aqueous solutions: kinetics and equilibrium studies. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 225, 1–12.
Ghoreishian, S. M., Badii, K., Norouzi, M., Rashidi, A., Montazer, M., Sadeghi, M., & Vafaee, M. (2014). Decolorization and mineralization of an azo reactive dye using loaded nano-photocatalysts on spacer fabric: kinetic study and operational factors. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 45, 2436–2446.
Gulnaz, O., Kaya, A., & Dincer, S. (2006). The reuse of dried activated sludge for adsorption of reactive dye. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 134, 190–196.
Handan, U. (2011). Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetics of reactive black 5 biosorption on loquat (Eriobotrya japonica) seed. Scientific Research and Essays, 6, 4113–4124.
Heibati, B., Rodriguez-Couto, S., Amrane, A., Rafatullah, M., Hawari, A., & Al-Ghouti, M. A. (2014). Uptake of Reactive Black 5 by pumice and walnut activated carbon: chemistry and adsorption mechanisms. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 20, 2939–2947.
Horwitz, W. (2000). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington, DC: APHA.
Iram, M., Guo, C., Guan, Y., Ishfaq, A., & Liu, H. (2010). Adsorption and magnetic removal of neutral red dye from aqueous solution using Fe3O4 hollow nanospheres. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 181, 1039–1050.
Jiang, H., Chen, P., Luo, S., Luo, X., Tu, X., Cao, Q., Zhou, Y., & Zhang, W. (2013). Synthesis of novel biocompatible composite Fe3O4 /ZrO2/chitosan and its application for dye removal. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials, 23, 393–400.
Karadag, D., Turan, M., Akgul, E., Tok, S., & Faki, A. (2007). Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics of Reactive Black 5 and reactive red 239 in aqueous solution onto surfactant-modified zeolite. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 52, 1615–1620.
Kim, S.-C., & Lee, D.-K. (2004). Preparation of Al–Cu pillared clay catalysts for the catalytic wet oxidation of reactive dyes. Catalysis Today, 97, 153–158.
Koyuncu, I. (2002). Reactive dye removal in dye/salt mixtures by nanofiltration membranes containing vinylsulphone dyes: effects of feed concentration and cross flow velocity. Desalination, 143, 243–253.
Kyzas, G. Z., Travlou, N. A., Kalogirou, O., & Deliyanni, E. A. (2013). Magnetic graphene oxide: effect of preparation route on Reactive Black 5 adsorption. Materials, 6, 1360–1376.
Liu, Y., & Liu, Y.-J. (2008). Biosorption isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. Separation and Purification Technology, 61, 229–242.
Mahmoodi, N. M. (2013). Magnetic ferrite nanoparticle–alginate composite: synthesis, characterization and binary system dye removal. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 44, 322–330.
Meriç, S., Kaptan, D., & Ölmez, T. (2004). Color and COD removal from wastewater containing Reactive Black 5 using Fenton’s oxidation process. Chemosphere, 54, 435–441.
Nabil, G. M., El-Mallah, N. M., & Mahmoud, M. E. (2014). Enhanced decolorization of Reactive Black 5 dye by active carbon sorbent-immobilized-cationic surfactant (AC-CS). Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 20, 994–1002.
Nethaji, S., Sivasamy, A., & Mandal, A. (2013). Preparation and characterization of corn cob activated carbon coated with nano-sized magnetite particles for the removal of Cr (VI). Bioresource Technology, 134, 94–100.
Ong, S.-A., Ho, L.-N., Wong, Y.-S., & Raman, K. (2012). Performance and kinetic study on bioremediation of diazo dye (Reactive Black 5) in wastewater using spent GAC–biofilm sequencing batch reactor. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 223, 1615–1623.
Ozdemir, O., Armagan, B., Turan, M., & Celik, M. S. (2004). Comparison of the adsorption characteristics of azo-reactive dyes on mezoporous minerals. Dyes and Pigments, 62, 49–60.
Patel, R., & Suresh, S. (2008). Kinetic and equilibrium studies on the biosorption of reactive black 5 dye by Aspergillus foetidus. Bioresource Technology, 99, 51–58.
Patterson, A. (1939). The Scherrer formula for X-ray particle size determination. Physical Review, 56, 978.
Pengthamkeerati, P., Satapanajaru, T., & Singchan, O. (2008). Sorption of reactive dye from aqueous solution on biomass fly ash. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 153, 1149–1156.
Poursaberi, T., & Hassanisadi, M. (2013). Magnetic removal of Reactive Black 5 from wastewater using ionic liquid grafted‐magnetic nanoparticles. CLEAN–Soil. Air, Water, 41, 1208–1215.
Sadaf, S., & Bhatti, H. N. (2014). Batch and fixed bed column studies for the removal of Indosol Yellow BG dye by peanut husk. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 45, 541–553.
Samarghandi, M., Azizian, S., Siboni, M. S., Jafari, S., & Rahimi, S. (2011). Removal of divalent nickel from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto modified holly sawdust: equilibrium and kinetics. Iranian Journal of Environmental Health Science & Engineering, 8, 167–174.
Şengil, I. A., & Özacar, M. (2009). The decolorization of CI Reactive Black 5 in aqueous solution by electrocoagulation using sacrificial iron electrodes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161, 1369–1376.
Shaheed, M. A., & Hussein, F. H. (2014). Adsorption of Reactive Black 5 on synthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles: equilibrium isotherm and kinetic studies. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2014, 3.
Shaker, M. A. (2015). Thermodynamics and kinetics of bivalent cadmium biosorption onto nanoparticles of chitosan-based biopolymers. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 47, 79–90.
Shirzad-Siboni, M., Samarghandi, M., Azizian, S., Kim, W., & Lee, S. (2011a). The removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions using modified holly sawdust: equilibrium and kinetics studies. Environmental Engineering Research, 16, 55–60.
Shirzad-Siboni, M., Samarghandi, M., Yang, J.-K., & Lee, S.-M. (2011b). Photocatalytic Removal of Reactive Black-5 dye from aqueous solution by UV irradiation in aqueous TiO2: equilibrium and kinetics study. Journal of Advanced Oxidation Technologies, 14, 302–307.
Shirzad-Siboni, M., Jafari, S. J., Giahi, O., Kim, I., Lee, S.-M., & Yang, J.-K. (2014a). Removal of acid blue 113 and Reactive Black 5 dye from aqueous solutions by activated red mud. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 20, 1432–1437.
Shirzad-Siboni, M., Khataee, A., & Joo, S. W. (2014b). Kinetics and equilibrium studies of removal of an azo dye from aqueous solution by adsorption onto scallop. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 20, 610–615.
Shirzad-Siboni, M., Khataee, A., Vafaei, F., & Joo, S. W. (2014c). Comparative removal of two textile dyes from aqueous solution by adsorption onto marine-source waste shell: kinetic and isotherm studies. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 1–9.
Soltani, T., & Entezari, M. (2013). Solar photocatalytic degradation of RB5 by ferrite bismuth nanoparticles synthesized via ultrasound. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 20, 1245–1253.
Travlou, N. A., Kyzas, G. Z., Lazaridis, N. K., & Deliyanni, E. A. (2013a). Functionalization of graphite oxide with magnetic chitosan for the preparation of a nanocomposite dye adsorbent. Langmuir, 29, 1657–1668.
Travlou, N. A., Kyzas, G. Z., Lazaridis, N. K., & Deliyanni, E. A. (2013b). Graphite oxide/chitosan composite for reactive dye removal. Chemical Engineering Journal, 217, 256–265.
Vijayaraghavan, K., & Yun, Y.-S. (2007). Utilization of fermentation waste (Corynebacterium glutamicum) for biosorption of Reactive Black 5 from aqueous solution. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 141, 45–52.
Vijayaraghavan, K., & Yun, Y.-S. (2008). Biosorption of CI Reactive Black 5 from aqueous solution using acid-treated biomass of brown seaweed Laminaria sp. Dyes and Pigments, 76, 726–732.
Vimonses, V., Lei, S., Jin, B., Chow, C. W. K., & Saint, C. (2009). Adsorption of congo red by three Australian kaolins. Applied Clay Science, 43, 465–472.
Xue, Y., Hou, H., & Zhu, S. (2009). Adsorption removal of reactive dyes from aqueous solution by modified basic oxygen furnace slag: isotherm and kinetic study. Chemical Engineering Journal, 147, 272–279.
Yang, N., Zhu, S., Zhang, D., & Xu, S. (2008). Synthesis and properties of magnetic Fe 3 O 4-activated carbon nanocomposite particles for dye removal. Materials Letters, 62, 645–647.
Yao, Y., Miao, S., Liu, S., Ma, L. P., Sun, H., & Wang, S. (2012). Synthesis, characterization, and adsorption properties of magnetic Fe3O4@graphene nanocomposite. Chemical Engineering Journal, 184, 326–332.
Yeom, S. H., & Jung, K.-Y. (2009). Recycling wasted scallop shell as an adsorbent for the removal of phosphate. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 15, 40–44.
Zawani, Z., Chuah, A., & Choong, T. (2009). Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamic studies: adsorption of Remazol Black 5 on the palm kernel shell activated carbon. European Journal of Scientific Research, 37, 67–76.
Zhang, Z., & Kong, J. (2011). Novel magnetic Fe3O4@C nanoparticles as adsorbents for removal of organic dyes from aqueous solution. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 193, 325–329.
Zhu, H.-Y., Jiang, R., & Xiao, L. (2010). Adsorption of an anionic azo dye by chitosan/kaolin/γ-Fe2O3 composites. Applied Clay Science, 48, 522–526.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Guilan and Iran Universities of Medical Sciences of Iran for their contributions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohagheghian, A., Vahidi-Kolur, R., Pourmohseni, M. et al. Application of Scallop shell-Fe3O4 Nano-Composite for the Removal Azo Dye from Aqueous Solutions. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 321 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2539-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2539-7