Abstract
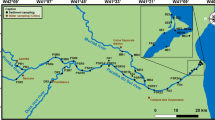
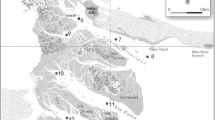
Sediment, suspended particulate matter (SPM), water and clam Scrobicularia plana samples were collected in a temperate coastal lagoon with anthropogenic impact. Arsenic levels in sediments, SPM and water presented a spatial concentration gradient. A significant linear regression between arsenic levels in S. plana and SPM suggests particulate matter as the main route of arsenic exposure. Trend analysis showed that total arsenic concentrations in S. plana generally increased with size class, reflecting lifespan bioaccumulation. Despite being efficient in reflecting environmental contamination levels, results suggest that arsenic accumulation by S. plana may not be a passive process, given the proportionally lower accumulation in high contamination areas. Annual bioaccumulation rates ranged from 5.6 to 1 mg kg−1 year−1, suggesting a possible toxicity risk for individuals of the most contaminated area. Despite the absence of regulatory guidelines, food safety assessment highlighted possible adverse effects of consuming S. plana in most contaminated areas.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azizur Rahman, M., Hasegawa, H., & Peter Lim, R. (2012). Bioaccumulation, biotransformation and trophic transfer of arsenic in the aquatic food chain. Environmental Research, 116, 118–135.
Caeiro, S., Costa, M. H., Ramos, T. B., Fernandes, F., Silveira, N., Coimbra, A., Medeiros, G., & Painho, M. (2005). Assessing heavy metal contamination in Sado Estuary sediment: an index analysis approach. Ecological Indicators, 5, 151–169.
Caetano, M., & Vale, C. (2002). Retention of arsenic and phosphorus in iron-rich concretions of Tagus salt marshes. Marine Chemistry, 79, 261–271.
Coelho, J. P., Rosa, M., Pereira, E., Duarte, A., & Pardal, M. A. (2006). Pattern and annual rates of Scrobicularia plana mercury bioaccumulation in a human induced mercury gradient (Ria de Aveiro, Portugal). Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 69, 629–635.
Coelho, J. P., Nunes, M., Dolbeth, M., Pereira, M. E., Duarte, A. C., & Pardal, M. A. (2008). The role of two sediment-dwelling invertebrates on the mercury transfer from sediments to the estuarine trophic web. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 78, 505–512.
Coelho, J. P., Duarte, A. C., Pardal, M. A., & Pereira, M. E. (2014). Scrobicularia plana (Mollusca, Bivalvia) as a biomonitor for mercury contamination in Portuguese estuaries. Ecological Indicators, 46, 447–453.
Costa, C., & Jesus-Rydin, C. (2001). Site investigation on heavy metals contaminated ground in Estarreja – Portugal. Engineering Geology, 60, 39–47.
Costa, P. M., Diniz, M. S., Caeiro, S., Lobo, J., Martins, M., Ferreira, A. M., Caetano, M., Vale, C., DelValls, T. A., & Costa, M. H. (2009). Histological biomarkers in liver and gills of juvenile Solea senegalensis exposed to contaminated estuarine sediments: a weighted indices approach. Aquatic Toxicology, 92, 202–212.
de Mora, S., Fowler, S. W., Wyse, E., & Azemard, S. (2004). Distribution of heavy metals in marine bivalves, fish and coastal sediments in the Gulf and Gulf of Oman. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 49, 410–424.
Garcia-Luque, E., DelValls, T. A., Casado-Martinez, C., Forja, J. M., & Gomez-Parra, A. (2004). Simulating a heavy metal spill under estuarine conditions: effects on the clam Scrobicularia plana. Marine Environmental Research, 58, 671–674.
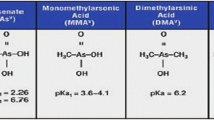
Jain, C. K., & Ali, I. (2000). Arsenic: occurrence, toxicity and speciation techniques. Water Research, 34, 4304–4312.
Liu, C.-W., Liang, C.-P., Lin, K.-H., Jang, C.-S., Wang, S.-W., Huang, Y.-K., & Hsueh, Y.-M. (2007). Bioaccumulation of arsenic compounds in aquacultural clams (Meretrix lusoria) and assessment of potential carcinogenic risks to human health by ingestion. Chemosphere, 69, 128–134.
McGeer, J. C., Brix, K. V., Skeaff, J. M., DeForest, D. K., Brigham, S. I., Adams, W. J. & Green, A. (2003). Inverse relationship between bioconcentration factor and exposure concentration for metals: Implications for hazard assessment of metals in the aquatic environment. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 22(5), 1017–1037.
Marques, A. P. G. C., Moreira, H., Rangel, A. O. S. S., & Castro, P. M. L. (2009). Arsenic, lead and nickel accumulation in Rubus ulmifolius growing in contaminated soil in Portugal. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 165, 174–179.
Pereira, M. E., Abreu, S., Pato, P., Coelho, J. P., Azeiteiro, U. M., Pardal, M. A., & Duarte, A. C. (2007). Seasonal mercury concentrations in plankton-net material from a contaminated coastal lagoon (Ria de Aveiro, Portugal). Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 16, 1442–1450.
Pereira, M. E., Abreu, S., Coelho, J. P., Pato, P., Pardal, M. A., & Duarte, A. C. (2008). Influence of tidal resuspension on seston lithogenic and biogenic partitioning in shallow estuarine systems: Implications for sampling. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 56, 348–354.
Rainbow, P. S., Kriefman, S., Smith, B. D., & Luoma, S. N. (2011). Have the bioavailabilities of trace metals to a suite of biomonitors changed over three decades in SW England estuaries historically affected by mining? Science of The Total Environment, 409, 1589–1602.
Ridgway, J., & Shimmield, G. (2002). Estuaries as repositories of historical contamination and their impact on shelf seas. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 55, 903–928.
Ringmann, S., Boch, K., Marquardt, W., Schuster, M., Schlemmer, G., & Kainrath, P. (2002). Microwave-assisted digestion of organoarsenic compounds for the determination of total arsenic in aqueous, biological, and sediment samples using flow injection hydride generation electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Analytica Chimica Acta, 452, 207–215.
Suñer, M. A., Devesa, V., Muñoz, O., López, F., Montoro, R., Arias, A. M., & Blasco, J. (1999). Total and inorganic arsenic in the fauna of the Guadalquivir estuary: environmental and human health implications. The Science of The Total Environment, 242, 261–270.
Tornero, V., Arias, A. M., & Blasco, J. (2011). Following the Aznalcollar toxic spill. Environmental Research, 111, 1033–1036.
Verdelhos, T., Neto, J. M., Marques, J. C., & Pardal, M. A. (2005). The effect of eutrophication abatement on the bivalve Scrobicularia plana. Estuarine Coastal And Shelf Science, 63, 261–268.
Wang, S., Xu, L., Zhao, Z., Wang, S., Jia, Y., Wang, H., & Wang, X. (2012). Arsenic retention and remobilization in muddy sediments with high iron and sulfur contents from a heavily contaminated estuary in China. Chemical Geology, 314–317, 57–65.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by European Funds through COMPETE and by National Funds through the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT) within project UID/AMB/50017/2013 (CESAM) and a Post-Doc grant to João Pedro Coelho (BPD/48449/2008).
Compliance with Ethical Standards
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest, that the research did not involve human participants and that all methodologies involving living organisms complied with animal welfare guidelines.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ereira, T., Coelho, J.P., Duarte, A.C. et al. Size-Dependent Arsenic Accumulation in Scrobicularia plana in a Temperate Coastal Lagoon (Ria de Aveiro, Portugal). Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 213 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2484-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2484-5