Abstract
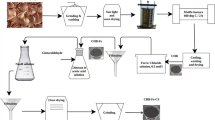
This paper presents the efficacy of zero-valent iron nanoparticles (ZVINs), magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (MINs), zero-valent iron nanoparticles/sugarcane bagasse (ZVIN-SB) composite and magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles/sugarcane bagasse (MIN-SB) composite in immobilizing chromium present in tannery sludge. The optimized values for the immobilization of chromium by the adsorbents were found to be 48 h, 100 g/kg and 7, respectively, for time, adsorbent dosage and pH. The maximum uptake capacity was found to be 429.75, 539.25, 587.25 and 625.8 mg/kg, respectively, for ZVIN, MIN, ZVIN-SB and MIN-SB. The desorption study of the unamended sludge and sludge amended by ZVIN, MIN, ZVIN-SB and MIN-SB was carried out with three different desorbing media (0.1 N HCL, DIW and 0.1 N NaOH). It was found that the cumulative concentration of leachate chromium was more in basic condition than in neutral and acidic conditions. In column studies, the concentration of leachate chromium attained 0 mg/L at 24, 15, 18 and 14 pore volumes, respectively, for the sludge amended by ZVIN, MIN, ZVIN-SB and MIN-SB. The experimental adsorption data fitted well with pseudo-first-order kinetics. The zero-order kinetics accurately predicted the experimental desorption capacity (q e) of the sludge amended by ZVIN, MIN, ZVIN-SB and MIN-SB. The Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis showed that the amine, carboxyl, iron compounds, etc. present in the adsorbents were the chief causes for the immobilization of chromium. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis of the sludge showed the presence of trivalent chromium compounds at a higher concentration.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- q t :
-
Amount of contaminant adsorbed/desorbed from sludge at time (min) (mg/kg)
- C 0 :
-
Initial concentration of the chromium (mg/L)
- C e :
-
Final concentration of the chromium (mg/L)
- V :
-
Volume of the solution (L)
- M :
-
Mass of the adsorbent (kg)
- C t (mg/L):
-
Concentration of the contaminant in the liquid at varying contact time
- W :
-
Weight of the sludge (kg)
- R 2 :
-
Correlation coefficient
- q e :
-
Experimental uptake capacity/desorption capacity (mg/kg)
- q e,cal :
-
Calculated uptake capacity/desorption capacity (mg/kg)
- k 1 :
-
First-order kinetic rate constant (1/min)
- h :
-
Initial adsorption rate (mg/kg/min)
- t 1/2 :
-
Half-life time (min)
- k 2 :
-
Rate constant of pseudo-second-order equation (kg/mg/min)
- α :
-
Elovich kinetic constant initial adsorption rate (mg/kg/min)
- β :
-
Elovich kinetic desorption constant (kg/mg)
- k :
-
Rate constant of the power function (mg/kg/min)
- kv:
-
Power kinetic specific adsorption rate at unit time (mg/kg/min)
- k 0 :
-
Zero-order rate constant (mg/kg/min)
- k p :
-
Parabolic diffusion rate constant (kg/g/min0.5)
References
Ahmad, M., Hashimoto, Y., Moon, D. H., Lee, S. S., & Ok, Y. S. (2012). Immobilization of lead in a Korean military shooting range soil using eggshell waste: an integrated mechanistic approach. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 209–210, 392–401.
An, B., & Zhao, D. (2012). Immobilization of As (III) in soil and groundwater using a new class of polysaccharide stabilized Fe–Mn oxide nanoparticles. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 211–212, 332–341.
APHA. (1998). Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater (20th ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Apte, A. D., Tare, V., & Bose, P. (2005). Oxidation of Cr(III) in tannery sludge to Cr(VI): field observations and theoretical assessment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 121(1–3), 215–222.
Apte, A. D., Tare, V., & Bose, P. (2006). Extent of oxidation of Cr(III) to Cr(VI) under various conditions pertaining to natural environment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 128(2–3), 164–174.
Basha, S., & Murthy, Z. V. P. (2007). Kinetic and equilibrium models for biosorption of Cr(VI) on chemically modified seaweed Cystoseira indica. Process Biochemistry, 42(11), 1521–1529.
Cao, J., & Zhang, W. X. (2006). Stabilization of chromium ore processing residue (COPR) with nanoscale iron particles. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 132(2–3), 213–219.
Cassano, A., Drioli, E., Molinari, R., & Bertolutti, C. (1996). Quality improvement of recycled chromium in the tanning operation by membrane processes. Desalination, 108(1–3), 193–203.
Ceribasi, I. H., & Yetis, U. (2001). Biosorption of Ni(II) and Pb(II) by Phanerochaete chrysosporium from binary metal system kinetics. Water SA., 27(1), 15–20.
Chang, G. R., Liu, J. C., & Lee, D. J. (2001). Co-conditioning and dewatering of chemical sludge and waste activated sludge. Water Research, 35(3), 786–794.
Chatterjee, S., Ghosh, I., & Mukherjea, K. K. (2011). Uptake and removal of toxic Cr(VI) by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: physico-chemical and biological evaluation. Current Science, 101(5), 645–652.
Cossich, E. S., Tavares, C. R., & Ravagnani, T. M. (2002). Biosorption of chromium (III) by Sargassum sp. Biomass. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology, 5(2), 133–137.
Costa, M. (2003). Potential hazards of hexavalent chromate in our drinking water. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 188(1), 1–5.
Costa, M., & Klein, C. B. (2006). Toxicity and carcinogenicity of chromium compounds in humans. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 36(2), 155–163.
Covington, A. D. (1998). John Arthur Wilson Memorial Lecture: new tannages for the new millennium. Journal of the American Leather Chemists Association, 93, 168–182.
Dang, Y. P., Dalal, R. C., Edwards, D. G., & Tiller, K. G. (1994). Kinetics of zinc desorption from vertisols. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 58(5), 1392–1399.
Errais, E., Duplay, J., Darragi, F., Rabet, I. M., Aubert, A., Huber, F., & Morvan, G. (2011). Efficient anionic dye adsorption on natural untreated clay: kinetic study and thermodynamic parameters. Desalination, 275(1–3), 74–81.
Farinella, N. V., Matos, G. D., & Arruda, M. A. Z. (2007). Grape bagasse as a potential biosorbent of metals in effluent treatments. Bioresource Technology, 98(10), 1940–1946.
Fonglim, S., Zheng, Y. M., Zou, S. W., & Chen, J. P. (2008). Characterization of copper adsorption onto an alginate encapsulated magnetic sorbent by a combined FTIR, XPS, and mathematical modeling study. Environmetal Science & Technology, 42(7), 2551–2556.
Fonseca, B., Maio, H., Quintelas, C., Teixeira, A., & Tavares, T. (2009). Retention of Cr (VI) and Pb(II) on a loamy sand soil: kinetics, equilibria and breakthrough. Chemical Engineering Journal, 152(1), 212–219.
Foo, K. Y., & Hameed, B. H. (2011). Preparation of activated carbon from date stones by microwave induced chemical activation: application for methylene blue adsorption. Chemical Engineering Journal, 170(1), 338–341.
Franco, D. V., Silva, L. M. D., & Jardim, W. F. (2009). Reduction of hexavalent chromium in soil and ground water using zero-valent iron under batch and semi-batch conditions. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 197(1–4), 49–60.
Gerente, C., Lee, V. K. C., Cloirec, P. L., & Mckay, G. (2007). Application of chitosan for the removal of metals from wastewaters by adsorption-mechanisms and models review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 37(1), 41–127.
Gong, Y., Liu, X., Huang, L., & Chen, W. (2010). Stabilization of chromium: an alternative to make safe leathers. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 179(1–3), 540–544.
Gu, H., Rapole, S. B., Sharma, J., Huang, Y., Cao, D., Colorado, H. A., Luo, Z., Haldolaarachchige, N., Young, D. P., Walters, B., Wei, S., & Guo, Z. (2012). Magnetic polyaniline nanocomposites toward toxic hexavalent chromium removal. RSC Advances, 2(29), 11007–11018.
Gu, H., Rapole, S. B., Huang, Y., Cao, D., Luo, Z., Wei, S., & Guo, Z. (2013). Synergistic interactions between multi-walled carbon nanotubes and toxic hexavalent chromium. Journal of Material Chemistry A, 1(6), 2011–2021.
Ho, Y. S., & Mckay, G. (1999). Pseudo second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochemistry, 34(5), 451–465.
Katz, S. A., & Salem, H. (1993). The toxicology of chromium with respect to its chemical speciation: a review. Journal of Applied Toxicology, 13(3), 217–224.
Kim, C. J., Yoon, H. S., Chung, K. W., Lee, J. Y., Kim, S. D., Shin, S. M., Lee, S. J., Joe, A. R., Lee, S. I., Yoo, S. J., & Kim, S. H. (2014). Leaching kinetics of lanthanum in sulfuric acid from rare earth element (REE) slag. Hydrometallurgy, 146, 133–137.
Kumar, P. A., Ray, M., & Chakraborty, S. (2009). Adsorption behaviour of trivalent chromium on amine-based polymer aniline formaldehyde condensate. Chemical Engineering Journal, 149(1–3), 340–347.
Kushwaha, S., Sreedhar, B., & Sudhakar, P. P. (2012). Adsorption of Hg2+ onto Borassus Flabellifer: a redox mechanis. Chemical Engineering Journal, 193–194, 328–338.
Labib, M., Dukhin, S. S., & Tabani, Y. (2010). Desorption kinetics during capillary flow. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 354(1), 45–50.
Levenspiel, O. (1972). Chemical Reaction Engineering (Secondth ed., p. 357). New York: Wiley.
Lu, W., Shen, Y., Xie, A., & Zhang, W. (2010). Green synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 322(13), 1828–1833.
Lu, M., Zhang, Y. M., Guan, X. H., Xu, X. H., & Gao, T. T. (2014). Thermodynamics and kinetics of adsorption for heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions onto surface amino-bacterial cellulose. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 24(6), 1912–1917.
Manohar, D. M., Krishnan, A. K., & Anirudhan, T. S. (2002). Removal of mercury (II) from aqueous solutions and chlor-alkali industry wastewater using 2-mercaptobenzimidazole-clay. Water Research, 36(6), 1609–1619.
Mishra, P. C., & Patel, R. K. (2009). Removal of lead and zinc ions from water by low cost adsorbents. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168(1), 319–325.
Mohan, J. (2004). Organic spectroscopy principles and applications (2nd ed., pp. 76–95). New Delhi: Narosa publishing house.
Mohan, D., Singh, K. P., & Singh, V. K. (2006). Trivalent chromium removal from wastewater using low cost activated carbon derived from agricultural waste material and activated carbon fabric cloth. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 135(1–3), 280–295.
Nakayama, E., Kuwamoto, T., Tsurubo, S., & Fujinaga, T. (1981). Chemical speciation of chromium in seawater. Analytica Chimica Acta, 130, 401–404.
Nandi, B. K., Goswami, A., & Purkait, M. K. (2009). Removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions by kaolin: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Applied Clay Science, 42(3–4), 583–590.
Nielsen, S. S., Petersen, L. R., Kjeldsen, P., & Jakobsen, R. (2011). Amendment of arsenic and chromium polluted soil from wood preservation by iron residues from water treatment. Chemosphere, 84(4), 383–389.
Park, D., Ahn, C. K., Kim, Y. M., Yun, Y. S., & Park, J. M. (2008). Enhanced abiotic reduction of Cr(VI) in a soil slurry system by natural biomaterial addition. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 160(2–3), 422–427.
Porter, S. K., Scheckel, K. G., Impellitteri, C. A., & Ryan, A. J. (2004). Toxic metals in the environment: thermodynamic considerations for possible immobilization strategies for Pb, Cd, As, and Hg. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 34(6), 495–604.
Qiu, B., Gu, H., Yan, X., Guo, J., Wang, Y., Sun, D., Wang, Q., Khan, M., Zhang, X., Weeks, B. L., Young, D. P., Guo, Z., & Wei, S. (2014a). Cellulose derived magnetic mesoporous carbon nanocomposites with enhanced hexavalent chromium removal. Journal of Material Chemistry A, 2(41), 17451–17462.
Qiu, B., Xu, C., Sun, D., Wei, H., Zhang, X., Guo, J., Wang, Q., Rutman, D., Guo, Z., & Wei, S. (2014b). Polyaniline coating on carbonfiber fabrics for improved hexavalent chromium removal. RSC Advances, 4(56), 29855–29865.
Qiu, B., Xu, C., Sun, D., Yi, H., Guo, J., Zhang, X., Qu, H., Guerrero, M., Wang, X., Noel, N., Luo, Z., Guo, Z., & Wei, S. (2014c). Polyaniline coated ethyl cellulose with improved hexavalent chromium removal. ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering, 2(8), 2070–2080.
Qiu, B., Wang, Y., Sun, D., Wang, Q., Zhang, X., Weeks, B. L., O'Connor, R., Huang, X., Wei, S., & Guo, Z. (2015a). Cr(VI) removal by magnetic carbon nanocomposites derived from cellulose at different carbonization temperatures. Journal of Material Chemistry A, 3(18), 9817–9825.
Qiu, B., Xu, C., Sun, D., Wang, Q., Gu, H., Zhang, X., Weeks, B. L., Hopper, J., Ho, T. C., Guo, Z., & Wei, S. (2015b). Polyaniline coating with various substrates for hexavalent chromium removal. Applied Surface Science, 334, 7–14.
Rashti, M. R., Esfandbod, M., Adhami, E., & Srivastava, P. (2014). Cadmium desorption behaviour in selected sub-tropical soils: effects of soil properties. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 144, 230–236.
Reddy, D. H. K., & Lee, S. M. (2013). Synthesis and characterization of a chitosan ligand for the removal of copper from aqueous media. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 130(6), 4542–4550.
Rivera-Utrilla, J., & Sanchez-Polo, M. (2003). Adsorption of Cr(III) on ozonized activated carbon. Importance of Cpi–cation interactions. Water Research, 37(14), 3335–3340.
Salimi, A., Pourbahram, B., Majd, S. M., & Hallaj, R. (2015). Manganese oxide nanoflakes/multi-walled carbon nanotubes/chitosan nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode as a novel electrochemical sensor for chromium (III) detection. Electrochimica Acta, 156, 207–215.
Sing, C., & Yu, J. (1998). Copper adsorption and removal from water by living mycelium of white-rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Water Research, 32(9), 2746–2752.
Singh, R., Misra, V., & Singh, R. P. (2011). Synthesis, characterization and role of zero-valent iron nanoparticle in removal of hexavalent chromium from chromium-spiked soil. Journal of Nanopartical Research, 13(9), 4063–4073.
Singh, R., Misra, V., & Singh, R. P. (2012). Removal of Cr(VI) by nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) from soil contaminated with tannery wastes. Bullatin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 88(2), 210–214.
Tseng, J. Y., Chang, C. Y., Chang, C. F., Chen, Y. H., Chang, C. C., Ji, D. R., Chiu, C. Y., & Chiang, P. C. (2009). Kinetics and equilibrium of desorption removal of copper from magnetic polymer adsorbent. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 171(1–3), 370–377.
Tseng, R. L., Wu, P. H., Wu, F. C., & Juang, R. S. (2011). Half-life and half-capacity concentration approach for the adsorption of 2, 4-dichlorophenol and methyl blue from water on activated carbons. Journal of Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 42(2), 312–319.
Tunay, O., Kabdasli, I., Orhon, D., & Ates, E. (1995). Characterization and pollution profile of leather tanning industry in turkey. Water Science and Technology, 32(12), 1–9.
Volesky, B., & Holan, Z. R. (1995). Biosorption of heavy metals. Biotechnology Progress, 11, 235–250.
Wang, G. H., & Grathwohl, P. (2009). Activation energies of phenanthrene desorption from carbonaceous materials: column studies. Journal of Hydrology, 369(3), 234–240.
Weber, W. J., & Smith, E. H. (1987). Simulation and design models for adsorption processes. Environmental Science & Technology, 21(11), 1040–1050.
Wei, S., Wang, Q., Zhu, J., Sun, L., Lin, H., & Guo, Z. (2011). Multifunctional composite core–shell nanoparticles. Nanoscale, 3(11), 4474–4502.
Xu, C., Qiu, B., Gu, H., Yang, X., Wei, H., Huang, X., Wang, Y., Rutman, D., Cao, D., Bhana, S., Guo, Z., & Wei, S. (2014). Synergistic interactions between activated carbon fabrics and toxic hexavalent chromium. ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology, 3(3), M1–M9.
Zhang, D., Wei, S., Kaila, C., Su, X., Wu, J., Karki, A. B., Young, D. P., & Guo, Z. (2010). Carbon-stabilized iron nanoparticles for environmental remediation. Nanoscale, 2(6), 917–919.
Zhu, J., Gu, H., Rapole, S. B., Luo, Z., Pallavkar, S., Haldolaarachchige, N., Benson, T. J., Ho, T. C., Hopper, J., Young, D. P., Wei, S., & Guo, Z. (2012a). Looped carbon capturing and environmental remediation: case study of magnetic polypropylene nanocomposites. RSC Advances, 2(11), 4844–4856.
Zhu, J., Sadu, R., Wei, S., Chen, D. H., Haldolaarachchige, N., Luo, Z., Gomes, J. A., Young, D. P., & Guo, Z. (2012b). Magnetic graphene nanoplatelet composites toward arsenic removal. ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology, 1(1), M1–M5.
Zhu, J., Wei, S., Gu, H., Rapole, S. B., Wang, Q., Luo, Z., Haldolaarachchige, N., Young, D. P., & Guo, Z. (2012c). One-pot synthesis of magnetic graphene nanocomposites decorated with core@double-shell nanoparticles for fast chromium removal. Environmental Science and Technology, 46(2), 977–985.
Zhu, J., Wei, S., Chen, M., Gu, H., Rapole, S. B., Pallavkar, S., Ho, T. C., Hopper, J., & Guo, Z. (2013). Magnetic nanocomposites for environmental remediation. Advanced Powder Technology, 24(2), 459–467.
Zhu, J., Gu, H., Guo, J., Chen, M., Wei, H., Luo, Z., Colorado, H. A., Yerra, N., Ding, D., Ho, T. C., Haldolaarachchige, N., Hopper, J., Young, D. P., Guo, Z., & Wei, S. (2014). Mesoporous magnetic carbon nanocomposite fabrics for highly efficient Cr(VI) removal. Journal of Material Chemistry A, 2(7), 2256–2265.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the VIT University, Vellore, for providing sufficient facilities to carry out this research work. The first author is thankful to the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, India, for providing financial assistance to her as a Senior Research Fellowship (SRF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 5736 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arthy, M., Phanikumar, B.R. Immobilization of Chromium in Tannery Sludge Using Iron-Based Nanoparticles and Nanobiocomposites. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 204 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2466-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2466-7