Abstract
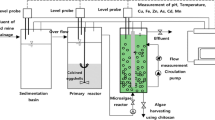
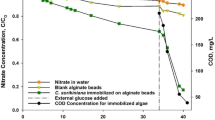
This study investigates the use of sericite beads and microalgae for the removal of heavy metals from acid mine drainage (AMD) and the simultaneous enhancement of biomass productivity. The experiment was conducted over a period of 6 days in a hybrid system containing sericite beads and microalgae Chlorella sp. The results show that the biomass production increased to ~8.04 times its initial concentration of 0.367 g/L as measured by an optical panel photobioreactor (OPPBR) and had a light transmittance of 95 % at a 305-mm depth. Simultaneous percent removal of Fe, Cu, Zn, Mn, As, and Cd from the AMD effluent was found to be 97.78 to 99.26 %. Biomass production was significantly enhanced by removal of heavy metal ions. We thus found that our hybrid system of sericite beads and microalgae was highly effective in removing heavy metal and in enhancing biomass production and could be a useful alternative treatment of AMD.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajjabi, L. C., & Chouba, L. (2009). Biosorption of Cu and Zn from aqueous solutions by dried marine green macroalga Chaetomorpha linum. Journal of Environmental Management, 90, 3485–3489.
An, J. H., Kim, C. C., Choi, S. B., Kim, S. R., Jung, J. Y., Lee, W. A., & Lee, T. S. (2007). A study on removal effect of heavy metals in mine wastewater by adsorbents. Report Institute of Health & Environment, 18, 138–149.
APHA (2012). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 22nd edition, Washington DC, USA.
Ata, A., & Koldas, S. (2006). Acid mine drainage (AMD): causes, treatment and case studies. Journal of Cleaner Production, 14(12–13), 1139–1145.
Carlozzi, P. (2003). Dilution of solar radiation through “culture” lamination in photobioreactor rows facing south–north: a way to improve the efficiency of light utilization by cyanobacteria (Arthrospira platensis). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 81(3), 305–315.
Chen, C. Y., Yeh, K. L., Aisyah, R., Lee, D. J., & Chang, J. S. (2011). Cultivation, photobioreactor design and harvesting of microalgae for biodiesel production: a critical review. Bioresource Technology, 102(1), 71–81.
Choi, H. J. (2014). Effect of optical panel distance in a photobioreactor for nutrient removal and cultivation of microalgae. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 30, 2015–2023.
Choi, H. J., & Lee, S. M. (2014). Effect of optical panel thickness for nutrient removal and cultivation of microalgae in the photobioreactor. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 37(4), 697–705.
Coulton, R., Bullen, C., & Hallet, C. (2003). The design and optimization of active mine water treatment plants. Land Contamination and Reclamation, 11, 273–279.
García-Malea López, M. C., Del Río Sánchez, E., Casas López, J. L., Acién Fernández, F. G., Rivas, J., Guerrero, M. G., & Molina, G. E. (2006). Comparative analysis of the outdoor culture of Haematococcus pluvialis in tubular and bubble column photobioreactors. Journal of Biotechnology, 123(3), 329–342.
Genc, H., Tjell, C. J., McConchie, D., & Schuiling, O. (2003). Adsorption of arsenate from water using neutralized red mud. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 264, 327–334.
Hsieh, C. H., & Wu, W. T. (2009). A novel photobioreactor with transparent rectangular chambers for cultivation of microalgae. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 46(3), 300–305.
Johnson, D. B., & Hallberg, K. B. (2003). The microbiology of acidic mine waters. Research in Microbiology, 154, 466–473.
Johnson, D. B., & Hallberg, K. B. (2005). Acid mine drainage remediation options: a review. Science of the Total Environment, 338, 3–14.
Kim, M. N., & Lee, S. M. (2010). Organo-sericite for the removal of phenol and Cu2+ from aqueous solution. Korean Society of Water Science and Technology, 18(5), 29–35.
Kim, J. O., Lee, S. M., & Jeon, C. (2014). Adsorption characteristics of sericite for cesium ions for an aqueous solution. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 92(2), 368–374.
Kwon, T. N., & Jeon, C. (2013). Adsorption characteristics of sericite for nickel ions from industrial waste water. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 25, 68–72.
Lee, S. M., & Tiwari, D. (2012). Organo and inorgano-organo-modified clays in the remediation of aqueous solutions: an overview. Applied Clay Science, 59–60, 84–102.
Lee, S. M., & Tiwari, D. (2014). Organo-modified sericite in the remediation of aquatic environment contaminated with As(III) or As(V). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 407–418.
Liu, C. B., Lin, L. P., & Su, Y. C. (1996). Utilization of Chlorella vulgaris for uptake of nitrogen, phosphorus and heavy metals. Journal of the Chinese Agricultural Chemical Society, 34, 331–343.
Mendoza-Co, L., Zatl, D. G., & Moreno-Sa, L. R. (2005). Cd2+ transport and storage in the chloroplast of Euglena gracilis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1706, 88–97.
Reddy, D. H. K., Lee, S. M., & Kim, J. O. (2013). A review on emerging applications of natural sericite and its composites. World Applied Sciences Journal, 27(11), 1514–1523.
Romera, E., Gonzáalez, F., Ballester, A., Bláazquez, M. L., & Muñnoz, J. A. (2007). Comparative study of biosorption of heavy metals using different types of algae. Bioresource Technology, 98(17), 3344–3353.
Shanab, S., Essa, A., & Shalaby, E. (2012). Bioremoval capacity of tree heavy metals by some microalgae species (Egyptian Isolates). Plant Signaling & Behavior, 7(3), 392–399.
Tiwari, D., & Lee, S. M. (2012). Novel hybrid materials in the remediation of ground waters contaminated with As(III) and As(V). Chemical Engineering Journal, 204–206, 23–31.
Tiwari, D., Kim, H. Y., & Lee, S. M. (2009). Application of sericite in wastewater treatment: removal of Cu(II) and Pb(II) from aqueous solutions. Environmental Engineering Research, 11(6), 303–310.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2013006899).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, HJ. Biosorption of Heavy Metals from Acid Mine Drainage by Modified Sericite and Microalgae Hybrid System. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 185 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2433-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2433-3