Abstract
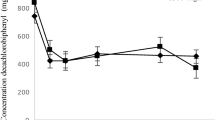
This study aimed to evaluate the removal of polychlorinated biphenyls, with a vermicomposting system, using the following as components: the earthworm Eisenia fetida, peat moss and rabbit excrement and a compound called decachlorobiphenyl, for a period of 91 days under non-sterile conditions. The results obtained were a removal of decachlorobiphenyl 79.6 % with an initial concentration of 100 mg L−1, 89.7 % with 150 mg L−1 and 95.38 % with 200 mg L−1; the earthworms bioaccumulated less than 5 mg L−1 in all concentrations of decachlorobiphenyl analysed without apparent toxic effect. Weight gain was observed in earthworms that assimilated contaminant during vermicomposting, as the number of cocoons produced in contrast to the control in which both the weight and the number of cocoons were lower. To our knowledge, this is the first study which suggests that vermicomposting may be a suitable mechanism for removal of decachlorobiphenyl with high recalcitrance from contaminated sediment or soils.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AOAC. (1996). Official methods of analysis of AOAC international (16th ed., Vol. 1). Gaithersburg: AOAC International.
Aira, M., Monroy, F., & Domínguez, J. (2006). C to N ratio strongly affects population structure of Eisenia fetida vermicomposting systems. European Journal of Soil Biology, 42(1), S127–S131.
Akira, K., Yasunari, M., Kazuyuki, H., Hisamitsu, N., & Hironao, S. (2008). Pd/C-catalyzed practical degradation of PCBs at room temperature. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 81(3–4), 274–282.
Arbeli, Z. (2009). Biodegradation of persistent organic pollutants (POPs): the case of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB). Acta Biológica Colombiana, 14(1), 55–86.
Binet, F., Kersanté, A., Munier-Lamy, C., Le Bayon, R. C., Belgy, M. J., & Shipitalo, M. J. (2006). Lumbricid macrofauna alter atrazine mineralization and sorption in a silt loam soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 38(6), 1255–1263.
Bonnard, M., Devin, S., Leyval, C., Morel, J. L., & Vasseur, P. (2010). The influence of thermal desorption on genotoxicity of multipolluted soil. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 73(5), 955–960.
Bremner, J. M., et al. (1996). Nitrogen-Total. In D. L. Sparks (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis: chemical methods part 3. Soil Science Society of America Inc (pp. 1085–1122). Madison: American Society of Agronomy, Inc.
Contreras-Ramos, S. M., Escamilla-Silva, E. M., & Dendooven, L. (2006). Vermicomposting of biosolids with cow manure and oat straw. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 41(3), 190–198.
Contreras-Ramos, S. M., Álvarez-Bernal, D., & Dendooven, L. (2008). Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from soil amended with biosolid or vermicompost in the presence of earthworms (Eisenia fétida). Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 40(7), 1954–1959.
Delgado-Balbuena, L., Aguilar-Chavez, A. R., Luna-Guido, M. L., & Dendooven, L. (2013). Mixing of an anthracene-contaminated soil: a simple but efficient remediation technique? Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 96, 238–241.
Dendooven, L., Alvarez-Bernal, D., & Contreras-Ramos, S. M. (2011). Earthworms, a means to accelerate removal of hydrocarbons (PAHs) from soil? A mini-review. Pedobiologia, 54(29), S187–S192.
El Morsy, F. A. M., El-Sadaawy, M. M., Ahdy, H. H. H., Abdel-Fattah, L. M., El-Sikaily, A. M., Khaled, A., & Tayel, F. M. T. (2013). Potential human health risks from toxic metals, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, polychlorinated biphenyls, and organochlorine pesticides via canned fish consumption: estimation of target hazard quotients. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part A, Toxic Hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering, 48(12), 1470–1478.
Engel, L. S., Lan, Q., & Rothman, N. (2007). Polychlorinated biphenyls and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, 16, 373–376.
Garg, V. K., & Gupta, R. (2011). Effect of temperature variations on vermicomposting of household solid waste and fecundity of Eisenia fetida. Bioremediation Journal, 15(3), 165–172.
Gomes, H. I., Dias-Ferreira, C., & Ribeiro, A. B. (2013). Review: Overview of in situ and ex situ remediation technologies for PCB-contaminated soils and sediments and obstacles for full-scale application. Science of the Total Environment, 445–446, 237–260.
Gunadi, B., Edwards, C. A., & Blount, C., IV. (2003). The influence of different moisture levels on the growth, fecundity and survival of Eisenia fetida (Savigny) in cattle and pig manure solids. European Journal of Soil Biology, 39(1), 19–24.
Hickman, Z.A., & Reid, B.J. (2008). Earthworm assisted bioremediation of organic contaminants. Environmental International, 34(7), 1072--1081.
Kale, R. D. (2002). Vermicomposting technology in India: an answer to shortages in nutrient supplies. In C. A. Edwards (Ed.), Earthworms in the processing and utilization of organic wastes. PA: Publishing J.G. Press. Chapter 22.
Leupromchai, E., Singer, A. C., Yang, C. H., & Crowley, D. E. (2002). Interactions of earthworms with indigenous and bioaugmented PCB-degrading bacteria. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 41(3), 191–197.
Li, L., Xu, Z., Wu, J., & Tian, G. (2010). Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in the earthworm Eisenia fetida in relation to bioavailable metal concentrations in pig manure. Bioresource Technology, 101(10), 3430–3436.
Llyas, M., Sudaryanto, A., Setiawan, I. E., Riyadi, A. S., Isobe, T., & Tanabe, S. (2013). Characterization of polychlorinated biphenyls and brominated flame retardants in sludge, sediment and fish from municipal dumpsite at Surabaya, Indonesia. Chemosphere, 93(8), 1500–1510.
Ludewig, G., & Robertson, L. W. (2013). Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) as initiating agents in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Letters, 334(1), 46–55.
Matschenko, N., Tysklind, M., de Wit, C., Bergek, S., Andersson, R., & Sellström, U. (2002). Application of sewage sludge to arable land-soil concentrations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans, and biphenyls, and their accumulation in earthworms. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 21, 2515–2525.
Moon, Y., Yim, U. H., Kim, H. S., Kim, Y. J., Shin, W. S., & Hwang, I. (2013). Toxicity and bioaccumulation of petroleum mixtures with Alkyl PAHs in earthworms. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 19(3), 819–835.
Ndegwa, P. M., Thompson, S. A., & Das, K. C. (2000). Effects of stocking density and feeding rate on vermicomposting of biosolids. Bioresource Technology, 71(1), 5–12.
OECD. (2009). Guideline for testing of chemicals. Proposal for new guideline: earthworms reproduction test (Eisenia fetida/andrei).<http://www.oecd.org> (June 25, 2014).
Singer, A. C., Jury, W., Luepromchai, E., Yahng, C. S., & Crowley, D. E. (2001). Contribution of earthworms to PCB bioremediation. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 33(6), 765–776.
Singh, R. P., Embrandiri, A., Ibrahim, M. H., & Esa, N. (2011). Management of biomass residues generated from palm oil mill: vermicomposting a sustainable option. Resource, Conservation and Recycling, 55(4), 423–434.
Sinha, R. K., Agarwal, S., Chauhan, K., Chandran, V., & Soni, B. K. (2010). Vermiculture technology: reviving the dreams of Sir Charles Darwin for scientific use of earthworms in sustainable development programs. Technology and Investment, 1, 155–172.
Sovcikova, E., Jusko, T. A., Drobna, B., Trnovec, T., Hertz-Picciotto, I., Palkovicova, L., & Kocan, A. (2008). Environmental prenatal and postnatal PCB exposure, and children mental development at 45 months of age. Toxicology Letters, 180(5), S202.
Statgraphics Plus for Windows. (1999). Design of experiments analyses software. Manugistics, Inc. 2115 East Jefferson Street. Rockville, Maryland 20852, USA.
Suthar, S. (2010). Pilot-scale vermireactor for sewage sludge stabilization and metal remediation process: Comparison with small-scale vermireactors. Ecological Engineering, 36, 703–712. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2009.12.016
Tejada, M., Gómez, I., & Del Toro, M. (2011). Use of organic amendments as a bioremediation strategy to reduce the bioavailability of chlorpyrifos insecticide in soils. Effects on soil biology. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 74(7), 2075–2081.
Tharakan, J. (2005). Application of microbes and earthworms for the biological remediation of polychlorinated biphenyl contaminated sludge. Jordan International Chemical Engineering Conference V (JICE05), Amman Jordan.
Tharakan, J., Tomlinson, D., Addagada, A., & Shafagati, A. (2006). Biotransformation of PCBs in contaminated sludge: potential for novel biological technologies. Engineering in Life Sciences, 6(1), 43–50.
USEPA. (2007). United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Method 8270D. Semivolatile organic compounds by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS).
Veltman, K., Huijbregts, M., Vijver, M., Peijnenburg, W., Hobbelen, P., Koolhaas, J., Van Gestel, C., Van Vliet, P., & Hendriks, A. (2007). Metal accumulation in the earthworm Lumbricus rubellus. Model predictions compared to field data. Environmental Pollution, 146(2), 428–436.
Vlčková, K., & Hofman, J. (2012). A comparison of POPs bioaccumulation in Eisenia fetida in natural and artificial soils and effects of aging. Environmental Pollution, 160, 49--56.
Wang, C., Li, F., Shi, H., Jin, Z., Sun, X., Zhang, F., Wu, F., & Kan, S. (2013). The significant role of inorganic matters in preservation and stability of soil organic carbon in the Baoji and Luochuan loess/paleosol profiles, Central China. Catena, 109, 186–194.
Ward, M. H., Colt, J. S., Metayer, C., Gunier, R. B., Lubin, J., Crouse, V., Nishioka, M. G., Reynolds, P., & Buffler, P. A. (2009). Residential exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides and risk of childhood leukemia. Environmental Health Perspectives, 117(6), 1007–1013.
Xie, X., Qian, Y., Wu, Y., Yin, J., & Zhai, J. (2013). Effects of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) on the avoidance response, survival, growth and reproduction (Eisenia fetida). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 90, 21–27.
Yuk, J., Simpson, M. J., & Simpson, A. J. (2013). 1-D and 2-D NMR-based metabolomics of earthworms exposed to endosulfan and endosulfan sulphate in soil. Environmental Pollution, 175, 35–44.
Zachary, A. H., & Brian, J. R. (2008). Earthworm assisted bioremediation of organic contaminants. Environmental International, 34(7), 1072–1081.
Zhao, L., Hou, H., Shimoda, K., Terada, A., & Hosomi, M. (2012). Formation pathways of polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs) in sediments contaminated with PCBs during the thermal desorption process. Chemosphere, 88(11), 1368–1374.
Acknowledgments
This research was done at the laboratory of Analytical Chemistry and Biotechnology Institute of Technology Tuxtla Gutiérrez, Chiapas. We thank MSc María Celina Luján Hidalgo for her technical assistance. J.J. V.M. received grant-aided support from Dirección General de Educación Superior Tecnológica.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Villalobos-Maldonado, J.J., Meza-Gordillo, R., Mancilla-Margalli, N.A. et al. Removal of Decachlorobiphenyl in Vermicomposting Process Amended with Rabbit Manure and Peat Moss. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 159 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2400-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2400-z