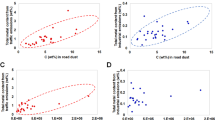
Abstract
Road dust organic matter plays a vital role in mobilization of contaminants. This study investigated and characterized organic matter (OM) presents in road dust particles of various sizes. Road dust samples were collected from an industrialized city of Ulsan, Republic of Korea and fractionated into four groups: <75, 75–180, 180–850, and 850–2000 μm. OM extracted from the four fractions was characterized by excitation-emission matrix fluorescence and analyzed by parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC). The PARAFAC identified four major fluorophore components (C1–C4). These components were related to microbial humic-like, anthropogenic organic, fulvic-like, and low molecular weight OM contributed by anthropogenic activity, respectively. There were subtle changes in specific OM composition with change in particle size. The finest fraction contained more microbial humic-like substances whereas the coarse fraction was enriched with fulvic acid. The OM in two fractions (75–180 and 180–800 μm) showed dual characteristics. Our findings demonstrated that PARAFAC approach can assist to assess the accumulation of pollutants in road dust.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrade-Eiroa, Á., Canle, M., & Cerdá, V. (2013). Environmental applications of excitation-emission spectrofluorimetry: an in-depth review I. Applied Spectroscopy Reviews, 48, 1–49.
Aryal, R. K., & Lee, B. K. (2009). Characteristics of suspended solids and micropollutants in first-flush highway runoff. Water Air and Soil Pollution Focus, 9, 339–346.
Aryal, R. K., Furumai, H., Nakajima, F., & Boller, M. (2005). Dynamic behavior of fractional suspended solids and particle-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in highway runoff. Water Research, 39, 5126–5134.
Aryal, R. K., Murakami, M., Furumai, H., Nakajima, F., & Jinadasa, H. K. P. K. (2006). Prolonged deposition of heavy metals in infiltration facilities and its possible threat to groundwater contamination. Water Science and Technology, 54, 205–212.
Aryal, R., Baral, B., Vigneswaran, S., Naidu, R., & Loganathan, P. (2011). Seasonal influence on urban dust PAH profile and toxicity in Sydney, Australia. Water Science and Technology, 63, 2238–2243.
Baghoth, S., Sharma, S., & Amy, G. (2011). Tracking natural organic matter (NOM) in a drinking water treatment plant using fluorescence excitation–emission matrices and PARAFAC. Water Research, 45, 797–809.
Baker, A., Inverarity, R., Charlton, M., & Richmond, S. (2003). Detecting river pollution using fluorescence spectrophotometry: Case studies from the Ouseburn, NE England. Environmental Pollution, 124, 57–70.
Baldock, J., Oades, J., Waters, A., Peng, X., Vassallo, A., & Wilson, M. (1992). Aspects of the chemical structure of soil organic materials as revealed by solid-state 13C NMR spectroscopy. Biogeochemistry, 16, 1–42.
Beltrán, J. L., Ferrer, R., & Guiteras, J. (1998). Multivariate calibration of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon mixtures from excitation–emission fluorescence spectra. Analytica Chimica Acta, 373, 311–319.
Bergamaschi, B. A., Tsamakis, E., Keil, R. G., Eglinton, T. I., Montluçon, D. B., & Hedges, J. I. (1997). The effect of grain size and surface area on organic matter, lignin and carbohydrate concentration, and molecular compositions in Peru Margin sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 61, 1247–1260.
Christensen, J. H., Hansen, A. B., Mortensen, J., & Andersen, O. (2005). Characterization and matching of oil samples using fluorescence spectroscopy and parallel factor analysis. Analytical Chemistry, 77, 2210–2217.
Coble, P. G. (1996). Characterization of marine and terrestrial DOM in seawater using excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy. Marine Chemistry, 51, 325–346.
Davis, A. P., Shokouhian, M., & Ni, S. (2001). Loading estimates of lead, copper, cadmium, and zinc in urban runoff from specific sources. Chemosphere, 44, 997–1009.
Dickens, A. F., Baldock, J. A., Smernik, R. J., Wakeham, S. G., Arnarson, T. S., Gélinas, Y., & Hedges, J. I. (2006). Solid-state 13C NMR analysis of size and density fractions of marine sediments: Insight into organic carbon sources and preservation mechanisms. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70, 666–686.
Duarte, R. M. B. O., Pio, C. A., & Duarte, A. C. (2004). Synchronous scan and excitation-emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy of water-soluble organic compounds in atmospheric aerosols. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry, 48, 157–171.
Duong, T. T. T., & Lee, B. K. (2009). Partitioning and mobility behavior of metals in road dusts from national-scale industrial areas in Korea. Atmospheric Environment, 43, 3502–3509.
Elcoroaristizabal, S., De Juan, A., García, J. A., Elorduy, I., Durana, N., & Alonso, L. (2014). Chemometric determination of PAHs in aerosol samples by fluorescence spectroscopy and second-order data analysis algorithms. Journal of Chemometrics, 28, 260–271.
Fergusson, J., & Ryan, D. (1984). The elemental composition of street dust from large and small urban areas related to city type, source and particle size. Science of the Total Environment, 34, 101–116.
Fu, P., Mostofa, K. M. G., Wu, F., Liu, C. Q., Li, W., Liao, H., Wang, L., Wang, J., & Mei, Y. (2010). Excitation-emission matrix characterization of dissolved organic matter sources in two eutrophic lakes (Southwestern China Plateau). Geochemical Journal, 44, 99–112.
Fuentes, M., González-Gaitano, G., & García-Mina, J. M. (2006). The usefulness of UV–visible and fluorescence spectroscopies to study the chemical nature of humic substances from soils and composts. Organic Geochemistry, 37, 1949–1959.
Guggenberger, G., Zech, W., Haumaier, L., & Christensen, B. T. (1995). Land-use effects on the composition of organic matter in particle-size separates of soils: II. CPMAS and solution 13C NMR analysis. European Journal of Soil Science, 46, 147–158.
Gunawardana, C., Goonetilleke, A., Egodawatta, P., Dawes, L., & Kokot, S. (2012). Source characterisation of road dust based on chemical and mineralogical composition. Chemosphere, 87, 163–170.
Guo, W., Xu, J., Wang, J., Wen, Y., Zhuo, J., & Yan, Y. (2010). Characterization of dissolved organic matter in urban sewage using excitation emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy and parallel factor analysis. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 22, 1728–1734.
Heiri, O., Lotter, A. F., & Lemcke, G. (2001). Loss on ignition as a method for estimating organic and carbonate content in sediments: Reproducibility and comparability of results. Journal of Paleolimnology, 25, 101–110.
Herngren, L., Goonetilleke, A., & Ayoko, G. A. (2006). Analysis of heavy metals in road-deposited sediments. Analytica Chimica Acta, 571, 270–278.
Hong, S., Aryal, R., Vigneswaran, S., Johir, M. A. H., & Kandasamy, J. (2012). Influence of hydraulic retention time on the nature of foulant organics in a high rate membrane bioreactor. Desalination, 287, 116–122.
Hua, B., Dolan, F., McGhee, C., Clevenger, T. E., & Deng, B. (2007). Water-source characterization and classification with fluorescence EEM spectroscopy: PARAFAC analysis. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 87, 135–147.
Hvitved-Jacobsen, T., Johansen, N., & Yousef, Y. (1994). Treatment systems for urban and highway run-off in Denmark. Science of the Total Environment, 146, 499–506.
Linton, R., Natusch, D., Solomon, R., & Evans, C. (1980). Physicochemical characterization of lead in urban dusts. A microanalytical approach to lead tracing. Environmental Science & Technology, 14, 159–164.
Luo, X.-S., Yu, S., Zhu, Y.-G., & Li, X.-D. (2012). Trace metal contamination in urban soils of China. Science of the Total Environment, 421, 17–30.
McKnight, D. M., Boyer, E. W., Westerhoff, P. K., Doran, P. T., Kulbe, T., & Andersen, D. T. (2001). Spectrofluorometric characterization of dissolved organic matter for indication of precursor organic material and aromaticity. Limnology and Oceanography, 46, 38–48.
Michaelson, G., & Ping, C. (1997). Comparison of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide with 0.1 M sodium pyrophosphate in the extraction of soil organic matter from various soil horizons. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 28, 1141–1150.
Muroski, A. R., Booksh, K. S., & Myrick, M. (1996). Single-measurement excitation/emission matrix spectrofluorometer for determination of hydrocarbons in ocean water. 1. Instrumentation and background correction. Analytical Chemistry, 68, 3534–3538.
Murphy, K. R., Stedmon, C. A., Waite, T. D., & Ruiz, G. M. (2008). Distinguishing between terrestrial and autochthonous organic matter sources in marine environments using fluorescence spectroscopy. Marine Chemistry, 108, 40–58.
Murphy, K. R., Hambly, A., Singh, S., Henderson, R. K., Baker, A., Stuetz, R., & Khan, S. J. (2011). Organic matter fluorescence in municipal water recycling schemes: toward a unified PARAFAC model. Environmental Science & Technology, 45, 2909–2916.
Murphy, K. R., Stedmon, C. A., Graeber, D., & Bro, R. (2013). Fluorescence spectroscopy and multi-way techniques. PARAFAC. Analytical Methods, 5, 6557–6566.
Pengchai, P., Furumai, H., & Nakajima, F. (2004). Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in road dust in Tokyo. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds, 24, 773–789.
Sartor, J. B. B., G. D. (1972) Water pollution aspects of street surface contaminants, Report No. EPA-R2-72/081.
Shutova, Y., Baker, A., Bridgeman, J., & Henderson, R. K. (2014). Spectroscopic characterisation of dissolved organic matter changes in drinking water treatment: from PARAFAC analysis to online monitoring wavelengths. Water Research, 54, 159–169.
Sidhu, J. P. S., Ahmed, W., Gernjak, W., Aryal, R., McCarthy, D., Palmer, A., Kolotelo, P., & Toze, S. (2013). Sewage pollution in urban stormwater runoff as evident from the widespread presence of multiple microbial and chemical source tracking markers. Science of the Total Environment, 463–464, 488–496.
Stedmon, C. A., & Bro, R. (2008). Characterizing dissolved organic matter fluorescence with parallel factor analysis: a tutorial. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods, 6, 572–579.
Stedmon, C. A., & Markager, S. (2005). Resolving the variability in dissolved organic matter fluorescence in a temperate estuary and its catchment using PARAFAC analysis. Limnology and Oceanography, 50, 686–697.
Stedmon, C. A., Markager, S., & Bro, R. (2003). Tracing dissolved organic matter in aquatic environments using a new approach to fluorescence spectroscopy. Marine Chemistry, 82, 239–254.
Sutherland, R. A., Tack, F. M., & Ziegler, A. D. (2012). Road-deposited sediments in an urban environment: a first look at sequentially extracted element loads in grain size fractions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 225, 54–62.
Tam, N. F. Y., & Wong, Y. S. (2000). Spatial variation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Hong Kong mangrove swamps. Environmental Pollution, 110, 195–205.
Tang, J. Y. M., Aryal, R., Deletic, A., Gernjak, W., Glenn, E., McCarthy, D., & Escher, B. I. (2013). Toxicity characterization of urban stormwater with bioanalytical tools. Water Research, 47, 5594–5606.
Thorpe, A., & Harrison, R. M. (2008). Sources and properties of non-exhaust particulate matter from road traffic: a review. Science of the Total Environment, 400, 270–282.
Vaze, J., & Chiew, F. H. (2002). Experimental study of pollutant accumulation on an urban road surface. Urban Water, 4, 379–389.
Veiga, L. L. A., Amorim, H., Moraes, J., Silva, M. C., Raices, R. S. L., & Quiterio, S. L. (2014). Quantification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in toasted guaraná (Paullinia cupana) by high-performance liquid chromatography with a fluorescence detector. Food Chemistry, 152, 612–618.
Wang, Z.-G., Liu, W.-Q., Zhao, N.-J., Li, H.-B., Zhang, Y.-J., Si-Ma, W.-C., & Liu, J.-G. (2007). Composition analysis of colored dissolved organic matter in Taihu Lake based on three dimension excitation-emission fluorescence matrix and PARAFAC model, and the potential application in water quality monitoring. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 19, 787–791.
Xie, S., Dearing, J. A., & Bloemendal, J. (2000). The organic matter content of street dust in Liverpool, UK, and its association with dust magnetic properties. Atmospheric Environment, 34, 269–275.
Yamashita, Y., Cory, R. M., Nishioka, J., Kuma, K., Tanoue, E., & Jaffé, R. (2010). Fluorescence characteristics of dissolved organic matter in the deep waters of the Okhotsk Sea and the northwestern North Pacific Ocean. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 57, 1478–1485.
Yao, X., Zhang, Y., Zhu, G., Qin, B., Feng, L., Cai, L., & Gao, G. (2011). Resolving the variability of CDOM fluorescence to differentiate the sources and fate of DOM in Lake Taihu and its tributaries. Chemosphere, 82, 145–155.
Yuan, D. H., Guo, N., Guo, X. J., Zhu, N. M., Chen, L. & He, L. S. (2014). The spectral characteristics of dissolved organic matter from sediments in Lake Baiyangdian, North China. Journal of Great Lakes Research.
Zhang, Y., Yin, Y., Feng, L., Zhu, G., Shi, Z., Liu, X., & Zhang, Y. (2011). Characterizing chromophoric dissolved organic matter in Lake Tianmuhu and its catchment basin using excitation-emission matrix fluorescence and parallel factor analysis. Water Research, 45, 5110–5122.
Zhao, H., Yin, C., Chen, M., & Wang, W. (2009). Risk assessment of heavy metals in street dust particles to a stream network. Soil and Sediment Contamination, 18, 173–183.
Zsolnay, A., Baigar, E., Jimenez, M., Steinweg, B., & Saccomandi, F. (1999). Differentiating with fluorescence spectroscopy the sources of dissolved organic matter in soils subjected to drying. Chemosphere, 38, 45–50.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aryal, R., Lee, BK., Beecham, S. et al. Characterisation of Road Dust Organic Matter as a Function of Particle Size: A PARAFAC Approach. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 24 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2289-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2289-y