Abstract
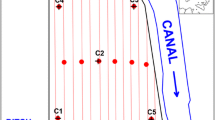
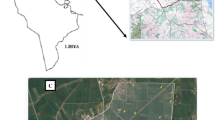
Groundwater samples collected from an unconfined shallow aquifer were analysed for major and trace element (TE) concentrations with the aim to investigate small-scale variations possibly linked to fertilizer residual products applied until 2004. The field site, located near Ferrara (Northern Italy), covers an area of 200 m2 and was a former agricultural field then converted into a park and equipped with a grid of 13 monitoring wells. Three monitoring campaigns were carried out in June 2007, March and June 2009 in order to detect spatial and temporal variations in water quality. Groundwater nitrate, chloride, bromide and sulphate concentrations decreased with time indicating that the fertilizer plume was slowly replaced by unpolluted groundwater. However, the groundwater composition showed values of TEs (Fe, Mn, Al, As and Hg) above the recommended international and national guideline values. Dissolved TE concentrations varied randomly in the three campaigns, while TEs in the solid matrix did not show particular enrichment factors induced by fertilizer use. The data indicated that the dominant factor involved in determining small-scale spatial variability of TE concentrations in this shallow aquifer was the sediment-water interaction, while the temporal variation of TEs was driven by the organic matter leaching from the topsoil and by water table oscillations, which in turn drove the groundwater redox status. This study emphasizes the need of small-scale TE spatial resolution to discriminate between anthropogenic non-point sources of pollution (like fertilizers) and background concentrations.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Haleem, A. S., Sroor, A., El-Bahi, S. M., & Zohny, E. (2001). Heavy metals and rare earth elements in phosphate fertilizer components using instrumental neutron activation analysis. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 55, 569–573.
Amorosi, A., & Sammartino, I. (2007). Influence of sediment provenance on background values of potential toxic metals from near-surface sediments of Po coastal plain (Italy). International Journal of Earth Sciences, 96, 389–396.
Amorosi, A., Colalongo, M. L., Fusco, F., Pasini, G., & Fiorini, F. (1999). Glacio-eustatic control of continental-shallow marine cyclicity from Late Quaternary deposits of the southeastern Po Plain (Northern Italy). Quaternary Resources, 52, 1–13.
Amorosi, A., Centineo, M. C., Dinelli, E., Lucchini, F., & Tateo, F. (2002). Geochemical and mineralogical variations as indicators of provenance changes in Late Quaternary deposits of SE Po plain. Sedimentary Geology, 151, 273–292.
Appelo, C. A. J., & Postma, D. (2005). Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution 2nd edition. Rotterdam: Balkema.
Christensen, T. H., Bjerg, P. L., Banwart, S. A., Jakobsen, R., Heron, G., & Albrechtsen, H. (2000). Characterization of redox conditions in groundwater contaminant plumes. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 45, 165–241.
Curzi, P. V., Dinelli, E., Ricci Lucchi, M., & Vaiani, S. C. (2006). Palaeoenvironmental control on sediment composition and provenance in the late Quaternary deltaic succession: a case study from the Po delta area (Northern Italy). Geological Journal, 41, 591–612.
D.L. 31/2001. Decreto legislativo 2 febbraio 2001, n. 31, attuazione della direttiva 98/83/CE relativa alla qualità delle acque destinate al consumo umano. Gazzetta Ufficiale n. 52 del 03/03/2001.
Davis, S. N., Whittemone, D. O., & Fabryka-Martin, J. (1998). Uses of chloride/bromide ratios in studies of potable water. Ground Water, 36(2), 338–350.
EU Directive 98/83/CE. (1998). Council directive of 3 November 1998 on the quality of water intended for human consumption. Official Journal of the European Union L, 330, 32 (5/12/1998).
Galloway, J. N., Townsend, A. R., Erisman, J. W., Bekunda, M., Cai, Z., Freney, J. R., Martinelli, L. A., et al. (2008). Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science, 320, 889–892.
Gehl, R. J., Schmidt, J. P., Stone, L. R., Schlegel, A. J., & Clark, G. A. (2002). In situ measurements of nitrate leaching implicate poor nitrogen and irrigation management on sandy soil. Journal of Environmental Quality, 34, 2243–2254.
Haitzer, M., Aiken, G. R., & Ryan, J. N. (2002). Binding of mercury (II) to dissolved organic matter: the role of the mercury-to-DOM concentration ratio. Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 3564–70.
Helena, B., Pardo, R., Vega, M., Barrado, E., Fernandez, J. M., & Fernandez, L. (2000). Temporal evolution of groundwater composition in an alluvial aquifer (Pisuerga River, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Researches, 34(3), 807–816.
Ibendahl, G., & Fleming, R. A. (2007). Controlling aquifer nitrogen levels when fertilizing crops: a study of groundwater contamination and denitrification. Ecological Modelling, 205, 507–514.
Katz, B. K., Ebert, S. M., & Kauffman, L. J. (2011). Using Cl/Br ratios and other indicators to assess potential impacts on groundwater quality from septic systems: a review and examples from principal aquifers in the United States. Journal of Hydrology, 397, 151–166.
Köhler, K., Duynisveld, W. H. M., & Böttcher, J. (2006). Nitrogen fertilization and nitrate leaching into groundwater on arable sandy soils. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 169, 185–195.
Lükewille, A., & Van Breemen, N. (1992). Aluminium precipitates from groundwater of an aquifer affected by acid atmospheric deposition in the Senne, northern Germany. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 63, 411–416.
Marconi, V., Dinelli, E., Antonellini, M., Capaccioni, B., Balugani, E., & Gabbianelli, G. (2009). Hydrogeochemical characterization of the phreatic system of the coastal wetland located between Fiumi Uniti and Bevano rivers in the southern Po plain (Northern Italy). Geophysical Research Abstract 11, EGU2009-9771, EGU General Assembly 2009.
Mastrocicco, M., Vignoli, G., Colombani, N., & Abu Zeid, N. (2010). Surface electrical resistivity tomography and hydrogeological characterization to constrain groundwater flow modelling in an agricultural field site near Ferrara (Italy). Environmental Earth Sciences, 61(2), 311–322.
Mastrocicco, M., Colombani, N., Castaldelli, G., & Jovanovic, N. (2011). Monitoring and modelling nitrate persistence in a shallow aquifer. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 217(1–4), 83–93.
Mastrocicco, M., Giambastiani, B. M. S., Severi, P., & Colombani, N. (2012). The importance of data acquisition techniques in saltwater intrusion monitoring. Water Resources Management, 26, 2851–2866.
McMahon, P. B., Böhlke, J. K., Kauffman, L. J., Kipp, K. L., Landon, M. K., Crandall, C. A., et al. (2008). Source and transport controls on the movement of nitrate to public supply wells in selected principal aquifers of the United States. Water Resources Research, 44, 1–17.
Molinari, A., Guadagnini, L., Marcaccio, M., & Guadagnini, A. (2012). Natural background levels and threshold values of chemical species in three large-scale groundwater bodies in Northern Italy. Science of the Total Environment, 425, 9–19.
Molinari, A., Guadagnini, L., Marcaccio, M., Straface, S., Sanchez-Villa, X., & Guadagnini, A. (2013). Arsenic release from deep natural solid matrices under experimentally controlled redox conditions. Science of the Total Environment, 44, 231–240.
Nouri, J., Mahvi, A. H., Jahed, G. R., & Babaei, A. A. (2008). Regional distribution pattern of groundwater heavy metals resulting from agricultural activities. Environmental Geology, 55, 1337–1343.
Otero, N., Vitòria, L., Soler, A., & Canals, A. (2005). Fertilizer characterisation: major, trace and rare earth elements. Applied Geochemistry, 20, 1473–1488.
Perego, A., Basile, A., Bonfante, A., De Mascellis, R., Terribile, F., Brenna, S., & Acutis, M. (2012). Nitrate leaching under maize cropping systems in Po Valley (Italy). Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 147, 57–65.
Senesi, N., & Polemio, M. (1981). Trace element addition to soil by application of NPK fertilizers. Fertilizer Research, 2, 289–302.
Stark, C. H., & Richards, K. G. (2008). The continuing challenge of agricultural nitrogen loss to the environment in the context of global change and advancing research. Dynamic Soil Dynamic Plant, 2, 1–12.
Tiessen, H., & Moir, J.O. (1993) Total and organic carbon. In M.R. Carter (Ed.), Soil sampling and methods of analysis, Chapter 21 (pp. 187–211). Lewis Publishers.
U.S.EPA. (2009). http://water.epa.gov/drink/contaminants/index.cfm#inorganic. Accessed 9 Jul 2014.
U.S.EPA, (2003). Drinking water standards. Washington: Office of Drinking Water, US Environmental Protection Agency.
Vengosh, A., & Pankratov, I. (1998). Chloride/bromide and chloride/fluoride ratios of domestic sewage effluents and associated contaminated ground water. Ground Water, 36, 815–824.
WHO. (1996). Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 2nd ed. Health criteria and other supporting information (Vol. 2). Geneva: World Health Organization.
WHO. (2008). Guidelines for drinking-water quality (Recommendations. Incorporating 1st and 2nd addenda 3rd ed., Vol. 1). Geneva: World Health Organization.
Wongsasuluk, P., Chotpantarat, S., Siriwong, W., & Robson, M. (2014). Heavy metal contamination and human health risk assessment in drinking water from shallow groundwater wells in an agricultural area in Ubon Ratchathani province, Thailand. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 36(1), 169–182.
Zhao, K., Liu, X., Xu, J., & Selim, H. M. (2010). Heavy metal contaminations in a soil–rice system: identification of spatial dependence in relation to soil properties of paddy fields. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 181, 778–787.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giambastiani, B.M.S., Colombani, N. & Mastrocicco, M. Detecting Small-Scale Variability of Trace Elements in a Shallow Aquifer. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 7 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2283-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2283-4