Abstract
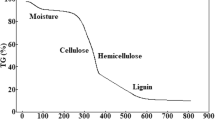
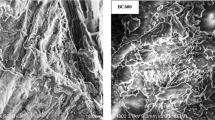
Biochar has attracted recent research interest as a metal adsorbent. The heavy metal adsorption capacity of biochar can be controlled by the carbonization of biochar. The adsorption characteristics of heavy metals (Pb, Cu, and Cd) by peat moss-derived biochars produced under different carbonization conditions were investigated by a series of batch experiments. Biochars were produced by the pyrolysis of peat moss over a temperature range of 400–1000 °C for 30–90 min. Biochar produced at 800 °C for 90 min was the most efficient for the removal of Pb and Cu, when weight loss ratio was considered. The pseudo-second-order and Langmuir models adequately described kinetics and isotherms, respectively, of heavy metal adsorption on peat moss-derived biochar, indicating that heavy metal ions were chemically adsorbed on the adsorption sites as uniform monolayer. The peat moss-derived biochar showed the highest maximum adsorption capacity for Pb (81.3 mg/g), followed by Cd and Cu, which were 39.8 and 18.2 mg/g, respectively. This study shows that peat moss-derived biochar is an effective adsorbent to remediate heavy metal-contaminated water.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah, H., & Wu, H. (2009). Biochar as a fuel: 1. Properties and grindability of biochars produced from the pyrolysis of mallee wood under slow-heating conditions. Energy & Fuels, 23(8), 4174–4181.
Ahmad, M., Lee, S. S., Dou, X., Mohan, D., Sung, J. K., Yang, J. E., & Ok, Y. S. (2012). Effects of pyrolysis temperature on soybean stover and peanut shell-derived biochar properties and TCE adsorption in water. Bioresource Technology, 118, 536–544.
Aksu, Z. (2002). Determination of the equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of the batch biosorption of lead(II) ions onto Chlorella vulgaris. Process Biochemisty, 38, 89–99.
Altland, J. E., & Locke, J. C. (2012). Biochar affects macronutrient leaching from a soilless substrate. Horticultural Science, 47(8), 1136–1140.
Babel, S., & Kurniawan, T. A. (2003). Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metal uptake from contaminated water: a review. Journal Hazard Materials, 97, 219–243.
Bailey, S. E., Olin, T. J., Bricka, R. M., & Adrian, D. D. (1999). A review of potentially low-cost sorbents for heavy metals. Water Research, 33(11), 2469–2469.
Bagreev, A., Bandosz, T. J., & Locke, D. C. (2001). Pore structure and surface chemistry of adsorbents obtained by pyrolysis of sewage sludge-derived fertilizer. Carbon, 39, 1971–1979.
Beesley, L., Moreno-Jiménez, E., Gomez-Eyles, J. L., Harris, E., Robinson, B., & Sizmur, T. (2011). A review of biochars’ potential role in the remediation, revegetation and restoration of contaminated soils. Environmental Pollution, 159(12), 3269–3282.
Bonelli, P. R., Della Rocca, P. A., Cerrella, E. G., & Cukierman, A. L. (2001). Effect of pyrolysis temperature on composition, surface properties and thermal degradation rates of Brazil Nut shells. Bioresource Technology, 76(1), 15–22.
Cao, X., & Harris, W. (2010). Properties of dairy-manure-derived biochar pertinent to its potential use in remediation. Bioresource Technology, 101(14), 5222–5228.
Choi, I. W., Seo, D. C., Kang, S. W., Lee, S. G., Seo, Y. J., Lim, B. J., Heo, J. S., & Cho, J. S. (2013). Adsorption characteristics of heavy metals using sesame waste biochar. Korean Journal of Soil Science and Fertilizer, 46(1), 8–15.
Girardello, F., Guégan, R., Esteves, V. I., Baumvol, I. J. R., Sierra, M. M. D., Crespo, J. S., Fernandes, A. N., & Giovanela, M. (2013). Characterization of Brazilian peat samples by applying a multi-method approach. Spectroscopy Letters: An International Journal for Rapid Communication, 46(3), 201–210.
Greener, Y., & Kochen, J. A. (1983). Methylmercury toxicity in the chick embryo. Teratology, 28(1), 23–28.
Herbert, L., Hosek, I. & Kripalani, R. (2012). The characterization and comparison of biochar produced from a decentralized reactor using forced air and natural draft pyrolysis. Diss. San Luis Obispo: California Polytechnic State University.
Ho, Y. S. (2006). Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 136(3), 681–689.
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (1999). Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochemisty, 34, 451–465.
Hossain, M. K., Strezov, V., Chan, Y., Ziolkowski, A., & Nelson, P. F. (2011). Influence of pyrolysis temperature on production and nutrient properties of wastewater sludge biochar. Journal of Environmental Management, 92, 223–228.
Huanliang, L., Weihua, Z., Yuxi, Y., Xiongfei, H., Shizhong, W., & Ringliang, Q. (2012). Relative distribution of Pb2+ sorption mechanisms by sludge-derived biochar. Water Research, 46, 854–862.
Inbar, Y., Chen, Y., & Hadar, Y. (1990). Humic substances formed during the composting of organic matter. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 54(5), 1316–1323.
Kim, H. S., & Kim, K. H. (2011). Physical properties of the horticultural substrate according to mixing ratio of peat moss, perlite and vermiculite. Korean Journal of Soil Science and Fertilizer, 44(3), 321–330.
Lagergren, S. (1898). Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption geloster stoffe. Kungl Svenska Vetenskapsakad Handl, 24, 1–39.
Lee, C. H. (2005). Characterization of Humin Extracted from Peat Moss and Adsorption of Heavy metals. Ph. D. Dissertation, Seoul National University of Science and Technology, Seoul.
Lee, J. W., Kidder, M., Evans, B. R., Paik, S., Buchanan Iii, A. C., Garten, C. T., & Brown, R. C. (2010). Characterization of biochars produced from cornstovers for soil amendment. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(20), 7970–7974.
Lu, G. Q., Low, J. C. F., Liu, C. Y., & Lua, A. C. (1995). Surface area development of sewage sludge during pyrolysis. Fuel, 74(3), 344–348.
Rajkovich, S., Enders, A., Hanley, K., Hyland, C., Zimmerman, A. R., & Lehmann, J. (2012). Corn growth and nitrogen nutrition after additions of biochars with varying properties to a temperate soil. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 48(3), 271–284.
Ruthven, D. M. (1984). Principle of adsorption and adsorption process. U.S.A.: John Wiley & Sons.
Seo, Y. C., Lee, H. J., & Kim, D. W. (2006). Characteristics of heavy metals biosorption by penicillium biomass. Journal of the Korea Society for Environmental Analysis, 9, 49–54.
Shinogi, Y., & Kanri, Y. (2003). Pyrolysis of plant, animal and human waste: physical and chemical characterization of the pyrolytic products. Bioresource Technology, 90(3), 241–247.
Song, J. S. (2009). Study on use of waste wood for enhancement of adsorption of carbide of sewage sludge. Ph. D. Dissertation, Chonnam National University, Gwang-ju.
Strubelt, O., Kremer, J., Tilse, A., Keogh, J., Pentz, R., & Younes, M. (1996). Comparative studies on the toxicity of mercury, cadmium, and copper toward the isolated perfused rat liver. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health. Part A, 47(3), 267–283.
Tong, X. J., Li, J. Y., Yuan, J. H., & Xu, R. K. (2011). Adsorption of Cu(II) by biochar generated from three crop straws. Chemical Engineering Journal, 172(2), 828–834.
Ünlü, N., & Ersoz, M. (2006). Adsorption characteristics of heavy metal ions onto a low cost biopolymeric sorbent from aqueous solutions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 136(2), 272–280.
Xincal, C., Guangcun, C., Linggui, C., Yingxu, C., Johannes, L., Murray, B. M., & Anthony, G. H. (2011). Adsorption of copper and zinc by biochars produced from pyrolysis of hardwood and corn straw in aqueous solution. Bioresource Technology, 102, 8877–8884.
Yang, W., Kim, H. Y., Chae, T. Y., Ibik, K., & Pohan, H. G. (2010). A study on carbonization characteristics of Indonesian and Korean bamboo for production of bamboo charcoal and vinegar. Journal of Korean Society of Combustion, 15(1), 30–37.
Yuan, J. H., Xu, R. K., & Zhang, H. (2011). The forms of alkalis in the biochar produced from crop residues at different temperatures. Bioresource Technology, 102, 3488–3497.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education [No. 2012R1A1A4A01014928] and the Basic Research Project of the Korea Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources (KIGAM) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, SJ., Park, J.H., Ahn, YT. et al. Comparison of Heavy Metal Adsorption by Peat Moss and Peat Moss-Derived Biochar Produced Under Different Carbonization Conditions. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 9 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2275-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2275-4