Abstract
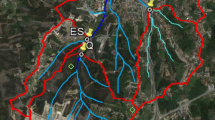
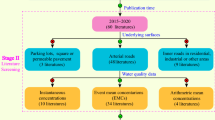
The effects of urbanization on runoff pollutant concentrations and pollutant loading were studied in three urban catchments of varying imperviousness and land use type in the city of Lahti, Finland. Imperviousness of the catchments were 19 % (“Low”), 62 % (“Intermediate”) and 89 % (“High”). During the 2-year study period, runoff quantity was measured continuously and samples were taken for water quality analysis. Besides imperviousness, land use type strongly affected pollutant concentrations: differences in total phosphorus (tot-P), Al, Cr, Zn and Pb concentrations were observed especially between the city centre catchments (High and Intermediate) and the residential catchment (Low), while total suspended solids (TSS), total nitrogen (tot-N), Mn, Co, Ni and Cu concentrations increased with increasing imperviousness. As for pollutant loads, imperviousness was strongly related to TSS, tot-P, Al, Mn, Zn, Cr, Co, Ni and Cu export. The effects of urbanization on runoff quality were season dependent: urbanization increased runoff volumes and, hence, pollutant loads, especially during warm seasons. Still, highest pollutant export in the catchments occurred during spring. Nevertheless, the warm period produced comparable loads to spring at the city centre catchments. Pollutant concentrations, especially in the city centre catchments, exceeded thresholds set for surface waters, indicating a need for runoff treatment in water quality protection.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ågren, A., Jansson, M., Ivarsson, H., Bishop, K., & Seibert, J. (2008). Seasonal and runoff-related changes in total organic carbon concentrations in the River Öre, Northern Sweden. Aquatisc Sciences, 70(1), 21–29.
Armhein, C., Strong, J. E., & Mosher, P. A. (1992). Effect of deicing salts on metal and organic matter mobilization in roadside soils. Environment Science and Technology, 26, 703–709.
Arnold, C. L., & Gibbons, C. J. (1996). Impervious surface coverage: the emergency of a key environmental indicator. Journal of the American Planning Association, 62(2), 243–258.
Bäckström, M., Nilsson, U., Håkansson, K., Allard, B., & Karlsson, S. (2003). Speciation of heavy metals in road runoff and roadside total deposition. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 147, 343–366.
Bedan, E. S., & Clausen, J. C. (2009). Stormwater runoff quality and quantity from traditional and low impact development watersheds. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 45(4), 998–1008.
Bengtsson, L., & Westerström, G. (1992). Urban snowmelt and runoff in northern Sweden. Hydrological Sciences, 37(3), 263–275.
Brezonik, L. P., & Stadelmann, T. (2002). Analysis and predictive models of stormwater runoff volumes, loads, and pollutant concentrations from watersheds in the Twin Cities metropolitan area, Minnesota, USA. Water Research, 36, 1743–1757.
Burton, G. A., Pitt, R. E. (2002). Stormwater effects handbook: a toolbox for watershed managers, scientists, and engineers. CRC Press. 929 p. ISBN: 0-87371-924-7.
Buttle, M. J. (1990). Effects of suburbanization upon snowmelt runoff. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 35(3), 285–302.
Charbeneau, R. J., & Barrett, M. E. (1998). Evaluation of methods for estimating stormwater pollutant loads. Water Environment Research, 70(7), 1295–1302.
Chiew, F. H. S., McMahon, T. A. (1998). Estimation of stormwater runoff and diffuse pollution loads. HydraStorm’98, Adelaide, Australia 27–30 September, 1998.
Clark, S. E., & Pitt, R. (2012). Targeting treatment technologies to address specific stormwater pollutants and numeric discharge limits. Water Research, 46, 6715–6730.
D’Arcy, J. B., Ellis, J. B., Ferrier, R. C., Jenkins, A., Dils R. (eds) (2000). Diffuse pollution impacts: the environmental and economic effects of diffuse pollution in the UK. Terence Dalton Publ. Ltd. (CIWEM), Lavenham.
Davis, A. P., Shokouhian, M., & Ni, S. (2001). Loading estimates of lead, copper, cadmium, and zinc in urban runoff from specific sources. Chemosphere, 44, 997–1009.
Dougherty, M. (2004). Quantifying long-term hydrologic and NPS pollutant response in an urbanizing watershed. Doctoral thesis, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University. 186 p.
Dougherty, M., Dymond, R. L., Grizzard, T. J., Godrej, A. N., Jr., Zipper, C. E., Randolph, J., et al. (2006). Empirical modeling of hydrologic and NFS pollutant flux in an urbanizing basin. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 42(5), 1405–1419.
Ellis, J. B., & Mitchell, G. (2006). Urban diffuse pollution: key data information approaches for the Water Framework Directive. Water and Environment Journal, 20, 19–26.
Finnish Meteorological Institute (2014). ACCLIM-hankkeen 2. osahanke. Roudan paksuun lumettomilla alueilla ilmaston lämmetessä: 2014/3/30; http://ilmatieteenlaitos.fi/c/document_library/get_file?uuid=94380b0f-96a0-4845-9048-40a089ac0a91&groupId=30106
Foster, I. D. L., & Charlesworth, S. M. (1996). Heavy metals in the hydrological cycle: trends and explanations. Hydrological Processes, 10, 227–261.
Foster, G. D., Roberts, E. C., Jr., Gruessner, B., & Velinsky, D. J. (2000). The contribution of urban runoff to organic contaminant levels in harbour sediments near two Norwegian cities. Applied Geochemistry, 15(7), 901–915.
Göbel, P., Diekers, C., & Coldewey, W. G. (2006). Storm water runoff concentration matrix for urban areas. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 91, 26–42.
Gottschalk, L., Jensen, J. L., Lundquist, D., Solantie, R., & Tollan, A. (1979). Hydrologic regions in the Nordic countries. Nordic Hydrology, 10(5), 273–286.
Groffman, P. M., Law, N. L., Belt, K. T., Band, L. E., & Fisher, G. T. (2004). Nitrogen fluxes and retention in urban watershed ecosystems. Ecosystems, 7, 393–403.
Hallberg, M. (2007). Treatment conditions for the removal of contaminants from road runoff. Doctoral thesis, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), Stockholm, Sweden. ISBN:978-91-7178-661-6.
Hallberg, M., Renman, G., & Lundbom, T. (2007). Seasonal variation of ten metals in highway runoff and their partition between dissolved and particulate matter. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 181, 188–191.
Harremoës, P. (1988). Stochastic model for estimation of extreme pollution from urban runoff. Water Research, 22(8), 1017–1026.
Hatt, B. E., Fletcher, T. D., Walsh, C. J., & Taylor, S. L. (2004). The influence of urban density and drainage infrastructure on the concentrations and loads of pollutants in small streams. Environmental Management, 34(1), 112–124.
Hautala, E. L., Rekilä, R., Tarhanen, J., & Ruuskanen, J. (1995). Deposition of motor vehicle emissions and winter maintenance along roadside assessed by snow analyses. Environmental Pollution, 87, 45–49.
Helmreich, B., Hilliges, R., Schriewer, A., & Horn, H. (2010). Runoff pollutants of a highly trafficked urban road—correlation analysis and seasonal influences. Chemosphere, 80, 991–997.
Hioki, A., & McLaren, J. W. (2008). Direct determination of nitrate ions in seawater by UV-detection ion-chromatography with hydrochloric acid/sodium chloride eluent. AIST Bulletin of Meteorology, 7(2), 51–59.
House, M. A., Ellis, J. B., Herricks, E. E., Hvitved-Jacobsen, T., Seager, J., Lijklema, L., et al. (1993). Urban drainage: impacts on receiving water quality. Water Science and Technology, 27(12), 117–158.
Huber, W. C. (1993). Contaminant transport in surface water. In D. R. Maidment (Ed.), Handbook of hydrology. Corvallis, Oregon, USA: Department of Civil Engineering, Oregon State University.
Kersalo, J., Pirinen, P. (2009). Suomen maakuntien ilmasto. Finnish Meteorological Institute. Reports 2009:8. ISBN: 978–951–697–711–2.
Kim, H., Seagren, E. A., & Davis, A. (2003). Engineered bioretention for removal of nitrate from stormwater runoff. Water Environment Research, 75, 355–367.
Laurén, A., Finér, L., Koivusalo, H., Kokkonen, T., Karvonen, T., Kellomäki, S., et al. (2005). Water and nitrogen processes along a typical water flowpath and streamwater exports from a forested catchment and changes after clear-cutting: a modelling study. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences Discussions, 9(6), 657–674.
Malmqvist, P. A. (1983). Urban stormwater pollutant sources: an analysis of inflows andoutflows of nitrogen, phosphorus, lead, zinc, and copper in urban areas. Doctoral thesis, Chalmers University of Technology. ISBN: 91-7032-106-X.
Marsalek, J. (2003). Road salts in urban storm water: an emerging issue in storm water management in cold climates. Water Science and Technology, 48(9), 61–70.
Matheussen, B. (2004). Effects of anthropogenic activities on snow distribution, and melt in an urban environment. Doctoral thesis. Norwegian University of Science and Technology,
Melanen, M. (1981). Quality of runoff water in urban areas. Publications of the Water Research Institute 42 (pp. 123-188). National Board of Waters, Helsinki, Finland. ISBN: 951-46-6066-8.
Mitchell, G. (2001). The quality of urban stormwater in Britain and Europe: database and recommended values for strategic planning models. Technical report. Leeds, UK: School of Geography, University of Leeds.
Mitchell, G. (2005). Mapping hazard from urban non-point pollution: a screening model to support sustainable urban drainage planning. Journal of Environmental Management, 74(1), 1–9.
Moy, F., Crabtree, R., Simms, T. (2003). Long term monitoring of pollution from highway runoff. Environment Agency R&D Report No. P2-038, WRC, Swindon.
Novotny, V. (1992). Unit pollutant loads. Their fit in abatement strategies. Water Environment & Technology, 4(1), 40–43.
Oberts, G. (1994). Influence of snowmelt dynamics on stormwater runoff quality. Watershed Protection Techniques, 1(2), 55–61.
Pitt, R., Clark, S., & Field, R. (1999). Groundwater contamination potential from stormwater infiltration practices. Urban Water, 1, 217–236.
Reinosdotter, K. (2007). Sustainable snow handling. Doctoral thesis, Division of Architecture and Infrastructure, Department of Civil, Mining and Environmental Engineering, Luleå University of Technology, Sweden.
Sansalone, J., & Buchberger, S. G. (1997). Partitioning and first flush of metals in urban roadway storm water. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 123(2), 134–143.
Schueler, T. R. (1994). The importance of imperviousness. Watershed Protection Techniques, 1(3), 100–111.
Semádeni-Davies, A., & Bengtsson, L. (1999). The water balance of a sub-Arctic town. Hydrological Processes, 13(12–13), 1871–1885.
Semádeni-Davies, A., Titus, D. (2003). Seasonal pollution flows in stormwater from an urban area. Proc. Northern Research Basins (pp. 173–182), 14th Int. Symposium and Workshop, Kangerlussuaq/Sdr. Strømfjord, Greenland.
Setälä, H., Viippola, V., Rantalainen, A.-L., Pennanen, A., & Yli-Pelkonen, V. (2014). Urban vegetation has little influence in mitigating air pollution in northern conditions. Environmental Pollution, 183, 104–112.
Sillanpää, N. (2013). Effects of suburban development on runoff generation and water quality. Doctoral thesis. Aalto University, Doctoral Dissertations 160/2013. 226 p. ISBN: 978-952-60-5373-8.
Sillanpää, N., & Koivusalo, H. (2013). Catchment-scale evaluation of pollution potential of urban snow at two residential catchments in southern Finland. Water Science and Technology, 68(10), 2164–2170.
Stockholm Vatten (2001). Klassificering av dagvatten och recipienter samt riktlinjer för reningskrav—Del 2 Reningskrav och Dagvattenklassificering (In Swedish).
Swedish Environmental Protection Agency (2000). Environmental quality criteria—lakes and watercourses. REPORT 5050. Stockholm, Sweden. ISBN: 91-620-5050-8
The City of Lahti (2011). Statistics database: 2012/4/4; http://www4.lahti.fi/verkkotilastointi/
The city of Lahti (2013). Statistics database: 2013/5/3; http://www4.lahti.fi/verkkotilastointi/
Valtanen, M., Sillanpää, N., & Setälä, H. (2014). Effects of land use intensity on stormwater runoff and its temporal occurrence in cold climates. Hydrological Processes, 28(4), 2639–2650.
Viklander, M. (1999). Substances in urban snow. A comparison of the contamination of snow in different parts of the city of Luleå, Sweden. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 114, 377–394.
Westerlund, C., & Viklander, M. (2006). Particles and associated metals in road runoff during snowmelt and rainfall. Science of the Total Environment, 362, 143–156.
Westerlund, M., Viklander, M., & Bäckström, M. (2003). Seasonal variations in road runoff quality in Luleå, Sweden. Water Science and Technology, 48, 93–101.
Acknowledgments
The study forms part of the Stormwater research programme funded by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF). This work was also financially supported by the Onni and Hilja Tuovinen foundation and the ERDF-funded “Urban Laboratory” project. We thank Lahti Energia for providing electricity for the measurement stations and Lahti Aqua for the provision of stormwater sewer map material and access to the sewer system. Many thanks also to Santeri Savolainen, Tuukka Ryynänen, Marianne Lehtonen, Jukka Pellinen, Juhani Järveläinen, Lisa Haddorf, Hanna Tuppurainen, Sanni Valtonen and Tamara Serna Alonso for technical arrangements and laboratory analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valtanen, M., Sillanpää, N. & Setälä, H. The Effects of Urbanization on Runoff Pollutant Concentrations, Loadings and Their Seasonal Patterns Under Cold Climate. Water Air Soil Pollut 225, 1977 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-1977-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-1977-y