Abstract
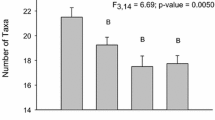
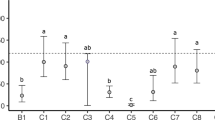
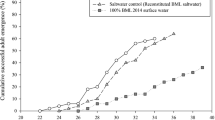
We investigated the effects of road deicer runoff on benthic macroinvertebrate communities in Korean freshwaters focusing on the effects of CaCl2 deicer. Quantitative field sampling was conducted at eight sites (lakes and streams) in South Korea, and toxicity tests were conducted on 48-h lethal and effective concentrations (LC50 and EC50) of road deicer (CaCl2 74 %) and high-grade CaCl2 (96 %) on five selected macroinvertebrate species (Gammarus sobaegensis, Caridina denticulata denticulata, Glyptotendipes tokunagai, Cloeon dipterum, and Ecdyonurus levis). Although Cl− concentrations were significantly different between the seasons (before and after snowfall) at most of the study sites, community values (species richness, density, dominance index, and diversity index) were not significantly different between the seasons. In the bioassay, 2.85 g L−1 CaCl2 elicited abnormal swimming behavior of test organisms based on EC50 values. The LC50 values of the five test species ranged from 3.54 to 20.73 g L−1. For all tested species, the LC50 of road deicer was higher than that of high-grade CaCl2. This study shows that despite the heavy application of road deicers during the snowy season, the deicer may not directly affect benthic macroinvertebrate communities over short time periods because Cl− concentrations in the field sites (<0.025 g L−1) were much lower than the LC50 values. Because the quantity of deicers used in this region continues to increase, long-term research into the effects of deicers on benthic macroinvertebrates is needed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baek, M. J., Yoon, T. J., & Bae, Y. J. (2012). Development of Glyptotendipes tokunagai (Diptera: Chironomidae) under different temperature conditions. Environmental Entomology, 41(4), 950–958.
Benbow, M. E., & Merritt, R. W. (2004). Road-salt toxicity of select Michigan wetland macroinvertebrates under different testing conditions. Wetlands, 24(1), 68–76.
Bervoets, L., Wils, C., & Verheyen, R. (1996). Tolerance of Chironomus riparius larvae (Diptera: Chironomidae) to salinity. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 57, 829–835.
Bidwell, J. R., & Gorrie, J. R. (2006). The influence of salinity on metal uptake and effects in the midge Chironomus maddeni. Environmental Pollution, 139, 206–213.
Blasiusa, B. J., & Merritt, R. W. (2002). Field and laboratory investigations on the effects of road salt (NaCl) on stream macroinvertebrate communities. Environmental Pollution, 120, 219–231.
Chadwick, M. A., & Feminella, J. W. (2001). Influence of salinity and temperature on the growth and production of a freshwater mayfly in the Lower Mobile River, Alabama. Limnology & Oceanography, 46(3), 532–542.
Corsi, S. R., Graczyk, D. J., Geis, S. W., Booth, N. L., & Richards, K. D. (2010). A fresh look at road salt: aquatic toxicity and water-quality impacts on local, regional, and national scale. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(10), 7376–7382.
Crowther, R. A., & Hynes, H. B. N. (1977). The effect of road deicing salt on the drift of stream benthos. Environmental Pollution, 14, 113–126.
Environment Canada. (2001). Priority substances list assessment report: Road salts. Environment Canada, En40-215/63E. Ottawa, Ontario.
Fay, L., & Shi, X. (2012). Environmental impacts of chemicals for snow and ice control: state of the knowledge. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 223, 2751–2770.
Findlay, S. E. G., & Kelly, V. R. (2011). Emerging indirect and long-term road salt effects on ecosystems. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1223, 58–68.
Hamilton, R. W., Buttner, J. K., & Brunetti, R. G. (1975). Lethal levels of sodium chloride and potassium for an Oligochaeta, a chironomid midge, and a caddisfly of Lake Michigan. Environmental Entomology, 4, 1003–1006.
Hopkins, G. R., French, S. S., & Brodie, E. D., Jr. (2013). Increased frequency and severity of developmental deformities in rough-skinned newt (Taricha granulosa) embryos exposed to road deicing salts (NaCl & MgCl2). Environmental Pollution, 173, 264–269.
Houska, C. (2007). Deicing salt—recognising the corrosion threat. International Molybdenum Association, Pittsburgh, TMR Consulting.
Kang, J. S., Joo, S. B., Nam, S. J., Jeong, G. R., Yang, D. W., Park, H. K., & Park, S. K. (2009). Secondary productivity of pelagic zooplankton in Lake Paldang and Lake Cheongpyeong. Journal of Ecology and Field Biology, 32(4), 257–265.
Kang, S. H. (2009). Pollutant flux releases during summer monsoon period based on hydrological modeling in two forested watersheds, Soyang Lake. Environmental Engineering Research, 14(1), 13–18.
Karraker, N. E., Gibbs, J. P., & Vonesh, J. R. (2008). Impacts of road deicing salt on the demography of vernal pool-breeding amphibians. Ecological Applications, 18, 724–734.
Karraker, N. E., & Gibbs, J. P. (2011). Road deicing salt irreversibly disrupts osmoregulation of salamander egg clutches. Environmental Pollution, 159, 833–835.
Kaushal, S. S., Groffman, P. M., Likens, G. E., Belt, K. T., Stack, W. P., Kelly, V. R., Band, L. E., & Fisher, G. T. (2005). Increased salinization of fresh water in the northeastern United States. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(38), 13517–13520.
Kawai, T., & Tanida, K. (2005). Aquatic insects of Japan: manual with keys and illustrations. Tokyo: Tokai University Press.
Kil, H. K., Kim, D. G., Jung, S. W., Jin, Y. H., Hwang, J. M., Bae, K. S., & Bae, Y. J. (2010). Impacts of impoundments by low-head and large dams on benthic macroinvertebrate communities in Korean streams and rivers. Korean Journal of Limnology, 43(2), 190–198.
Kim, B. S., Park, Y. K., Park, K. H., Kim, J. K., Shin, J. S., Kim, J. H., Yoon, S. M., & Ahn, Y. J. (2006). Selection of optimal culture media for developing standard ecological toxicity test methods using Korean freshwater Cladocera. Korean Journal of Pesticide Science, 10(3), 189–195.
Lee, H. G., & Bae, Y. J. (2011). Recovery of aquatic insect communities after a catastrophic flood in a Korean stream. Animal Cells and Systems, 15(2), 169–177.
Lewis, W. L., Jr. (1999). Studies of environmental effects of magnesium chloride deicer in Colorado. Final Report for the Colorado Department of Transportation.
Lob, D. W., & Silver, P. (2012). Effects of elevated salinity from road deicers on Chironomus riparius at environmentally realistic springtime temperatures. Freshwater Science, 31(4), 1078–1087.
Merritt, R. W., & Cummins, K. W. (2008). An introduction to the aquatic insects of North America (4th ed.). Dubuque: Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company.
NIER (National Institute of Environmental Research)/Han River Environment Research Center. (2010). Evaluation of aquatic ecosystem disturbed by environmental factors in the Han River Basin, MONO1201033594. Yangpyeong: Ministry of Environment (in Korean).
Riva-Murray, K., Bode, R. W., Phillips, P. J., & Wall, G. L. (2002). Impact source determinations with biomonitoring data in New York State: concordance with environmental data. Northeastern Naturalist, 9, 127–162.
Robertson, J. L., & Preisler, H. K. (1991). Pesticide bioassay with arthropods. Florida: CRC Press.
Silver, P., Rupprecht, S. M., & Stauffer, M. F. (2009). Temperature-dependent effects of road deicing salt on chironomid larvae. Wetlands, 29(3), 942–951.
Shi, X., Akin, M., Pan, T., Fay, L., Liu, Y., & Yang, Z. (2009). Deicer impacts on pavement materials: introduction and recent developments. Open Civil Engineering Journal, 3, 16–27.
Shin, S. P., Yang, C. H., Ha, D. S., Baek, B. K., & Cha, J. S. (2010). Study of assumption of functional adequate amount for the additional deicer save. Korean Society of Road Engineers, 12(4), 51–54 (in Korean).
Thornton, K. W., & Sauer, J. R. (1972). Physiological effects of NaCl on Chironomus attenuatus (Diptera: Chironomidae). Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 65, 872–875.
Tromp, K., Lima, A. T., Barendregt, A., & Verhoeven, J. T. A. (2012). Retention of heavy metals and poly-aromatic hydrocarbons from road water in a constructed wetland and the effect of de-icing. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 203–204, 290–298.
US EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency). (1994). Short-term methods for estimating the chronic toxicity of effluents and receiving water to freshwater organisms. 3rd Edition. EPA/600/4-19/002.
US EPA (US Environmental Protection Agency). (2002). National recommended water quality criteria, US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, USA. EPA-882-R02-047.
Weltje, L., Rufli, H., Heimbach, F., Wheeler, J., Vervliet Scheebaum, M., & Hamer, M. (2010). The chironomid acute toxicity test: development of a new test system. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, 6, 301–307.
Williams, D. D., Williams, N. E., & Cao, Y. (1999). Road salt contamination of groundwater in a major metropolitan area and development of a biological index to monitor its impact. Water Research, 34(1), 127–138.
Yoon, I. B. (1995). Aquatic insects of Korea. Seoul: Junghaengsa.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Eco-Innovation Project of the Ministry of Environment, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baek, M.J., Yoon, T.J., Kim, D.G. et al. Effects of Road Deicer Runoff on Benthic Macroinvertebrate Communities in Korean Freshwaters with Toxicity Tests of Calcium Chloride (CaCl2). Water Air Soil Pollut 225, 1961 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-1961-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-1961-6