Abstract
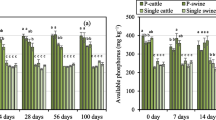
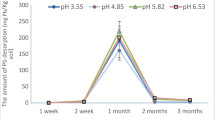
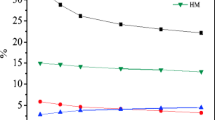
This study investigated lead (Pb) sorption by inorganic and acid-non-soluble organic fractions, which were physicochemically fractionated from cattle, swine, and poultry composts, to understand how Pb is immobilized by animal manure compost and to evaluate the contribution of each fraction in Pb immobilization. Pb was predominantly sorbed on humic acid in the acid-non-soluble organic fraction; on the other hand, Pb sorption by the inorganic fraction could be attributed to the precipitation of Pb compound minerals such as lead phosphate and lead sulfate. The amounts of Pb sorbed on the inorganic fraction were 4.1–8.1 times higher than that sorbed on the acid-non-soluble organic fraction. The amount of Pb sorbed on the inorganic fraction and acid-non-soluble organic fractions was 37–60 and 19–43 %, respectively, of the total Pb sorbed. The results of this study clearly show that the inorganic fraction in the composts effectively immobilizes Pb. Furthermore, the high content of the inorganic components, particularly phosphorus, is important in Pb immobilization.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarenga, P., Goncalves, A. P., Fernandes, R. M., de Varennes, A., Vallini, G., Duarte, E., & Cunha-Queda, A. C. (2008). Evaluation of composts and liming materials in the phytostabilization of a mine soil using perennial ryegrass. Science of the Total Environment, 406, 43–56.
Alvarenga, P., Goncalves, A. P., Fernandes, R. M., de Varennes, A., Vallini, G., & Duarte, E. (2009). Organic residues as immobilizing agents in aided phytostabilization: (Ι) effects on soil chemical characteristics. Chemosphere, 74, 1292–1300.
AOAC. (1997). Official methods of analysis (16th ed.). Gaithesburg: Association of Official Analytical Chemists International.
Aoyama, M. (1991). Properties of fine and water-soluble fractions of several composts ΙΙ. Organic forms of nitrogen, neutral sugars, and muramic acid in fractions. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 37, 629–637.
Aoyama, M. (1996). Fractionation of water-soluble organic substances formed during plant residue decomposition and high performance size exclusion chromatography of the fractions. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 42, 31–40.
Baghaie, A., Khoshgoftarmanesh, A. H., Afyuni, M., & Shulin, R. (2011). The role of organic and inorganic fractions of cow manure and biosolids on lead sorption. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 57, 11–18.
Basta, N. T., Gradwohl, R., Snethen, K. L., & Schroder, J. L. (2001). Chemical immobilization of lead, zinc, and cadmium in smelter-contaminated soils using biosolids and rock phosphate. Journal of Environmental Quality, 30, 1222–1230.
Boisson, J., Ruttens, A., Mench, M., & Vangronsveld, J. (1999). Evaluation of hydroxyapatite as a metal immobilizing soil additive for the remediation of polluted soils. Part 1. Influence of hydroxyapatite on metal exchangeability in soil, plant growth and plant metal accumulation. Environmental Pollution, 104, 225–233.
Brown, S., Chaney, R. L., Hallfrisch, J. G., & Xue, Q. (2003). Effect of biosolids processing on lead bioavailability in an urban soil. Journal of Environmental Quality, 32, 100–108.
Cao, X., Ma, L. Q., Singh, S. P., & Zhou, Q. (2008). Phosphate-induced lead immobilization from different lead minerals in soils under varying pH conditions. Environmental Pollution, 152, 184–192.
Cao, X., Wahbi, A., Ma, L., Li, B., & Yang, Y. (2009). Immobilization of Zn, Cu, and Pb in contaminated soils using phosphate rock and phosphoric acid. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164, 555–564.
Chen, S. B., Zhu, Y. G., & Ma, Y. B. (2006). The effect of grain size of rock phosphate amendment on metal immobilization in contaminated soils. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 134, 74–79.
Chen, H. S., Huang, Q.Y., Liu, L.N., Cai, P., Liang, W., Li, M. (2010). Poultry manure compost alleviates the phytotoxicity of soil cadmium: Influence on growth of pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.). Pedosphere, 20: 63–70.
Chiron, M., Guilet, R., & Deydier, E. (2003). Adsorption of Cu(II) and Pb(II) onto a grafted silica: isotherms and kinetics models. Water Research, 37, 3079–3086.
Chiu, S. W., Gao, T., Chan, C. S. S., & Ho, C. K. M. (2009). Removal of spilled petroleum in industrial soils by spent compost of mushroom Pleurotus pulmonarius. Chemosphere, 75, 837–842.
Clemente, R., & Bernal, M. P. (2006). Fractionation of heavy metals and distribution of organic carbon in two contaminated soils amended with humic acid. Chemosphere, 64, 1264–1273.
Clemente, R., Escolar, A., & Bernal, M. P. (2006). Heavy metals fractionation and organic matter mineralization in contaminated calcareous soil amended with organic materials. Bioresource Technology, 97, 1894–1901.
de la Fuente, C., Clemente, R., & Bernal, M. P. (2008). Changes in metal speciation and pH in olive processing waste and sulphur-treated contaminated soil. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 70, 207–215.
Doelsch, E., Masion, A., Moussard, G., Chevassus-Rosset, C., & Wojciechowicz, O. (2010). Impact of pig slurry and green waste compost application on heavy metal exchangeable fractions in tropical soils. Geoderma, 155, 390–400.
Dong, C. F., Shen, Y. X., Ding, C. L., Xu, N. X., Cheng, Y. H., & Gu, H. R. (2013). The feeding quality of rice (Oryza sativa L.) straw at different cutting heights and the related stem morphological traits. Field Crops Research, 141, 1–8.
Farfel, M. R., Orlova, A. O., Chaney, R. L., Lees, P. S. J., Rohde, C., & Ashley, P. J. (2005). Biosolids compost amendment for reducing soil lead hazards: a pilot study of Orgro® amendment and grass seeding in urban yards. Science of Total Environment, 340, 81–95.
Farrell, M., & Jones, D. L. (2010). Use of composts in the remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 175, 575–582.
Farrell, M., Perkins, W. T., Hobbs, P. J., Griffith, G. W., & Jones, D. L. (2010). Migration of heavy metals in soil as influenced by compost amendments. Environmental Pollution, 158, 55–64.
Frossard, E., Tekely, P., & Grimal, J. Y. (1994). Characterization of phosphate species in urban sewage sludges by high-resolution solid-state 31P NMR. European Journal of Soil Science, 45, 403–408.
Furuta, S., Katsuki, H., & Komarneni, S. (1998). Porus hydroxyapatite monoliths from gypsum waste. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 8, 2803–2806.
García, C., Hernández, T., & Costa, F. (1991). Study on water extract of sewage sludge composts. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 37, 399–408.
Gardea-Torresdey, J. L., Tnag, L., & Salvador, J. M. (1996). Copper adsorption by esterified and unesterified fractions of Sphagnum peat moss and its different humic substances. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 48, 191–206.
Hashimoto, Y., & Sato, T. (2007). Removal of aqueous lead by poorly-crystalline hydroxyapatites. Chemosphere, 69, 1775–1782.
Honda, M., Tamura, H., Kimura, T., Kinoshita, T., Matsufuru, H., & Sato, T. (2007). Control of lead polluted leachate in a box-scale phytoremediation test using common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) grown on lead contaminated soil. Environmental Technology, 28, 425–431.
Ito, T., Komiyama, T., Saigusa, M., & Morioka, M. (2010). Phosphate composition of swine and poultry manure composts. Japanese Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 81, 215–223 (in Japanese with English abstract).
Karaca, A. (2004). Effect of organic wastes on the extractability of cadmium, copper, nickel, and zinc in soil. Geoderma, 122, 297–303.
Katoh, M., Gotoh, S., & Sato, T. (2012). Estimation of lead sorption based on phosphorus dissolution from apatite. Journal of Japan Society of Civil Engineering, Series G Environmental Research, 68, 435–442 (in Japanese with English abstract.)
Logan, E. M., Pulford, I. D., Cook, G. T., & Mackenzie, A. B. (1997). Complexation of Cu2+ and Pb2+ by peat and humic acid. European Journal of Soil Science, 48, 685–696.
Low, K. S., Lee, C. K., & Mak, S. M. (2004). Sorption of copper and lead by citric acid modified wood. Wood Science and Technology, 38, 629–640.
Madejόn, E., Pérez de Mora, A., Felipe, E., Burgos, P., & Cabrera, F. (2006). Soil amendments reduce trace element solubility in a contaminated soil and allow regrowth of natural vegetation. Environmental Pollution, 139, 40–52.
Miretzky, P., & Cirelli, F. A. (2008). Phosphate for Pb immobilization in soil: a review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 6, 121–133.
Narwal, R. P., & Singh, B. R. (1998). Effect of organic materials on partitioning, extractability and plant uptake of metals in an alum shale soil. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 103, 405–421.
O’Dell, R., Silk, W., Green, P., & Classen, V. (2007). Compost amendment of Cu–Zn minespoil reduces toxic bioavailable heavy metal concentrations and promotes establishment and biomass production of Bromus carinatus (Hook and Arn.). Environmental Pollution, 148, 115–124.
Paré, T., Dinel, H., Schnitzer, M., & Dumontet, S. (1998). Transformation of carbon and nitrogen during composting of animal manure and shredded paper. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 26, 173–178.
Ruttens, A., Mench, M., Colpaert, J. V., Boisson, J., Carleer, R., & Vangronsveld, J. (2006). Phytostabilization of a metal contaminated sandy soil. Ι: influence of compost and/or inorganic metal immobilizing soil amendments on phytotoxicity and plant availability of metals. Environmental Pollution, 144, 524–532.
Sato, A., Takeda, H., Oyanagi, W., Nishihara, E., & Murakami, M. (2010). Reduction of cadmium uptake in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) by soil amendment with animal waste compost. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 181, 298–304.
Stevenson, F. J. (1976). Stability constants of Cu2+, Pb2+, and Cd2+ complexes with humic acids. Soil Science Society of American Journal, 40, 665–672.
van Herwijnen, R., Hutchings, T. R., Al-Tabbaa, A., Moffat, A. J., Johns, M. L., & Ouki, S. K. (2007). Remediation of metal contaminated soil with mineral-amended composts. Environmental Pollution, 150, 347–354.
Walker, D. J., Clemente, R., & Bernal, M. P. (2003). Contrasting effects of manure and compost on soil pH, heavy metal availability and growth of Chenopodium album L. in a soil contaminated by pyritic mine waste. Chemosphere, 57, 215–224.
Walker, D. J., Clemente, R., Roig, A., & Bernal, M. P. (2004). The effects of soil amendments on heavy metal bioavailability in two contaminated Mediterranean soils. Environmental Pollution, 122, 303–312.
Yamaguchi, T., Harada, Y., & Tsuiki, M. (2000). Basic data of animal waste composts. Miscellaneous Publication of The National Agriculture Research Center, 41, 1–178 (in Japanese).
Zhang, P., & Ryan, J. A. (1998). Formation of pyromorphite in anglesite-hydroxyapatite suspensions under varying pH conditions. Environmental Science and Technology, 32, 3318–3324.
Acknowledgments
The ICP-OES and NC analyzer instruments used for the chemical analyses in this study were made available by the Division of Instrumental Analysis at Gifu University. The authors are grateful to Prof. F. Li, Prof. T. Yamada, and Prof. Y. Ohya (Gifu University) for allowing the use of the TOC analyzer and XRD. This study was supported by JSPS KAKENHI grant number 23710089.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katoh, M., Kitahara, W. & Sato, T. Sorption of Lead in Animal Manure Compost: Contributions of Inorganic and Organic Fractions. Water Air Soil Pollut 225, 1828 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1828-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1828-2