Abstract
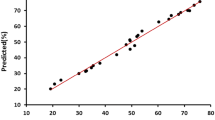
Effluents of resin production, petrochemicals, refineries, paper mills, and iron foundry industries may present high concentrations of phenol. The high toxicity, solubility, and stability of phenolic compounds hamper the treatment of this wastewater by conventional methods. In this work, the effect of inorganic ion mixtures, such as chloride, nitrate, sulfate, carbonate, and monophosphate on the phenol mineralization by the photo-Fenton process, was investigated. The kinetic of phenol mineralization was monitored with the analysis of total organic carbon. Two experimental designs were employed to evaluate the influence of inorganic ions on mineralization efficiency: fractional experimental design and central composite rotatable design (CCRD). The pollutant degradation reached 100 % at 60 min in the absence of salts, but in a saline medium, this value was reduced to 10 %. The sequence of the inhibitory effect was H2PO4 − ≫ Cl− > SO4 2− > NO3 − ≈ CO3 2. The statistical data analysis showed that the phosphate and chloride ion concentrations were studied variables and statistically significant on the mineralization process. The analysis of variance showed: (1) good fit between the observed and prediction values for fractional experiment design and CCRD and (2) according to Fisher distribution, the models that were obtained were considered significant and predictive.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babuponnusami, A., & Muthukumar, K. (2011). Degradation of phenol in aqueous solution by Fenton, sono-Fenton and sono-photo-Fenton methods. Clean - Soil Air Water, 39, 142–147.
Bacardit, J., Stötzner, J., Chamarro, E., & Esplugas, S. (2007). Effect of salinity on the photo-Fenton process. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 46, 7615–7619.
Box, G. E. P., Hunter, J. S., & Hunter, W. G. (2005). Statistics for experimenters: design, innovation, and discovery (2ªth ed.). New Jersey: Wiley.
Butler, J. N., & Cogley, D. R. (1998). Ionic equilibrium: solubility and pH calculations. Canada: Wiley.
Devi, L. G., Kumar, S. G., Raju, K. S. A., & Rajashekhar, K. E. (2010). Photo-Fenton and photo-Fenton-like processes for the degradation of methyl orange in aqueous medium: influence of oxidation states of iron. Chemical Papers, 64, 378–385.
Devi, L. G., Raju, K. S. A., Kumar, S. G., & Rajashekhar, K. E. (2011). Photo-degradation of di azo dye Bismarck Brown by advanced photo-Fenton process: influence of inorganic anions and evaluation of recycling efficiency of iron powder. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 42, 341–349.
Gernjak, W., Krutzler, T., Glaser, A., Malato, S., Caceres, J., Bauer, R., et al. (2003). Photo-Fenton treatment of water containing natural phenolic pollutants. Chemosphere, 50, 71–78.
Huang, Y.-H., Huang, Y.-J., Tsai, H.-C., & Chen, H.-T. (2010). Degradation of phenol using low concentration of ferric ions by the photo-Fenton process. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 41, 699–704.
Kavitha, V., & Palanivelu, K. (2004). The role of ferrous ion in Fenton and photo-Fenton processes for the degradation of phenol. Chemosphere, 55, 1235–1243.
Krutzler, T., & Bauer, R. (1999). Optimization of a photo-Fenton prototype reactor. Chemosphere, 38, 2517–2532.
Laat, J., Le, G. T., & Legube, B. (2004). A comparative study of the effects of chloride, sulfate and nitrate ions on the rates of decomposition of H2O2 and organic compounds by Fe(II)/H2O2 and Fe(III)/ H2O2. Chemosphere, 55, 715–723.
Machulek, A., Jr., Moraes, J. E. F., Vautier-Giongo, C., Silverio, C. A., Friedrich, L. C., Nascimento, C. A. O., et al. (2007). Abatement of the inhibitory effect of chloride anions on the photo-Fenton process. Environmental Science and Technology, 41, 8459–8463.
Maciel, R., Sant’anna, G. L., Jr., & Dezotti, M. (2004). Phenol removal from high salinity effluents using Fenton’s reagent and photo-Fenton reaction. Chemosphere, 57, 711–719.
Masomboon, N., Chen, C.-W., Anotai, J., & Lu, M.-C. (2010). A statistical experimental design to determine o-toluidine degradation by the photo-Fenton process. Chemical Engineering Journal, 159, 116–122.
Moraes, J. E. F., Quina, F. H., Nascimento, C. A. O., Silva, D. N., & Chiavone-Filho, O. (2004). Treatment of saline wastewater contaminated with hydrocarbons by the photo-Fenton process. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 1183–1187.
Navarro, R. R., Ichikawa, H., & Tatsumi, K. (2010). Ferrite formation from photo-Fenton treated wastewater. Chemosphere, 80, 404–409.
Reis, M. T. A., Freitas, O. M. F., Agarwal, S., Ferreira, L. M., Ismael, M. R. C., Machado, R., et al. (2011). Removal of phenols from aqueous solutions by emulsion liquid membranes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 192, 986–994.
Riga, A., Soutsas, K., Ntampegliotis, K., Karayannis, V., & Papapolymerou, G. (2007). Effect of system parameters and of inorganic salts on the decolorization and degradation of Procion H-exl dyes. Comparison of H2O2/UV, Fenton, UV/Fenton, TiO2/UV and TiO2/UV/H2O2 processes. Desalination, 211, 72–86.
Rodrigues, L. A., Silva, M. L. C. P., Alvarez-Mendes, M. O., Coutinho, A. R., & Thima, G. P. (2011). Phenol removal from aqueous solution by activated carbon produced from avocado kernel seeds. Chemical Engineering Journal, 74, 49–57.
Saitoh, T., Asano, K., & Hiraide, M. (2011). Removal of phenols in water using chitosan-conjugated thermo-responsive polymers. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 185, 1369–1373.
Siedlecka, E. M., Wieckowska, A., & Stepnowski, P. (2007). Influence of inorganic ions on MTBE degradation by Fenton’s reagent. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 147, 497–502.
Silva, S. S., Chiavone-Filho, O., Neto, E. L. B., & Nascimento, C. A. O. (2012). Integration of processes induced air flotation and photo-Fenton for treatment of residual waters contaminated with xylene. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 199–200, 151–157.
Teófilo, R. F., & Ferreira, M. M. C. (2006). Quimiometria II: Planilhas eletrônicas para cálculos de planejamentos experimentais, um tutorial. Quimica Nova, 29, 338–350.
Trinh, T. K., & Kang, L. S. (2011). Response surface methodological approach to optimize the coagulation–flocculation process in drinking water treatment. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 89, 1126–1135.
Acknowledgments
The Brazilian financial support that was provided by ANP (Agência Nacional do Petróleo, Gás Natural e Biocombustíveis), Petrobrás S.A., CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior), CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico), and INCT of Environmental Studies (Institutos Nacionais de Ciência e Tecnologia de Estudos do Meio Ambiente) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santos da Silva, S., Chiavone-Filho, O., de Barros Neto, E.L. et al. Effect of Inorganic Salt Mixtures on Phenol Mineralization by Photo-Fenton-Analysis via an Experimental Design. Water Air Soil Pollut 225, 1784 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1784-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1784-x