Abstract
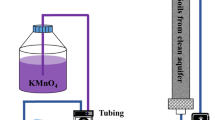
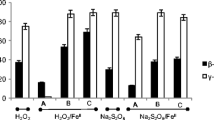
In situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) is one of the effective technologies used for source zone remediation of dense nonaqueous phase liquids (DNAPLs) such as chlorinated solvents in the subsurface environments. In karst systems, DNAPL source zones reside in epikarst where the contaminant is generally trapped in the soil or at the carbonate bedrock contact. The efficiency of oxidation of residual trichloroethylene (TCE) masses trapped in such environments by potassium permanganate was characterized via a series of batch, column, and flow cell experiments. The performance of oxidation reaction was evaluated by considering numerous factors, such as soil oxidant demand, mineralogy, heterogeneity and kinetics of dissolution, and oxidation processes. Batch experiments showed that at the low permanganate concentrations (2-10 mM), the rate of TCE oxidation by permanganate (0.86–5.1 × 10−3 s−1) was in a range similar to the rate of soil oxidant consumption (0.55–2.1 × 10−3 s−1); however, at the high permanganate concentrations (40–120 mM), this rate was about two orders of magnitude higher than the rate of soil oxidant consumption (2.4–2.9 × 10−4 s−1). In addition, at the high oxidant concentrations, the oxidation kinetics of pure phase TCE (1.1–1.5 × 10−3 s−1) was limited by the dissolution kinetics (1.4–1.6 × 10−3 s−1). Column and flow-cell experiments showed that significant fraction of residual TCE masses trapped in the soil and at the bedrock contact were oxidized by ISCO technology using permanganate, however the efficiency of ISCO was limited by the rate-limited kinetics of TCE dissolution and the desorption. The results of flow-cell experiments also indicated that instead of continuous permanganate flushing of the TCE source zones, periodic permanganate injections providing sufficient time and oxidant dosage would enhance the performance of ISCO in epikarst environment much efficiently.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASTM D7262-07 (2007). Standard Test Method for Estimating the Permanganate Natural Oxidant Demand of Soil and Aquifer Solids.
Brusseau, M. L., Carroll, K. C., Allen, T., Baker, J., Diguiseppi, W., Hatton, J., Morrison, C., Russo, A., & Berkompas, J. (2011). Impact of in-situ chemical oxidation on contaminant mass discharge: linking source-zone and plume-scale characterizations of remediation performance. Environmental Science and Technology, 45(12), 5352–5358.
Bryant, D., Battey, T., Coleman, K., Mullen, D., Wood, R. (2003). Permanganate in-situ chemical oxidation of TCE in a fractured bedrock aquifer. EPA-Groundwater Currents, 43.
Cohen, R. M., & Mercer, J. W. (1993). DNAPL site evaluation. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Conrad, S. H., Glass, R. J., & Peplinski, W. J. (2002). Bench-scale visualization of DNAPL remediation processes in analog heterogeneous aquifers: surfactant floods and in situ oxidation using permanganate. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 58(1–2), 13–49.
Crimi, M., & Ko, S. (2009). Control of manganese dioxide particles resulting from in situ chemical oxidation using permanganate. Chemosphere, 74(6), 847–853.
Dickson, J. R., & Stenson, R. (2011). Insufficient source area remediation results in the rebound of TCE breakdown products in groundwater. Remediation Journal, 87–103.
Difilippo, E. L., Carroll, K. C., & Brusseau, M. L. (2010). Impact of organic-liquid distribution and flow-field heterogeneity on reductions in mass flux. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 115(1–4), 14–25.
Dobson, R., Schroth, M. H., Oostrom, M., & Zeyer, A. J. (2006). Determination of NAPL-water interfacial areas in well-characterized porous media. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 815–822.
Erol, O. (1993). Travertine formations in the Antalya area as correlated sediments of karstic erosional phases in the surrounding Taurus mountains. Hyrogeological Processes in Karst Terranes. IAHS Publ. No. 207. 53-64.
Gates-Anderson, D. D., Siegrist, R. L., & Cline, S. R. (2001). Comparison of potassium permanganate and hydrogen peroxide as chemical oxidants for organically contaminated soils. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 127(4), 337–347.
Haselow, J. S., Siegrist, R. L., Crimi, M., & Jarosch, T. (2003). Estimating the total oxidant demand for in situ chemical oxidation design. Remediation Journal, 13, 5–16.
Heiderscheidt, J. L., Siegrist, T. H., & Illangasekare, T. H. (2008). Intermediate-scale 2D experimental investigation of in situ chemical oxidation using potassium permanganate for remediation of complex DNAPL source zones. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 102(1–2), 3–16.
Honning, J., Broholm, M. M., & Bjerg, P. L. (2007). Quantification of potassium permanganate consumption and PCE oxidation in subsurface materials. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 90(3–4), 221–239.
Hood, E. D., Thomson, N. R., Grossi, D., & Farquhar, G. J. (1999). Experimental determination of the kinetic rate law for oxidation of perchloroethylene by potassium permanganate. Chemosphere, 40(12), 1383–1388.
Huang, K.C., Hoag, G.E., Chheda, P., Woody, B.A., Dobbs, G.M. (2000). A pilot scale study of oxidation of trichloroethylene by sodium permanganate. In: Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Remediation of Chlorinated and Recalcitrant Compounds. Monterey, CA, USA, pp. 145–152.
Huang, K. C., Hoag, G. E., Woody, B. A., Bernard, A., & Dobbs, G. M. (2001). Oxidation of chlorinated ethenes by potassium permanganate: a kinetic study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 87(1–3), 155–169.
Huang, K. C., Hoag, G. E., Chheda, P., Woody, B. A., & Dobbs, G. M. (2002). Chemical oxidation of trichloroethylene with potassium permanganate in a porous medium. Advances in Environmetal Research, 7(1), 217–229.
Hunkeler, D., Aravena, R., Parker, B. L., Cherry, J. A., & Diao, X. (2003). Monitoring oxidation of chlorinated ethenes by permanganate in groundwater using stable isotopes: laboratory and field studies. Environmental Science and Technology, 37(4), 798–804.
Imhoff, P. T., Thyrum, G. P., & Miller, C. T. (1996). Dissolution fingering during the solubilization of nonaqueous phase liquids in saturated porous media. 2. Experimental observations. Water Recourses Research, 32(7), 1929–1942.
Kao, C. M., & Wu, M. J. (2000). Enhanced TCDD degradation by Fenton reagent preoxidation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 74(3), 197–211.
Kao, C. M., Huang, K. D., Wang, J. Y., Chen, T. Y., & Chien, T. Y. (2008). Application of potassium permanganate as an oxidant for in situ oxidation of trichloroethylene-contaminated groundwater: a laboratory and kinetics study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 153(3), 919–927.
Karagüzel, R., Scholz, R., & Ebel, B. (1999). Hydrogeological investigation of Antalya basin concerning the future domestic water needs of Antalya City (Turkey). Environmental Geology, 38(2), 159–167.
Kim, K., & Gurol, M. D. (2005). Reaction of nonaqueous phase TCE with permanganate. Environmental Science and Technology, 39(23), 9303–9308.
Krothe, N. C. (2003). Groundwater flow and contaminant transport through the epikarst in two karst drainage systems. Materials and Geoenvironment, 50(1), 177–180.
Li, Z. H., & Hong, H. L. (2008). Combination of surfactant solubilization with permanganate oxidation for DNAPL remediation. Water Research, 42(3), 605–614.
Li, X. D., & Schwartz, F. W. (2004a). DNAPL Remediation with in-situ chemical oxidation using potassium permanganate, I. Mineralogy of Mn Oxide and its dissolution in organic acids. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 68(1–2), 39–53.
Li, X.D., Schwartz, F.W. (2004b). DNAPL mass transfer and permeability reduction during in-situ chemical oxidation with permanganate. Geophysical Research Letters, 31 (6).
Li, X. D., & Schwartz, F. W. (2004c). DNAPL remediation with in-situ chemical oxidation using potassium permanganate, II. Increasing removal efficiency by dissolving Mn oxide precipitates. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 68(3–4), 269–287.
Mahal, M. K., Murao, A., Johnson, G. R., Russo, A., & Brusseau, M. L. (2010). Non-ideal behavior during complete dissolution of organic immiscible liquid: 2. Ideal porous media. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 213(1–4), 191–197.
Marble, J. C., Carroll, K. C., Janousek, H., & Brusseau, M. L. (2010). In-situ oxidation and associated mass-flux-reduction/mass-removal behavior for systems with organic liquid located in lower-permeability sediments. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 117(1–4), 82–93.
McKay, D.J., Stark, J.A., Young, B.L., Govoni, J.W., Berini, C.W., Cronan, T.J., Hewitt, T.J. (2000). A field demonstration of trichloroethylene oxidation using potassium permanganate. In: Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Remediation of Chlorinated and Recalcitrant Compounds, Monterey, CA, USA, pp. 109–116.
Mumford, K. G., Thomson, N. R., & Allen-King, R. M. (2005). Bench-scale investigation of permanganate natural oxidant demand kinetics. Environmental Science and Technology, 39(8), 2835–2840.
Pankow, J. F., & Cherry, J. A. (1996). Dense chlorinated solvents and other DNAPLS in groundwater, history, behavior, and remediation. Portland, Oregon: Waterloo Press.
Poulson, S. R., & Naraoka, H. (2002). Carbon isotope fractionation during permanganate oxidation of chlorinated ethylenes (cDCE, TCE, PCE). Environmental Science and Technology, 36(15), 3270–3274.
Rinaldi, A., & Da Silva, M. R. (2011). Degradation of BTX in contaminated soil by using hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and potassium permanganate (KMnO4). Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 217(1–4), 245–254.
Russo, A. E., Mahal, M. K., & Brusseau, M. L. (2009). Nonideal behavior during complete dissolution of organic immiscible liquid: 1. Natural porous media. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172(1), 208–213.
Schnar, M., Truax, C., Farquhar, G., Hood, E., Gonulla, T., & Stickney, B. (1998). Laboratory and controlled field experiments using potassium permanganate to remediate trichloroethylene and perchloroethylene DNAPLs in porous media. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 29(3), 205–224.
Schwille, F. (1998). Dense chlorinated solvents in porous and fractured media. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Scroth, M. H., Oostrom, M., Wietsma, T. W., & Istok, J. D. (2001). In situ oxidation of trichloroethylene by permanganate-effects on porous medium hydraulic properties. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 50(1–2), 79–98.
Siegrist, R. L., Lowe, K. S., Murdoch, L. C., Case, T. L., & Pickering, D. A. (1999). In-situ oxidation by fracture emplaced reactive solids. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 125(4), 429–440.
Siegrist, R. L., Urynowicz, M. A., West, O. R., Crimi, M. L., & Lowe, K. S. (2001). Principles and practices of in situ chemical oxidation using permanganate. Columbus, OH: Battelle Press.
Silva, P. T., Silva, V. L., Neto, B. B., & Simonnot, B. (2009). Potassium permanganate oxidation of phenanthrene and pyrene in contaminated soils. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168(2–3), 1269–1273.
Struse, A. M., Siegrist, R. L., Dawson, H. E., Siegrist, R. L., & Urynowicz, M. A. (2002). Diffusive transport of permanganate during in-situ oxidation. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 128, 327–334.
Thomson, N. R., Hood, E. D., & Farguhar, G. J. (2007). Permanganate treatment of an emplaced DNAPL source. Groundwater Monitoring and Remediation, 27(4), 74–85.
Tsai, T. T., Kao, C. M., Yeh, T. Y., Liang, S. H., & Chien, H. Y. (2009). Application of surfactant enhanced permanganate oxidation and biodegradation of trichloroethylene in groundwater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161(1), 111–119.
Tsitonaki, A., Petri, B., Crimi, M., Mosbaek, B., Siegrist, R. L., & Bjerg, P. L. (2010). In-situ chemical oxidation of contaminated soil and groundwater using persulfate: a review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 55–91.
Urynowicz, M. A., & Siegrist, R. L. (2005). Interphase mass transfer during chemical oxidation of TCE DNAPL in an aqueous system. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 80(3–4), 93–106.
Urynowicz, M. A., Balu, B., & Udayasankar, U. (2008). Kinetics of natural oxidant demand by permanganate in aquifer solids. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 96(1–4), 187–194.
Vella, P.A., Veronda, B. (1992). Oxidation of trichloroethylene: a comparison of potassium permanganate and fenton’s reagent chemical oxidation. Technology for the nineties. In: Proceedings of the Third International Symposium, PA, USA, pp. 75–82.
Waldemer, R.H., Tratnyek, P.G. (2006). Kinetics of contaminant degradation by permanganate. Environmental Science and Technology, 40(3), 1055–1061.
Werner, P. G., & Helmke, M. F. (2003). Chemical oxidation of tetrachloroethylene in a fractured saprolite/bedrock aquifer. Remediation Journal, 14(1), 95–107.
West, M. R., Grant, G. P., Gerhard, J. I., & Kueper, B. H. (2008). The influence of precipitate formation on the chemical oxidation of TCE DNAPL with potassium permanganate. Advances in Water Research, 31(2), 324–338.
Wolfe, W.J., Connor, J.H. (2001). Preliminary conceptual models of chlorinated solvent accumulation in karst aquifers. In: U.S. Geological Survey Karst Interest Group Proceedings. Water-Resources Investigations Report, 01-4011, pp. 157–162.
Xu, X., & Thomson, N. R. (2009). A long-term bench-scale investigation of permanganate consumption by aquifer materials. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 110(3–4), 73–86.
Yan, Y. E., & Schwartz, F. W. (1999). Oxidative degradation and kinetics of chlorinated ethylenes by potassium permanganate. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 37(3–4), 345–1365.
Yan, Y. E., & Schwartz, F. W. (2000). Kinetics and mechanisms for TCE oxidation by permanganate: a kinetic study. Environmental Science and Technology, 34, 2535–2541.
Acknowledgments
The Scientific and Technological Research Council of TURKEY (project No, 104Y063) provided the funding for this research. We thank Dr. Ahmet Karagündüz for his assistance in TCE analyses. We also thank anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akyol, N.H., Yolcubal, I. Oxidation of Nonaqueous Phase Trichloroethylene with Permanganate in Epikarst. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1573 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1573-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1573-6